* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Answer - Imagine School at Lakewood Ranch
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
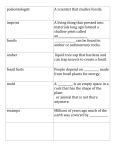
Ideas About Evolution A. Evolution: changes in inherited characteristics of a species over time SPECIES: is a group of organisms – – share similar characteristics can reproduce among themselves Lamarck's the Hypothesis of Acquired Characteristics –Traits acquired by parents => offspring (large muscles) –was not supported by evidence. Charles Darwin – – hypothesized that plants and animals on Galapagos Islands came from Central and South America. Observed that species of finches on the islands looked similar to a mainland finch species. Darwin’s Voyage Map DARWIN’S THEORY – Reasoned that members of a population best able to survive and reproduce will pass their traits to the next generation; over time, differences can result in separate species. – Published in book, Origin of Species, in 1859 Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection Darwin’s observations => experiments by other Scientists => theory Natural Selection: organisms with traits best suited to their environment will more likely survive and reproduce. Variation and Adaptation Variation: an inherited trait that makes an individual different from other members of its species Adaptation: is a variation that makes an organism better suited to its environment. – – Many kinds of environmental factors can cause changes in the sources of genes. Geographic Isolation can make two populations so different they become different species. Speed of Evolution Scientists disagree on speed of evolution Evidence supports both – Gradualism Model: describes evolution as a slow, ongoing process – Punctuated Equilibrium model: gene mutation can result in a new species in a relatively short time. Clues about Evolution Fossils found in sedimentary rock show evidence that living things evolved. Fossil age can be determined by two basic methods. – – Relative Dating looks at fossil location in a particular layer of rock; older rock layers are under newer rock layers. Radiometric Dating: compares the amount of radioactive element with the amount of nonradioactive element in a rock. Fossil records have gaps. – Incomplete rock record; most organisms do not become fossils. – Enough fossils have been discovered for scientists to conclude that complex organisms appeared later than simpler ones. – Most organisms that ever existed are now extinct. More Clues… Direct evidence, such as the development of antibiotic resistance in bacteria, supports evolution. Example: •Pesticide-resistant insect species Indirect Evidence Supports idea – does NOT provide proof – Embryology: the study of embryos and their development, shows similarities among all vertebrate species. – Homologous body parts can indicate two or more species share common ancestors. Vestigial structures that don't seem to have a function but might have once functioned in an ancestor – DNA can provide evidence about how closely related organisms are. Evolution of Primates Primates—group of mammals with opposable thumbs, binocular vision, and flexible shoulders – Hominids - appeared about 4 to 6 million years ago and had larger brains than apes. – Fossils, such as Australopithecus, point to Africa as the origin of hominids. – Homo habilis and Homo erectus are thought to be early human ancestors Lucy Fossil Adaptations Over Time Homo Sapiens began evolving about 400,000 years ago. – Neanderthals had short, heavy bodies with thick bones, small chins, and heavy brow ridges. – Disappeared about 30,000 years ago Not thought to be direct ancestors of modern humans Cro-Magnon Human fossils date from around 10,000 to 40,000 years ago; thought to be direct ancestors of early Homo sapiens. Cave Men Neandrathal vs. Cro-Magnon Reviewing Main Ideas 3 The Evolution of Primates • Primates include monkeys, apes, and humans. Hominids are humanlike primates. • The earliest known hominid fossil is Australopithecus. • Homo sapiens are thought to have evolved from Cro-Magnon humans about 400,000 years ago. Chapter Review Question 1 Charles Darwin observed that the beak shape of each species of finch is related to its eating habits. Which beak would best be used for probing beneath tree bark? A. long, slender B. long, fat C. medium-sized D. short, strong Chapter Review Answer The answer is A. A long, slender beak would be best for probing beneath tree bark. Chapter Review Question 2 What would a short, strong beak be best used for? A. eating insects B. drinking nectar C. prying insects out of small holes D. breaking hard shells Chapter Review Answer The answer is D. Finches that eat nuts and seeds have short, stout, “crushing” beaks. Chapter Review Question 3 A _______ is an inherited trait that makes an individual different from other members of its species. Answer The answer is variation. Variations result from permanent changes, or mutations, in an organism’s genes. Chapter Review Question 4 _______ are scientists who study the past by collecting and examining fossils. A. Biologists B. Entomologists C. Ecologists D. Paleontologists Chapter Review Answer The answer is D. Paleontologists study fossils in order to learn which plants and animals lived during various periods of Earth’s history. Chapter Review Question 5 _______ and _______ are two basic methods used to estimate the ages of rocks and fossils? Chapter Review Answer The answer is relative dating and radiometric dating. Relative dating is based on rock layers and radiometric dating compares the amount of radioactive element with the amount of nonradioactive element in the rock. Standardized Test Practice Question 1 Which is an imprint on sediment that later hardens to become rock? A. cast fossil B. frozen fossil C. imprint fossil D. mineralized fossil Standardized Test Practice Answer The answer is C. A leaf, feather, bones, or even the entire body of an organism can leave an imprint on sediment that later hardens to become rock. Standardized Test Practice Question 2 Which is NOT an example of an adaptation? A. albinism B. camouflage C. hibernation D. nocturnal behavior Standardized Test Practice Answer The answer is A. An adaptation is any variation that makes an organism better suited to its environment. Albinism prevents an organism from blending into its environment. Standardized Test Practice Question 3 Which is the best example of punctuated equilibrium? A. alligator evolution B. camel evolution C. human evolution D. penicillin-resistant bacteria Standardized Test Practice Question 4 According to the Principles of Natural Selection, which of the following is the best answer? Standardized Test Practice A. Organisms produce just enough offspring to survive. B. All variations are helpful. Standardized Test Practice C. Organisms with traits best suited to their environment are more likely to survive. D. Variations are never passed to offspring. Standardized Test Practice Answer The answer is C. Organisms produce more offspring that can survive, not all variations are helpful, and some variations are passed to offspring. Standardized Test Practice Question 5 Body parts that are similar in origin and structure are called _______. A. homologous B. hominids C. sedimentary D. vestigial