* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Section I Desert Bloom-Caravan Cities
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Imamah (Shia) wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Twelver Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
The Jewel of Medina wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Violence in the Quran wikipedia , lookup
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
Satanic Verses wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Succession to Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Muhammad and the Bible wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Islamic–Jewish relations wikipedia , lookup
Historicity of Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
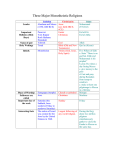
Chapter 3 of Across the Centuries Rise of Islam Section I Desert Bloom-Caravan Cities -Peninsula of Arabia was surrounded by water but was a desert, dry area -Barren, sandy desert and rocky grasslands -Oasis-small area watered by springs and wells in the desert -Arabs were nomads living in the area -Oases acted as trading areas as well -Most people lived in close family groups -Men guarded against raiders and took care of animals while women watched children and prepared meals -Families joined together to form tribes, each tribe led by a sheik -Tribes worshipped gods and carried idols-sacred images of their gods -Jews and Christians lived in the desert area, Jews in northwest -Christians lived north, east and south of Arabia -Some tribes had other tribes pay them to use oases and for protection -As tribes worked out agreements, first towns emerged Towns in the desert -Trade extended from Arabia into Egypt, Syria, India and China -Petra was an early trading city known foe abundant water -Wheat, olive oil, hides; wines, spices, etc. were traded -Petra means rock in Greece -The Bazaar was an open-air market, important along with wells Holy City of Mecca -By 500, Mecca was a leading city in terms of trade -In the 400s the Quraysh (kuh-rysh) was a tribe that made treaties with other tribes in the area and increased trade -For centuries, people worshipped in Mecca and brought idols to be included in a cube called “Kaaba” -There were icons of Christians and Jews in the Kaaba and a cornerstone was supposed to have a been a gift from angel Gabriel to Abraham for belief in one god -For four months out of the year, there was no fighting along the path to the Kaaba and thus, merchants could travel and trade without fear -People made pilgrimages-journeys to a scared place to Mecca -Quraysh began to demand money from travelers for the right o worship there and the more money they made, the less religious they were -They did business with others from outside of their tribes and this caused anger among the tribe Section II Muhammad and Islam -Each year Muhammad a Meccan trader spent a month in a cave for quiet reflection In 610, the Koran, the written account of God’s word retells an event of great importance -Muhammad was selected to be a messenger of God -He was born into Quraysh tribe around 570 -Some believe God spoke to him in 610 -There was another vision in which he met Abraham, Moses and Jesus in Jerusalem -This was Monotheism-belief in one god -Allah is Arabic word for God -By 620, only about 100 people belived in Muhammad’s message of Allah -He spoke against local gods and idols and about the poor being exploited by the rich -In 622, Muhammad fled to Medina, fearing for his life for he had converted powerful families to his message -This is called Hegira (hih Jy ruh) marks beginning of Muslim lunar calendar -New faith was Islam “submission to Allah” and followers are Muslims, ‘those who submit to Allah’s will” Jews and Arabs welcomed Muhammad -He first selected Jerusalem as city to which all Muslim should pray -Some Jewish leaders would not accept him so he changed to Mecca -He expelled all Jews who did not support him -Muhammad went about conquering enemies in Mecca and he was able to form an army of over 10,000 and took over Mecca in 630 -He destroyed all idols in Kaaba -The real around Kaaba became first mosque-holy Muslim house of worship -He appointed a leader in Mecca and returned to medina -By 632, Muhammad’s armies had conquered central west coastal regions of Arabia Teachings of Islam -After taking medina, Muhammad established a city with unique traditions and customs -The Sunna is a collection of his words and deeds -In 633, the Koran was started -It completes earlier revelations of Old testament -Islam ahs close ties Judaism and ChristianityAb5raham is father of Jews through Issac and father of Arabs through Ishmael -Jews and Christians are “people of the book” -Muslim considered other religions to be less correct but it was wrong to compel Jews or Christians to convert -Koran means “recitation” The Sunna -Five Pillars of Islam 1) Profession of faith 2) Prayer-pray five times a day 3) Give charity to the poor 4) Fast during Ramadan 5) Hajj-the pilgrimage to Mecca Islam as a way of Life -Koran and Sunna cover diet, marriage, divorce, ways of life, etc. -One of the acts called for is “jihad- which means struggle, as in the resistance of evil -Islamic wars against non-believers were sometimes called “jihad” -The Sunna called for women to have rights of their own -Women are supposed to be allowed to take a greater role in daily life -There are as many as 99 names for Allah and prayer beads may have 33 or 99 beads Section III Early Islam -Muhammad was able to spread the message based on his sense of morality, courage -Abu Bakr was an assistant to Muhammad who became successor after Muhammad died suddenly (Abu Bakr was father in law, Umar and Uthman were friends and advisors and Ali, blood cousin) -His advisors met after his death to chose a caliph “successor”-act as administrator and military leader -Abu Bakr was named successor and put down revolts by tribes in the are who abandoned Islam after Muhammad’s death -He united tribes with Arabian Peninsula and extended Muslim territory outside Arabia into Syria and Mesopotamia -Abu Bakr died in 634 and appointed Umar as successor -He encouraged armies to conquer more land -Jews and Christians were tolerated, these were outside of this were encouraged to convert -In 644, Umar named a council-assembly, to name net caliph -Uthman was appointed -He continued to conquered lands including Persia by 661 Early political Division -Uthman was murdered in 656 for only appointing his own family members as leaders -Muawiya, Uthman’s cousin challenged Ali’s right to rule -Ali was murdered and Muawiya became caliph in 661 -Ali’s followers, those who belived family of Muhammad should lead became known as Shiites “party of Ali” -Belived caliphs should be more spiritual than political -Those who belived the first three non-relatives of Muhammad caliphs was fine were Sunnis -They followed the Sunna, customs of Muhammad -They believe every individual has a connection to Allah -Sunnis make up 80 percent of Muslims -The Muslims are split into groups but are united in Allah