* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Earth Science
Meteorology wikipedia , lookup
History of climate change science wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Atmosphere of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
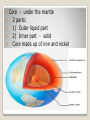
Earth Science California Standard 1f, 1g, 1i, 1l, 1j, 1k, 1n, Four major areas of Specializations · Astronomy - Study of objects beyond earth’s atmosphere : universe, earth, other planets, and bodies in the universe Big Bang Theory : The formation of galaxies, stars, etc. · Meteorology - Study of the air that surrounds our planet. Meteorologist - person that studies the forces and processes that causes the atmosphere to change to produce weather. They predict the weather. · Geology - Study of the materials that make up earth and the processes that form and change the weather. Geologist - person who interprets earth’s 4.6 billion year history · Oceanography - Study of earth’s oceans. Oceans cover 3/4 of the earth. Oceanographers - person who studies creatures that inhabits salty water, measure different physical and chemical properties of the oceans, human effects. Earth Science – Blend of Sciences Climatology - Study of weather patterns over a long period of time Paleontology - Study of remains of organisms that once lived on earth and ancient environments Hydrology - Study of water flow on and below the earth’s system and solution to water pollution Ecology - Study of habitats Geochemistry - Study of earth’s composition and process that change it Tectonics - Study of the effects of internal processes on earth’s Surface (earthquakes and mountain building) Subspecialties of Earth Science Four Main Earth’s Systems Lithosphere - The rigid outer shell of the planet that in the crust, the solid and the uppermost part of the mantle. 2 kinds of crust: Continental Crust - made of granite Oceanic Crust - made of basalt. Basalt is denser than granite Also contains a partially molten rock layer asthenosphere -it flows like soft plastic Lithosphere – Rock layer Core - under the mantle 2 parts: 1) Outer liquid part 2) Inner part - solid Core made up of iron and nickel Water in the earth’s oceans, seas, lakes, rivers, glaciers and atmosphere 97% - salt water 3% Freshwater contained in glaciers, lakes and rivers, ground water 3/4 of all fresh water in glaciers/icebergs and ground water. Hydrosphere Blanket of gases that surrounds our planet. It is Needed for respiration, protection from UV radiation (Ozone layer), Regulate temperature. Composition of atmosphere: 78% Nitrogen 21% Oxygen 1% (H2O vapor, argon, CO2, other trace gases) Atmosphere Includes all organisms on earth and the environments in which they live. 7 kilometers above and below the earth’s surface. Biosphere 1.2 Methods of Scientists The Nature of Scientific Investigations A Scientific Method - planned, organized approach to solving a problem. 1) Problems defined and research completed 2) Hypothesis - suggested explanation for an observation. Stated in the form of a question. 3) Experimentation - organized procedure that involves measurements and observations. Test only one variable or changeable factor at a time. · Independent variable - factor manipulated · Dependent variable - factor that can change if the independent variable is changed · Control - standard condition used for comparison 4) Analysis and Conclusion - data placed in organized tables: graphs, tables, and charts used to format and display data. Conclusion drawn. If conclusion is contrary to hypothesis, retesting is needed. System International d’ Unites or SI Standard system of units. Modern version of the metric system. Based on a decimal system, Uses the number 10 as the base unit. 1) Length - Base unit — meter. Meter divided into 100 equal parts called a centimeter. 1 cm = 100th of a meter 1 millimeter = 1000ths of a meter 1 meter = 100 cm or .01 m = 1 cm Measurement 10 mm = 1 centimeter Long distance = kilometer (km) 1000 m in 1 km 1000ml = 1 liter I mole is a quantity of a substance. That quantity varies with the substance. Example: 1 mole of Carbon= 12 g of Carbon 1 mole of Oxygen = 16 g of Oxygen 100 cg = 1 g or 1 cg = .01 g 36 inches = 1 yd 12 inches = 1ft 1000mg =1 g 1 mole of any gas = 22.4 liters of that gas. I mole of any substance = 6.022 X 10 23 particles (molecules, ions, atoms, etc.) More Conversions 2) Weight and Mass - Weight - gravitation force on an object Varies with location. Measured in Newton (N). Mass - SI unit kilogram (kg). Amount of matter in an object depends on the number and kinds of atoms that make up the object. Mass does not change with object position. Require combination of SI Units Area - Amount of surface included with in a set of boundaries. Expresses in square units of length. Ex. Square Meters (m²) Length x Width Volume - Amount of space occupied by an object. V = l x w x h Si unit - cubic meter = m³ Fluid volume - made in milliliters (ml) or liters (l) Cubic centimeters (cm³) 1cm³ = 1ml Area and Volume measure of the amount of matter that occupies a given space. Density = mass = d = m Volume v Units = g/cm³ or g/ml or kg/m³ Density 1) A block of aluminum occupies a volume of 15.0 mL and weighs 40.5 g. What is its density? 2) Mercury metal is poured into a graduated cylinder that holds exactly 22.5 mL. The mercury used to fill the cylinder weighs 306.0 g. From this information, calculate the density of mercury. 3) What is the weight of the ethyl alcohol that exactly fills a 200.0 mL container? The density of ethyl alcohol is 0.789 g/mL. 4) A rectangular block of copper metal weighs 1896 g. The dimensions of the block are 8.4 cm by 5.5 cm by 4.6 cm. From this data, what is the density of copper? Density Problems intervals between 2 events Atomic clock - most precise measure of time. SI unit - seconds 60 sec = 1 min 24hrs= 1 day 60 min =1hr Time Measures the average vibration of particles that make up materials. Measure in degrees with thermometer. Science - Celsius (C) scale Room temperature 25° C Normal body temperature 37° C SI Unit - Kelvin Scale (K) (used to measure very high temp, there are negative temp values) Coldest temperature - absolute zero or O K or – 273°C Temperature Expresses numbers or a multiple and a power of 10. Ex. 1000 = 1.0 x 10³ .001 = 1 x 10‾³ Scientific Notation Lab Reports - Documenting your data, analyzing of data and general conclusion Graphs - line graphs Models - scientific model - is an idea, a system or a mathematical Expression that is similar to the idea being explained. Models can change with more data. Theories and Laws - Theory explanation based on many Observations during repeated experiments. Law - Basic principle that describes the behavior of a natural phenomenon. Communicating in Science