* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Crusades - Union Academy
Albigensian Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Rhineland massacres wikipedia , lookup
Church of the Holy Sepulchre wikipedia , lookup
Despenser's Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Third Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Northern Crusades wikipedia , lookup
Siege of Acre (1189–1191) wikipedia , lookup
Fourth Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Siege of Acre (1291) wikipedia , lookup
Second Crusade wikipedia , lookup
History of Jerusalem during the Kingdom of Jerusalem wikipedia , lookup
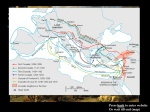
The Crusades 14.1 Main Idea The Crusades, a series of attempts to gain Christian control of the Holy Land, had a profound economic, political, and social impact on the societies involved. Muslim control of the Holy Land By year 1,000 during the Middle Ages Muslims had gained control of the Christian holy land and the holy city of Jerusalem and stories of Christian Persecution spread through Europe. 1071 1071 The Turks attacked the Byzantine Empire at the battle of Manzikert and in fear of the fall of Constantinople the emperor called for help from Western Europe and the pope Urban II. Council of Clermont Pope Urban II called The Council of Clermont to order (made up of church leaders) in Clermont France. Here he called for “Christian Warriors” to help defend the Christian city of Constantinople with the battle cry of “GOD WILLS IT” 1096 The first of Nine Crusades will leave France to conquer the Muslims and push then out of Christian holy Lands ending in 1291. First Crusade First Crusade 1096 made up of two groups: Mostly made up of unskilled peasants left France and travelled through Germany. Anxious to defeat non-Christians they began to slaughter communities of non-Christians within Europe including Jews among protests of the clergy. Made up of skilled knights took three years to reach Jerusalem to successfully take back the city among heavy losses. Outcome The Christians created four states as a stronghold to prevent future conquests of the region. Jerusalem Edessa Antioch Tripoli Second Crusade 1144 the Muslims took back Edessa and the Christians attacked only to return to Europe unsuccessful in 1147. Third Crusade 30 years later Saladin was Sultan of the Muslim world and drove all Christians out of Jerusalem. Led by three men King Richard the Lion Hearted – England King Philip Augustus – France—argued with Richard and left with his army. Emperor Frederick Barbarossa – Germany--drowned before reaching the holy land Fourth Crusade 1201 Europeans attacked the port city of Zara (a Christian city) and were excommunicated from the church by the pope. The crusaders then pressed on the Constantinople and attacked this city and appointed a new emperor but never regain control of the holy land and by 1291 the Muslims completely drove out the Christians from the holy land. Effects of the Crusades Economic: Trading of spices & Textiles increased between the Muslims, Byzantines, and Western Europeans Political: Kings took control of lands that were left vacant after battles Social Changes: Muslim knowledge was brought into Europe. Some had respect of others Many Europeans viewed all non-Christians as enemies