* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1.2 PPT - gessramsey
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Conservation biology wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Ecological resilience wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
River ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
Lake ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem services wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
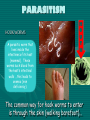
1.2 Ecosystems • Ecosystem – a part of a biome in which abiotic (non-living) factors interact with biotic (living) components – Can be many hectares of land, or the size of an old log. • Within an ecosystem, there are many habitats. • A habitat is where an organism lives. The habitat of the red fox often includes the edges of forests or marshlands There are all sorts of different ‘habitats’ that different species occupy: • The Blind Flatworm shrimp Live in dark caves. They are called “troglobites” (cavedwellers). They have adapted to darkness - do not require eyes... White-Spotted Puffer Fish • Lives in coral reefs (in tropical waters) Second most poisonous vertebrate in the world... It’s muscles, skin, liver and ovaries contain toxin 3x deadlier than cyanide. The Rattle Snake Occupies different habitats depending on the time of year... SUMMER WINTER Open grassland (areas with high rodent density) Hibernating dens (rock fissures or caves) Abiotic Interactions in Ecosystems • It is the abiotic components that allow the biotic components to survive in an ecosystem. – Abiotic factors include : • Oxygen - produced by green plants & microorganisms. • Water - necessary for all life. • Nutrients - for growth. • Light - required for photosynthesis. • Soil - contains water & nutrients. Home to many plants & animals. Biotic Interactions in Ecosystems • Community: all organisms that interact within an ecosystem. • Population: all members of a certain species within an ecosystem. • Species: all organisms within an ecosystem that have the same structure & who can reproduce with each other (and produce fertile offspring). Biotic Interactions in Ecosystems • Species can have many types of relationships in a population. – Symbiosis refers to the interaction between the members of two different species. • Commensalism - one species benefits, one is not affected For example, the barnacles on a whale • Mutualism - both species benefit For example, a bee gathering nectar from a flower • Parasitism - one species benefits, the other is harmed For example, hookworm living in dogs COMMENSALISM (Biological hitch-hiking) The Imperial shrimp hitches a ride on a large sea cucumber. It rides along through areas of potential food, at no cost to the other organism. Anyone home? The pearlfish is a small fish (5-10cm) that lives inside a seacumber in the day and at night, exits through the anus of the seacumber to feed. MUTUALISM • Leaf Cutter Ants Cut the leaf.. These ants cultivate (grow) a fungus. They feed the fungus and the fungus serves as their food! Teachers' Domain: Ancient Farmers of the Amazon Chew into a pulp Store the pulp with ant feces and fungus spores Fungus begins to grow... MUTUALISM LICHEN = algae + fungus The algae provides food (glucose) for the fungus through photosynthesis. PARASITISM HOOK WORMS A parasitic worm that lives inside the intestines of its host (mammal). These worms such blood from the host’s intestinal walls ...this leads to anemia (iron deficiency). M O U T H The common way for hook worms to enter is through the skin (walking barefoot)... PARASITISM • The Pine Beetle The pine beetle has infested lodgepole pine trees in BC’s Central Interior. Burrows in the tree, feeds on trees phloem (nutrients) and lays its eggs. Provincial Exam Question Provincial Exam Question Niches, Competition and Predation • Niche: the role an organism has within an ecosystem. – also refers to the environment in which a species prospers • Competition: occurs when a limited resource is desired by 2 or more individuals in a niche. – this limits the size & health of individual organisms, & perhaps the population . • Predation: the relationship between the “eaters” & the “eaten”. – Predators have adaptations to help them catch prey. – Prey have adaptations to help avoid predators. • Eg. spines & shells, camouflage and mimicry. Provincial Exam Question Biodiversity in Ecosystems • Biodiversity: the variety & number of different individuals & species in an ecosystem. – Healthy ecosystems generally have high biodiversity. – Most biodiversity losses occur from the loss of habitat. – Humans often have a negative impact on biodiversity. – Ecological management programs try to balance human progress with maintaining biodiversity. Take the Section 1.2 Quiz