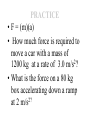* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MOTION
Derivations of the Lorentz transformations wikipedia , lookup
Frame of reference wikipedia , lookup
Inertial frame of reference wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic angular momentum wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Length contraction wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
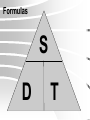
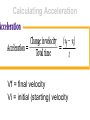
Motion Notes Measurement • A measurement is a quantity with a unit that tells what time the quantity means. • For example: – 3 seconds is a measurement of time that includes a quantity ( 3 ) and a unit (seconds). – A quantity is a number. – A unit is a Units for Motion • Length (Distance) – Milimeters – Meters – Kilimeters • Time – Seconds – Minutes – hours MOTION • Motion change in your position compared to a frame of reference. – as a train moves past a platform, people on the platform see those on the train speeding by. when people on the train look at one another, they don't seem to be moving at all OR moving backwards MOTION • frame of reference comparing an object’s motion to another object –Your house stays still as the cars drive past –a frame of reference is necessary in order to describe motion • Speed distance traveled per unit of time – S = d/t –A car travels 70 km per hour –Choose units that make sense: m/s, km/h Formulas S D T MOTION • Distance the length of a path between two points. –GO METRIC: km, m, mm, cm, etc. Time • the measured or measurable period during which an action, process, or condition exists or continues : duration. • Average speed- the total distance traveled, d, divided by the total time, t, it takes to travel that distance. speed= distance/time • Ex- on vacation: 60 km in 0.8 hr, and 35 km in 0.5 hr. What is your average speed? • Instantaneous speed the rate at which an object is moving at a given moment in time –Speedometer in a car **Average speed is computed for the entire duration of a trip, and instantaneous speed is measured at a particular instant. Graphing Motion • The slope of a line on a distance-time graph is speed. Velocity • Velocity- the speed and direction in which an object is moving –Sometimes you need to know the direction…If two trains are traveling… • Velocity is a vector. Acceleration • Acceleration-The rate of change in velocity –Changes in speed, direction or both – Can Increase or decrease, (be positive or negative) – acceleration = zero if it is moving at the same speed in thesame direction • Constant acceleration is a steady change in velocity over time. –the velocity of the object changes by the same amount each second –A jet taking off. Calculating Acceleration Vf = final velocity Vi = initial (starting) velocity Graphing Acceleration • The slope of a speed-time graph is acceleration Can be linear or non linear graph #76 & 77 I will be able to investigate the effect of speed on the severity of a collision. Vocabulary: • Acceleration • Force • Balanced force • Unbalanced force • Net force • Speed • Momentum • Conservation of momentum Force • force is a push or a pull that acts on an object. –can cause a resting object to move –can accelerate a moving object (change in ____ & ____) • Newtons(N)- measurement of force • One N is the force that causes 1-kilogram (mass) to accelerate at a rate of 1 meter per second each second (1 m/s2). • Unit for force:(1 N = 2 1 kg·m/s ) FORCE • Balanced force- when forces are balanced, net force = 0. No change in motion (arm wrestle) • Unbalanced force- causes object to accelerate FORCE • NET FORCE - Combine forces in the same direction, (subtract in opposite direction) • Ex. If two people are pushing a cart at the same time, you would combine. • In a tug of war, the two forces would be subtracted. FRICTION • Friction – force that opposes the motion of objects that are touching –Static –Sliding –Rolling –Fluid GRAVITY • Gravity – force that attracts or pulls objects together –Acts downwards toward center of Earth –Causes objects to accelerate as they fall Newton’s Laws 1st - An object at rest remains at rest OR an object in motion remains in motion,unless acted on by an outside force Newton’s Laws • 1st law = Law of inertia. • Inertia- tendency of object to resist change in motion. –Think seat belts, airbags, etc. Newton’s Laws • 2nd –acceleration of an object depends on the force on the object and the mass of the object • F= (m)(a) OR a= f / m PRACTICE • F = (m)(a) • How much force is required to move a car with a mass of 2 1200 kg at a rate of 3.0 m/s ? • What is the force on a 80 kg box accelerating down a ramp at 2 m/s2? Newton’s Laws • Mass – measure of inertia, amount of matter in an object • Weight- force of gravity on an object • This formula is a substitute for F= (m)(a)… – g = 9.8 m/s2 (on earth) • Units for weight = newtons (N) Newton’s Laws • 3rd – for every action or force, there is an equal and opposite reaction or force –Bumper cars –If the forces both act on the same object the object will not move (net force = 0) MOMENTUM •Momentum = units are kgm/s •No velocity? no momentum! •Describes how mass and velocity are effected by each other. Conservation of momentum- • The loss of momentum in an object is the gain of momentum in another object