* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download penicillins
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of non-nucleoside reverse-transcriptase inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Ciprofloxacin wikipedia , lookup
Prescription drug prices in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Levofloxacin wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Antibiotics wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of cephalosporins wikipedia , lookup
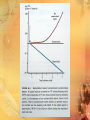
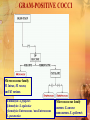
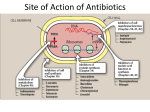
Antimicrobials Reporter: I1, Lin YH. Introduction Patients in the ICU are often infected with multiresistant organisms. Frequently exposed to broad-spectrum antibiotics and invasive procedures Judicious used of empiric antimicrobial therapy is needed to minimize emergence of resistant organisms. Choice of antibiotic: suspected source of infection, severity of the illness, local (hospital or ICU) microbiologic flora Chapter Outline ◇ Learning objectives ◇ Antibacterial Antibiotics ◇ Antifungal Drugs ◇ Antiviral Drugs ◇ Summary ◇ Review Questions Learning Objectives Recognize the different classes of antimicrobials and their mechanisms of action. Identify the spectrum of coverage for specific antimicrobials. Describe possible adverse effects and drug interactions caused by antimicrobials. Select appropriate antimicrobials for various pathogens. Chapter Outline ◇ Learning objectives ◇ Antibacterial Antibiotics • Mechanisms of action and resistance • Spectrum of coverage • Pharmacology and adverse effects ◇ Antifungal Drugs ◇ Antiviral Drugs ◇ Summary ◇ Review Questions Pharmacology Basctericidal / bacteriostatic Mode of action: concentration-dependent / time-dependent killing effect Minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) Postantibiotic effect (PAE) Syngery / Indifference / Antogonism GRAM-POSITIVE COCCI Micrococcaceae family M. luteus, M. roseus, and M. varians. α-hemolysis: S. pyogenes β-hemolysis: S. agalactiae γ-hemolysis: Enterococcus / non-Enterococcus S. pneumoniae Micrococcaceae family aureus: S. aureus non-aureus: S. epidermis GRAM-POSITIVE RODS Aerobic: Endospore-forming: Bacillus Regular, non-endospore-forming: Listeria Irregular, non-endospore-forming: Corynebacterium Anaerobic: Endospore-forming: clostridium Non-endospore-forming: Actinomycetes GRAM-NEGATIVE Aerobic cocci: Neisseria-- N. gonorrhoeae, N. meningitidis; Moraxella Anaerobic cocci: Vellionella Rods: (1) Enterobacteriaceae: Escherichia coli, Shigella, Salmonella, Klebsiella, Enterobacter, Proteus… (2) Pleomorphic: Haemophilus, Legionella, Pasteurella, Brucella (3) Miscellaneous: Vibrio, Campylobacter, Helicobacter (4) Nonfermenters: Pseudomonas, Acinebacter, Flavobacterium ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ β-Lactams Binding to penicillin-binding-protein (PBP) inner cell membrane endogeneous bacterial autolysis Activity depend on: (1) PBP type (2) degree of affinity to a particular PBP β-Lactams Resistance: (1)β-Lactamase enzyme: • nosocomial G (-) organisms: encoded on bacterial chromosomes, plasmid mediated, or carried on transposons •G(+): either inducible or constitutive and are ofter plasmid mediated (2) Change permeability of outer membrane (3) Altering their PBP β-Lactams Penicillin groups: penicillin ring Cephalosporin groups: cephalosporin ring Monobactams: Aztreonam Carbapenems: (1) Imipenem-Cilastatin (Tienam) (2) meropenem (Mepem) β-Lactams : Penicillins Penicillin G-like drugs: Penicillin G/ Penicillin V Penicillinase-resistant penicillins: Dicloxacillin / Oxacillin / Methicillin / Nafcillin Ampicillin-like drugs (Amino-PCNs) Ampicillin / Ampicillin + sulbactam (Unasyn) Amoxicillin / Amoxicillin + clavulanic acid (Augmentin) Broad-spectrum (antipseudomonal) penicillins: Ticarcillin/ Ticarcillin + Clavulanic Acid ( Timentin ) Piperacillin / Piperacillin + tazobactam (Tazocin ) β-Lactams : PCNs Fallen out as 1st line empiric therapy Drug of choice for treatment of susceptible pathogens Most excreted rapidly by kidney (except: Nafcillin) Hypersensitivity most common side effect Immunogenicity Penicillin: a. GPC: Streptococci, Treotococcus pneumoniae, Enterococci b. Anaerobics: except Bacteroides fragilis c. Treptonema pallidum (syphilis) Ampicillin / ampicillin-like drugs : GNB Hydrolyzed by many β-Lactamase Unasyn / Augmentin a) Ampicillin: ‧ GPC: Liesteria monocytogenes & many Entecoccus spp. ‧ Community-acquired Enterobacteriaceae and Neiserria spp. b) Amoxicillin: analog, superior oral bioavailability New generation of penicillins: (1) β-lactam + β-lactamase inhibitor: a) Unasyn: Community acquired soft-tissue infection, intraabdomen or pelvic infection, polymicrobial RI. b) Augmentin: UTI, otitis media, sinusitis, bite wounds. (empiric coverage against β-lactamase-producing staphylococci, H. influenzae, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Moraxella catarrhalis, Bacteroides, and Klebsiella spp.) (2) Antipseudomonal penicillins: GP + GN a) Timentin & Tazocin: polymicrobial soft-tissue infection intra-abdomen or pelvic infection, LRI. b) Timentin Stenotrophomonas maltophilia; Tazocin p. aeruginosa. β-Lactams: Cephalosporins First-generation Cefadroxil Cefazolin (Veterin) Cephalexin (Ceflexin/ Keflex) Cephalothin Cephapirin Cephradine Second-generation Cefaclor (Keflor) Cefamandole Cefmetazole Cefonicid Cefotetan Cefoxitin Cefprozil Cefuroxime (Zinacef) Loracarbef Third-generation Cefixime (Cefspan) Cefoperazone (Cefobid) Cefotaxime Cefpodoxime Ceftazidime (Kefadin) Ceftibuten (Seftem) Ceftizoxime Ceftriaxone (Rocephin ) Latamoxcef (Shimarin) Fourth-generation Cefpirome(Cefrom ) Cefepime (Maxipime) 2.5 generation- Cephamycins cefmetazole, ceftetan, cefoxitin Similar mechanism to PCNs Side chain Coverage spectrum, pharmacokinetics, side effect Resistance: Enterobacter, Pseudomonas, Serratia, Citrobacter spp. Not effect against enterococci or ORSA Most renally excreted Side effect: a) Hypersensitivity b) MTT side chain (N-methylthiotetrazole): ( 2nd- Cefamandole, Cefmetazole, Cefotetan) caugulopathy (vit. K dependent CF) ; disulfiram-like reaction with ethanol flushing, sensation of warmth, giddiness, nausea, and occasionally tachycardia β-Lactams: Cephalosporins Against GPC 1st > 2nd > cephamycins > 3rd Against GNB 1st < 2nd < cephamycins < 3rd st 1 -generation cephalosporins Activity: a) Against most GPC, including β-Lactamase producine strains b) CAI-GNB, E. coli, Klebsiella spp. c) Typically resistance: B. fragilis, P. aeruginosa, Enterobacter spp. d) No BBB penetration Cefazolin (Veterin ): Longest T1/2 (1.7h) q8h; most effective to E. coli nd 2 -generation cephalosporins Expanded coverage to GNB No BBB penetration Cefuroxime (Zinacef): a) very active against MSSA and Streptococcal species b) β-Lactamase stable 3rd-generation cephalosporins More active in GNB but less active in GPC (especially S. aureus) Drug of choice for GNB meningitis Lead to superinfection with fungi. and enterococci (induce production of β-Lactamase. Ex: p. aerugnosa, Citrobacter species…) Anti-pseudomonal cephalosprins a) Ceftazidime (Kefadin) b) Cefoperazone (Cefobid) Broad-spectrum cephalosporins: bac. Meningitis a) Ceftriaxone ( Rocephin= Sintrix) b) Cefotaxime th 4 -generation cephalosporins Anti-pseudomonas + Broad-spectrum 3rd Less BBB peneration Cefepime (Maxipime) a) Enhanced stability against GNBβ-Lactamase ( Enterocobecter spp. Klebsiella…) b) significant activity against GPC: S.aureus, pneumococci c) Neutropenic fever: monotherapy Penicillin groups: penicillin ring Cephalosporin groups: cephalosporin ring Monobactams: Aztreonam Carbapenems: (1) Imipenem-Cilastatin (Tienam) (2) meropenem (Mepem) β-Lactams : Monobactams Aztreonam a) only binds PBPs of aerobic G(-) bac. (many strains of P.aeruginosa) b) completely ineffective to all G(+) bac. c) useful in allergic to PCNs β-Lactams : Carbapenems Tienam/ mepem Widest spectrum: 1) anaerobes, 2) most GPC (except Enterococcus faecium and ORSA) 3) most GNB (except: Stenotrophomonas maltophilia and Burkholderia cepacia ) Special stereochemical characteristics β-lactamase stable Hypersensitivity similar with PCNs Seizure attack with predisposing factors (e.g., advanced age, renal insufficiency, Hx. of seizure) ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ Amikacin (Amikin)/ Gentamicin/ Neomycin / Netromycin Aminoglycosides Amikacin (Amikin)/ Gentamicin/ Neomycin / Netromycin Bactericidal for numerous G(+) & G(-) bacteria Not active in 1) oxygen-poor environment 2) low PH ineffective to anaerobes and abscesses Usually with β-Lactam antibiotics to GNB Synergy with PCNs to streptococcal, enterococcal endocarditis Aminoglycosides Interfering with protein synthesis during aerobic metabolism. Good potensy: concentration-dependent killing effect and time-dependent PAE on G(+) and G(-) organisms Potency depend on 1) susceptibility to aminoglycoside-inactivating enzyme 2) permeability to cell wall Freeze initiation Block peptide bond formation Misreading of mRNA Aminoglycosides Excreted rapidly by normally functioning kidney TBW-dependent distribution: ↑dose in pregnancy, burns, ascites, septic shock ↓dose in renal insufficiency Adverse effect: 1) Nephrotoxicity reversible but possible permanent renal failure monitor renal function during therapy 2) ototoxicity prolonged use (>14 days) , renal insufficiency, concurrent use with other ototoxic agents. ★ Fluoroquinolones: Ciprofloxacin (Ciproxin) Levofloxacin (Cravit ) / Nofloxacin ( Noxacin ) ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ Fluoroquinolones Ciprofloxacin (Ciproxin) / Levofloxacin (Cravit ) / Nofloxacin ( Noxacin ) 快速且完全自腸胃道吸收 Synergic effect with some β-lactam antibiotics Active against: 1) Most GNB : Enterobacteriaceae, H. influenza, P. aeruginosa… 2) Many GPC 目前為一對P. aeruginosa有效的口服抗生素 Resistance: mutations in DNA gyrase ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ Glycopeptides (Vancomycin ) Bactericidal against most G(+) bacteria Bacteriostatic to enterococci VRE↑ Indication: 1) Serious infection with resistance to β-lactam-resistance G(+) bac. 2) Allergy with β-lactam antibiotics 3) Orally treatment of C. difficile colitis that lift-threatening 4) Endocarditis prophylaxis 5) prophylaxis in prosthetic implant 6) empiric use for suspected pneumococcal spp. meningitis Histamine-related reaction: red men syndrome Macrolides Erythromycin/ Azithromycin / Clarithromycin (Klaricid) / Clindamycin Bateriostatic High tissue concentration but unreliable CSF penetration Hepatic elimination Resistance: alteration of ribosomal binding sites Increase plasma level of theophylline, wafarin… Sulfonamide Buktar: Trimethoprim + Sulfomethoxazol Bacteriostatic antibiotics with a wide spectrum against most G(+)& many G(-) organisms. Uncomplicated UTI, nocardiosis (土壤絲菌 病),chancroid(軟下疳) 1) combine with pyrimethamine toxoplasmosis, 2) substitute for penicillin in prophylaxis of rheumatic fever 3) prophylaxis against susceptible meningococcal strains, in ulcerative colitis (as sulfasalazine), in burns (as silver sulfadiazine or mafenide), in chloroquine-resistant Plasmodium falciparum infection, and in combination with trimethoprim Nitromidazole (Metronidazole) Active only against protozoa, such as Giardia lamblia(腸梨形蟲), Entamoeba histolytica(痢疾 阿米巴), and Trichomonas vaginalis(陰道滴蟲), and strictly anaerobic bacteria (Bacteroides fragilis). (Not active against aerobic or microaerophilic bacteria.) Drug of choice in Clostridium difficile colitis. Drug of choice for bacterial vaginosis. It has also been used successfully in Crohn's disease penetrates into the CSF in high concentrations Disulfiram-like reaction may occur if alcohol is ingested Others Antituberculous antibiotics: Rifampin Tetracyclin Thanks For Your Attention !!!