* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download General Introduction to the Crusades
Rhineland massacres wikipedia , lookup
Third Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Nicopolis wikipedia , lookup
Kingdom of Jerusalem wikipedia , lookup
Northern Crusades wikipedia , lookup
Albigensian Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Savoyard crusade wikipedia , lookup
Siege of Acre (1291) wikipedia , lookup
History of Jerusalem during the Kingdom of Jerusalem wikipedia , lookup
Despenser's Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Fourth Crusade wikipedia , lookup
First Crusade wikipedia , lookup
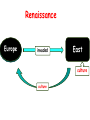
--------In The Name Of Jerusalem Fion.JW Causes and Background The Early Crusades Clare The First Crusade Clare The Second Crusade Process Evo The Third Crusade The Crusades of the Thirteenth Century Effects Cathy Spring General Introduction to the Crusades— the Holy War ●When ● What ● Why ● Who Why It Is Called The Holy War? External The Byzantine Empire The Seljuk Turks Internal The West The Byzantine Empire External Treats Moved to Asia Minor 1071Manzikert Anatolia, where many peasants, readily accepted Turkish control. The Byzantine Empire Internal struggles ●Ambitious military leaders aristocratic families. A self-destructive policy The Byzantine Empire Internal struggles ● The Catholic Church of the West the Eastern Orthodox Church Reach a climax in 1054 ● Pope Leo IX Patriarch Michael Cerularius, formally excommunicated each other The Seljuk Turks ●Nomadic ●Islam ●Flourished as military mercenaries ●Sultan” holder of power” ●In the late 11th century, exerting military power on Egypt and the Byzantine Empire The west The acess to Jerusalem was cut off Piligrames Did not develop isolated Preparations for The “Peasants’ Crusade : 1.Pope(教皇) Urban's speech: ·remission of sins; ·made glorious with the name of god. 2.Emperor Alexius: assemble their armies, raise money The initial response to Urban’s speech : call to military arms and religious fervor(狂热). Leader: Peter the Hermit (self-appointed) his reputation and preaching(说教) Assembled a large army most of them poor and many of them peasant Bad things they did: terrorizing the natives looting food and supplies. the persecution of the Jews They lose the fight: Emperor Alexis wisely shipped them over to Asia Minor where the Turks stationed. Pope Urban II inclined to trust Knights Crusading armies: The warriors of Western Europe particularly French Religious fervor Motivated by: Opportunity to pursue their favorite past time—Fight Gain territory, riches, status 1096-1099 1096 Begun 1097 Reached Constantinople 1098 The capture of Antioch 1099 Jerusalem was taken, the massacre Against the wished of the Byzantine Emperor Organized 4 Crusader state: Edessa, Antioch, Tripoli and Jerusalem 1147-1149 ●The Crusader States were soon foundered, by 1120s, Muslims were striking back. ●1144, Edessa was recaptured ●Leaders: Leaders: King Louis VII of France Emperor Conrad of III of Germany 1189-1192 ● 1187 The fall of the holy city Jerusalem ● Muslim Leader: Saladin ● Emperor Frederick Barbarossa of Germany Drowned, army fell apart Philip II Augustus, King of France Went home King Richard I The Lionhearted of England Negotiated a settlement – free access to Jerusalem The Crusades Fourth Crusade — sack of Constantinople 1024 Latin Empire of Constantinople 1024-1261 Children’s Crusade 1212 Fifth Crusade 1219-1221 Frederick II occupies Jerusalem (Sixth Crusade) 1228 First Crusade of Louis IX (Seventh Crusade) 1248-1254 Second Crusade of Louis IX (Eighth Crusade) 1270 Surrender of Acre and end of Christian 1291 presence in the Holy Land ●Opened the door to the Oriental trade. ● Promoted urban development of the city and benefited for budding capitalism. ●The Crusades also prompted the famous Voyages of discovery and the Renaissance. Renaissance Europe invaded East culture culture ●Western Civilization—Jackson.J.Spielvogel ●Crusades—In the name of Jerusalem ●Wiki ●历史—人教版