* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 04-Atoms_ molecules_ ions_etc
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
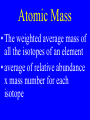
Drill: • Calculate the mass in kg of material with a density of 7.50 g/mL in a 2.0 m x 500.0 5 mm 4.00 x 10 mm container. 3 • 1 cm = 1 mL Chapter 2 •Atoms, Molecules, & Ions Atomic Theory • Elements composed of atoms • Atoms can’t be changed • Compounds of multiple atoms • John Dalton Conservation of Mass •In ordinary chemical reactions, matter can be neither created nor destroyed Constant Composition •Compounds contain elements that are always in the same proportions Multiple Proportions •The elements making up a compound will form whole number ratios Atom •The smallest particle that an element can be broken down into and still maintain the properties of the element Nuclear Atom •Proved by Rutherford & Bohr in the famous gold foil experiments Atomic Composition •Proton: in the nucleus •Neutron: in the nucleus •Electron: outside the nucleus Proton •In Nucleus •+1 charge •About 1 amu in mass Neutron •In nucleus •Neutral in charge •Mass is about 1 amu Electron •Outside the nucleus •-1 in charge •Negligible mass about 1/2000 amu Electron Charge •Determined by Robert Milliken in the famous oil droplet experiment Drill: Convert: 1) 23 cm/ms to km/ns 2) 56 mg/nL to kg/ML Atomic Number •The number of protons in an element •Z number Mass Number •The number of protons and neutrons in an atom •A - number Nuclear Symbol • A • • 4 X Z He 2 Isotopes •Atoms that contain the same number of protons, but different number of neutrons •Z constant, A variable Atomic Mass • The weighted average mass of all the isotopes of an element • average of relative abundance x mass number for each isotope Periodic Table •Graphic representation of all the elements indicating size, charge, electronic structure, & reactivity Periods •Rows which indicate energy level or shell or size of the atoms Groups or Families •Columns which indicate the number of electrons in the outermost energy level determining charge & reactivity Metals •Left three quarters of the chart •Lose electrons •Become positive Nonmetals •Upper right portion •Gain, lose, or share electrons when they react Metalloids •Along the stair-stepped line from B to At •Share properties of metals & nonmetals Radioactivity •The spontaneous breakdown of an unstable nucleus Radioactive Decay •Alpha radiation •Beta radiation •Gamma radiation Alpha Particle •Helium nucleus •2 protons & two neutrons •mass = 4 & charge = +2 •Low penetrating power Beta Particle •High speed electron •Mass = 0 & charge = -1 •Medium penetrating power Gamma Rays •High energy electromagnetic wave •No mass or charge •Very high penetrating power Drill: •List & describe each of the three radioactive particles Compound •A group of atoms that are chemically combined Molecule •A compound that can exist by itself Diatomic Molecule •Two atoms of the same element that are chemically combined •Cl2, F2, O2 Ion •Charged Particle -1 •Cl Polyatomic Ion •A group of atoms chemically combined that together has a charge -2 •SO4 Binary Compound •A compound made up of two elements in any ratio •NaCl •Mg3P2 Chemical Formula •A formula that shows the number and kinds of atoms in a compound •CaCO3 Molecular Formula •A formula that shows the number and kinds of atoms in a molecule •C6H12O6 Atomic Structure •List & describe the three subatomic particles Atomic Structure •Fill in the Chart: • Isotope protons neutrons electrons • U-235 • 56 80 • 14 13 Calculate the atomic mass of the element made up of the following isotopes: 99.50 % H-1 0.30 % H-2 0.20 % H-3 Calculate the atomic mass of the element made up of the following isotopes: 5.0 % Pu-242, 5.0 % Pu-243 80.0 % Pu-244, & 10.0 % Pu-245 Determine the number of of atoms in each compound •C6H12O6 NaNO3 •H3PO4 Al2(SO4)3 List & describe each of the three types of radiation Chapter 2 General •Define all the Key Terms on page 48 Nuclear Symbols •Work problems: 11 - 18 on page 50 Nuclear Symbols •Work problems: 19 - 24 on page 50 Elements & PT •Work problems: 27 - 88 on page 51 Nomenclature •Work problems: 45 - 48 on page 51 Nomenclature •Work problems: 49 - 54 on page 51 Nomenclature •Work problems: 55 & 56 on page 52