* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AP Biology Body System Test Review Test on April 19th!!! Chapter
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Induced pluripotent stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
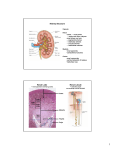
AP Biology Body System Test Review Test on April 19th!!! Chapter 43: The Immune System Vocabulary Leukocytes Lymphocytes Phagocytes NK cells Basophil Neutrophil Eosinophil Monocyte (Macrophage) B cells Plasma cells Antibodies Cytotoxic T cells Helper T cells Memory cells Antigen Histamine Lysozyme MHC Differentiate between the three lines of defense. Know the four ways antibodies work Active immunity vs. Passive immunity Primary vs. Secondary response Chapter 44: The Excretory System Vocabulary Homeostasis Hypertonic Hypotonic Ammonia Urea Uric Acid Kidney Nephron Glomerulus Bowman’s capsule Loop of Henle (proximal tubule, descending limb, ascending limb, distal tubule) Collecting duct ADH Know how to describe the steps of the mammalian kidney using the following terms: nephron, glomerulus, proximal tubule, loop of Henle, distal tubule, collecting duct. (What is being absorbed and filtered?) Chapter 45: The Endocrine System Vocabulary (Study Bozeman video sheet and diagram in your notebook) Hypothalamus Pituitary gland (Anterior vs. Posterior) Thyroid gland Parathyroid Adrenal glands Pancreas Ovary Testis Pineal gland Adrenal cortex Adrenal Medulla Know the following hormones: melatonin, growth hormone, T3, T4, calcitonin, PTH, insulin, glucagon, epinephrine, estrogen and testosterone Chapter 48: The Nervous System Vocabulary Neuron Neurotransmitter Dendrite Axon Node of Ranvier Axon terminal Schwann cells Myelin sheath Saltatory conduction Central Nervous System (CNS) Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Explain the production of action potentials and label on graph. Know how the membrane becomes polarized (what are the charges inside and out?) Know the major neurotransmitters. Practice Questions: 1. Which action below is affected by an antihistamine? A) blood vessel dilation B) phagocytosis of antigens C) MHC presentation by macrophages D) the secondary immune response E) clonal selection by antigens 2. Inflammatory responses may include which of the following? A) clotting proteins migrating away from the site of infection B) increased activity of phagocytes in an inflamed area C) reduced permeability of blood vessels to conserve plasma D) release of substances to decrease the blood supply to an inflamed area E) inhibiting the release of white blood cells from bone marrow 3. A person exposed to a new cold virus would not feel better for one to two weeks because A) specific B cells and T cells must be selected prior to a protective response. B) it takes up to two weeks to stimulate immunologic memory cells. C) no memory cells can be called upon, so adequate response is slow. D) antigen receptors are not the same as for a flu virus to which she has previously been exposed. E) V-J gene rearrangement must occur prior to a response. Use the graph in Figure 43.1 to answer the following questions. Figure 43.1 4. When would B cells produce effector cells? A) between 0 and 7 days B) between 7 and 14 days C) between 28 and 35 days D) A and B E) A and C 5. When would memory cells be produced? A) between 0 and 7 days B) between 7 and 14 days C) between 28 and 35 days D) between 35 and 42 days E) both A and C 6. When would you find antibodies being produced? A) between 3 and 7 days B) between 14 and 21 days C) between 28 and 35 days D) 14-21 and 42-56 days E) both A and C 7. The MHC is important in a T cell's ability to A) distinguish self from nonself. B) recognize specific parasitic pathogens. C) identify specific bacterial pathogens. D) identify specific viruses. E) recognize differences among types of cancer. 8. The following events occur when a mammalian immune system first encounters a pathogen. Which shows the correct sequence in which they occur? I. Pathogen is destroyed. II. Lymphocytes secrete antibodies. III. Antigenic determinants from pathogen bind to antigen receptors on lymphocytes. IV. Lymphocytes specific to antigenic determinants from pathogen become numerous. V. Only memory cells remain. A) I → III → II → IV → V B) III → II → I → V → IV C) II → I → IV → III → V D) IV → II → III → I → V E) III → IV → II → I → V 9. A marine sea star was mistakenly placed in freshwater and it died. What is the most likely explanation for its death? A) The sea star was stressed and needed more time to acclimate to new conditions. B) The sea star is hyperosmotic to the freshwater, and it could not osmoregulate. C) The osmoregulatory system of the sea star could not handle the change in ionic content presented by the freshwater. D) The contractile vacuoles used to regulate water content ruptured in the freshwater. E) The cells of the sea star dehydrated and lost the ability to metabolize. 10. The advantage of excreting wastes as urea rather than as ammonia is that A) urea can be exchanged for Na+. B) urea is less toxic than ammonia. C) urea requires more water for excretion than ammonia. D) urea does not affect the osmolar gradient. E) less nitrogen is removed from the body. 11. Which structure descends deep into the renal medulla only in juxtamedullary nephrons? A) loop of Henle B) collecting duct C) Bowman's capsule D) proximal convoluted tubule E) glomerulus 12. Natural selection should favor the highest proportion of juxtamedullary nephrons in which of the following species? A) a river otter B) a mouse species living in a tropical rain forest C) a mouse species living in a temperate broadleaf forest D) a mouse species living in the desert E) a beaver 13. Which of the following statements about hormones is incorrect? A) They are produced by endocrine glands. B) They are modified amino acids, peptides, or steroid molecules. C) They are carried by the circulatory system. D) They are used to communicate between different organisms. E) They elicit specific biological responses from target cells. 14. Blood samples taken from an individual who had been fasting for 24 hours would have which of the following? A) high levels of insulin B) high levels of glucagon C) low levels of insulin D) low levels of glucagon E) both B and C 15. After the depolarization phase of an action potential, the resting potential is restored by A) the opening of sodium activation gates. B) the opening of voltage-gated potassium channels and the closing of sodium activation gates. C) a decrease in the membrane's permeability to potassium and chloride ions. D) a brief inhibition of the sodium-potassium pump. E) the opening of more voltage-gated sodium channels.