* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SPD terminology, references SPD terminology
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Portable appliance testing wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Protective relay wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic compatibility wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
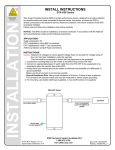
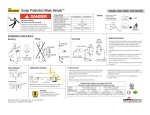
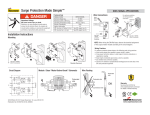
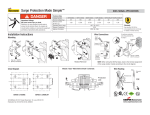
SPD terminology, references 14 SPD terminology 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. Surge protection device (SPD): device for limiting overvoltages. Maximum continuous operating voltage (Uc): the maximum voltage which may be connected to the SPD (sometimes referred to as its "rated voltage". Voltage protective level (Up): the limiting voltage which appears across the terminals of an SPD under conduction of a surge of defined waveshape an amplitude. If no such waveshape or amplitude is defined, Up is assumed to be stated when the SPD is subjected to the nominal discharge current In. Residual voltage (URES): the peak value of voltage that appears between the terminals of an SPD due to the passage of discharge current. Temporary overvoltage (UT): the ability of an SPD to withstand (or safely disconnect from) an overvoltage of magnitude (UT) applied for a specified duration (usually 5 s and 200 ms). Impulse current (Iimp): peak value of current having a wave shape of 10/350 µs. It is used in the classification of SPDs to test class I, for direct strike lightning discharges. Nominal discharge current (In): used in the classification of SPDs to test Class II. It shows the SPDs ability to withstand 15 impulses of peak magnitude In with an 8/20 µs waveshape. Combination wave: a generator capable of delivering a 1,2/50 µs voltage waveshape (UOC) into an open circuit, and 8/20 µs current into a short circuit. It is used in the classification of SPDs to test class III. Environmental protective rating (IP) : the protective rating of the SPD enclosure against the environment (e.g. water, dust, etc.) Disconnector: a device, internal or external to the SPD, which is used to provide safe disconnection under fault conditions. Disconnectors may provide isolation by operating as thermal devices, or overcurrent devices. Following current (IF): generally applies to voltage-switching type SPDs. This is the current delivered by the power distribution system which can be safely extinguished by the SPD during operation. Backup protection: the required protection to be placed in series with an SPD which ensure its safe isolation from the prospective fault current at the point of installation during a fault condition. Voltage withstand (UW): the voltage withstand level (insulation withstand) at the point of installation of the SPD. It is generally classified into one of the following four levels: 1500 V, 2500 V, 4000 V, 6000 V (see PN-EN 60664-1). MB: main-distribution board. SB: sub-distribution board. SA: socket outlet - the point directly in front of the device to be protected. MOV: metal oxide varistor. GDT: gas discharge tube. Typical component typologies used in SPDs SPD comprising metal oxide varistor (MOV) - no problems with following current IF, - quick response time tA (≤ 25 µs) means low residual voltage, - responds well to very low overvoltages, - high surge capacity up to 50 kA, 10/350 µs. SPD comprising gas discharge tube (GDT) - high surge capacity up to 100 kA, 10/350 µs, - no exhausting of ionized gases, - used in TT systems as galvanic separation between N-PE conductors. References PN-IEC 61643-1:2001 Surge protective devices connected to low voltage power distribution systems - Part 1: Performance requirements and testing methods. IEC 61643-12 Surge protective devices connected to low voltage power distribution systems. Selection and application principles. PN-IEC 61312-1:2001 Protection against lightning electromagnetic impulse - General principle. ÖVE NORM E 8001-1 Erection of electrical installations with rated voltages up to a.c. 1000 V and d.c. 1500 V - Part 1: Definitions and measures against electric shock. PN-IEC 60364-4-443:1999 Electrical installations of buildings - Part: 4-443: Protection for safety - Protection against overvoltages and electromagnetic disturbances - Protection against overvoltages of atmospheric origin due to switching. PN-EN 61000-4-5:1998 Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) - Testing and measurements techniques - Surge immunity test. PN-EN 62305-1:2006 (U) Protection against lightning - Part 1: General principles. PN-EN 62305-2:2006 (U) Protection against lightning - Part 2: Risk management. PN-EN 62305-3:2006 (U) Protection against lightning - Part 3: Physical damage to structures and life hazard. PN-EN 62305-4:2006 (U) Protection against lightning - Part 4: Electrical and electronic systems within structures. www.relpol.com.pl SPD comprising series arrangement of metal oxide varistor and gas discharge tube (MOV+GDT) - no following current IF, - quick response time tA (≤ 25 µs) means low residual voltage, - responds well to low overvoltages, - high surge capacity up to 25 kA, 10/350 µs. Export Sales Department Phone +48 68 47 90 832 • Marketing Department Phone +48 68 47 90 900