* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 5 pairs of sacral nerves
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
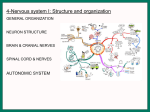
The Nervous System Master control unit of the body 1 Objectives • Describe the structures of the nervous system: central and peripheral. • Discuss the functions of the nervous system: central and peripheral • State the functions of neuroglia cells in the central nervous system • Identify the structural parts of a neuron. • Explain how an impulse is transmitted via a neuron, including the role of neurotransmitters and their functions. 2 Objectives, cont’d • Identify the lobes of the brain and the function(s) of each lobe. • Describe a reflex arc. • List the names and functions of the 12 cranial nerves. • Apply knowledge of anatomy and principles of physiology, chemistry, microbiology and physics to nursing situations related to the coordination. 3 Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Central Nervous System Brain Spinal Cord Autonomic Nervous System Sympathetic Nervous System Motor Sensory (Efferent) Neuron (Afferent) Neuron Somatic Nervous System Parasympathetic Nervous System 4 The Nervous System Structural divisions Peripheral (PNS) 5 Central (CNS) Action Potential: a) A stimulus is received by the dendrites of a nerve cell. This causes the Na+ channels to open. If the opening is sufficient to drive the interior potential from -70 mV up to -55 mV, the process continues. b) As depolarization reaches threshold of -55mV, the action potential is triggered and Na+ rushes into cell. Membrane potential reaches +30mV on action potential c) Propagation of the action potential at 110 m/sec (which is 225 mph) d) Repolarization occurs with K+ exiting the cell to return to 70mV RMP e) Return of ions (Na+ and K+) to their extracellular and intracellular sites by the sodium potassium (Na+K+) pump 6 7 Neurotransmission 8 9 Name Dopamine Type Amine Postsynaptic Effect Excitatory Location(s) CNS, PNS Function(s) Controls movement and arousal levels, creates sense of feeling good Inhibitory CNS, intestine regulates appetite, sleep, memory and learning, temperature, mood Amine Excitatory CNS, PNS Induce arousal, heighten mood, low levels may lead to depression Amino acid Inhibitory CNS Control anxiety level Neuropeptid Inhibitory CNS Reduce stress, promote calm, natural painkiller (inhibits substance P Substance P Neuropeptid Excitatory PNS Transmission of pain Acetylcholine (ACH) Acetic acid Excitatory & Inhibitory CNS, PNS Role in memory, vasodilation Controls skeletal muscle actions Serotonin Noradrenaline (norepinephrine) GABA Endorphins Enkephalin (opiate) Amine 10 The Brain The Brain is made up of more than 10 billion nerves Divided into three parts: Cerebrum, Cerebellum and Brain Stem Protected by: Skull mainly but the Meninges/Cerebral-spinal fluid act as shock absorbers 11 The Brain 12 13 The Brain - Protection 14 BRAIN The Cerebrum • Largest part of the brain Medulla • Connects the brain and the spinal cord 15 The Cerebellum The cerebellum is below and to the back of the cerebrum The cerebellum controls: 1.Balance 2.Coordination 16 Spinal Cord 17 18 19 20 21 22 Spinal Nerves 23 Spinal Nerves • 31 pairs • Each pair arise from a spinal segment - 8 pairs of cervical nerves - 12 pairs of thoracic nerves - 5 pairs of lumbar nerves - 5 pairs of sacral nerves - 1 pair of coccygeal nerves 24 Cranial Nerves 25 Cranial Nerves "On Old Olympic Towering Top A Famous Vocal German Viewed Some Hops“ ... standing for: Olfactory, Optic, Oculomotor, Trochlear, Trigeminal, Abducens, Facial, Vestibulocochlear, Glossopharyngeal, Vagus, Spinal accessory, Hypoglossal. 26 Autonomic Nervous System 27 Peripheral Nervous System •Somatic nervous system – voluntary control over skeletal muscle •Autonomic nervous system – involuntary control over the contraction of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, gland secretion 28 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) • Sympathetic – “flight or fight” • Ready for immediate stress • Increase of body systems • Parasympathetic – “rest and digest” • Nonstressful conditions • Decrease body systems • Digestion increased 29 Parasympathomimetics •AKA – cholinergic agents •Cholinergic = parasympathetic •Classic – acetylcholine •Does not stay long in body, rapidly destroyed after receptor binding •Direct acting – bind to cholinergic receptors to produce rest/digest response – AKA muscarinic agonist •Indirect acting – avoids destruction of Ach and allow to remain on cholinergic receptors for longer time – AKA cholinesterase inhibitors 30 Autonomic Drug Classes •Adrenergic antagonists or adrenergic blockers – inhibit SNS •Anticholinergics or parasympatholytics or muscarinic blockers – inhibit PNS 31 Baroreceptor Reflex The baroreceptor reflex regulates BP •The receptors are located in the carotid sinus and aortic arch •The brain sends impulses to the ANS •When there is a decrease in BP there is vasoconstriction and an increase in CO •When there is an increase in BP vasodilation and a decrease in BP 32 Neurotransmitter Disintegration •Ach •Destroyed by acetylcholinesterase •Norepinephrine (NE) •Reuptake of NE into nerve terminals for reuse •Inactivation by monoamine oxidase (MAO) 33 ANS Transmitters •Norepinephrine (NE) – catecholamine •Alpha receptors – alpha1 and alpha 2 •Beta receptors – beta 1 and beta 2 34 ANS Neurotransmitters • Acetylcholine (Ach) – released by cholinergic nerves • Nicotinic receptors – Ach receptors in the preganglionic ganglia, effects similar to effects of nicotine • Muscarinic receptors – Ach receptors in postganglionic ending in target tissues, similar to effects of amanita muscaria 35 Drug Effects •Affect synthesis of neurotransmitters •Prevent storage of neurotransmittters •Influence the release of neurotransmitters •Bind to the receptor site of postsynaptic neuron – increase autonomic function 36 37