* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download circumflex artery
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Drug-eluting stent wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
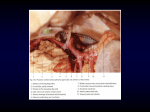
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Normal ECG Lead Placement is Important Each positive electrode acts as a camera looking at the heart Ten leads attached for twelve lead diagnostics. The monitor combines 2 leads. Mnemonic for limb leads White on right Smoke(black) over fire(red) Snow(white) on grass(green) 2004 Anna Story Precordial Leads 2004 Anna Story 4 Rhythm I and AVL(LATERAL) V3 & v4(ANTERIOR) V1 & v2(SEPTAL) V5 & v6(LATERAL) II, III and AVF(INFERIOR) 2004 Anna Story Where the positive electrode is positioned, determines what part of the heart is seen! 7 angina CORONARY CIRCULATION The left coronary artery distributes blood to the left side of the heart, the left atrium and ventricle, and the interventricular septum The circumflex artery arises from the left coronary artery The larger anterior interventricular artery, also known as the left anterior descending artery (LAD), is the second major branch arising from the left coronary artery. The right coronary artery proceeds along the coronary sulcus and distributes blood to the right atrium, portions of both ventricles, and the heart conduction system. marginal arteries arise from the right coronary artery inferior to the right atrium. marginal arteries supply blood to the superficial portions of the right ventricle On the posterior surface of the heart, the right coronary artery gives rise to the posterior interventricular artery, also known as the posterior descending artery. supply the interventricular septum and portions of both ventricles.[1] ECG leads Location of MI Coronary Artery II, III, aVF Inferior MI Right Coronary Artery V1-V4 Anterior or Anteroseptal MI Left Anterior Descending Artery V5-V6, I,aVL Lateral MI Left Circumflex Artery ST depression in V1, V2 Posterior MI Left Circumflex Artery or Right Coronary Artery acute infero-postero-lateral MI. Acute Anterior Myocardial Axis Left or right axis deviation? Look at limb leads I and aVF. Normal: I +, aVF + LAD: I +, aVF – RAD: I -, aVF + HEART AXIS Many factors may alter the electrical heart axis including: Anatomic Factors: Abnormal anatomic position of the heart in the thoracic cavity (such as in dextrocardia) Abnormal thoracic anatomy Abnormal position of the diaphragm (such as in obesity, pregnancy, ascites) Cardiopulmonary Pathology: Prior myocardial infarction Recent ischemia Pulmonary embolism Pulmonary obstructive disease Myocardial hypertrophy Dilated cardiomyopathy Conduction abnormalities Others Left axis deviation Right axis deviation Sinus Bradycardia - SB Sinus Tachycardia - ST Sinus Arrhythmia - SA Irregular irregular Atrial Fibrillation : A Fib Atrial Flutter : A Flutter Junctional rhythms Premature Ventricular Contraction: PVC Ventricular Tachycardia - VT Ventricular Fibrillation - VF Asystole Artifact: nd 2 Degree AV Block, Type I (Wenckebach) 2nd Degree AV Heart Block, Type II rd 3 Degree Heart Block LBBB cardioversion automated external defibrillators or AEDs. X-ray on chest showing pacemaker Left ventricular hypertrophy Left ventricular hypertrophy (the left ventricle is enlarged and generates more electrical activity, so the heart axis is “pulled” to the left) S in V1 + R in V5 or V6 (whichever is larger) ≥ 35 mm (≥ 7 large squares) Left ventricular hypertrophy Left ventricular hypertrophy