* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chemistry of Living Things
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
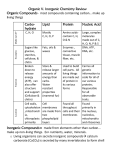
Chemistry of Living Things Study Guide Part 2 Inorganic Chemicals: Simple compounds A.__________________________ (___ ): A. Water (H2O) Most common substance in all living things (about 60% of body mass) – – Needed for chemical reactions ( which won’t happen in “dry” conditions) Dissolves other molecules into solution, allowing them to be transported through the body. Inorganic Chemicals: B.__________________________ (____): B. Oxygen (O2) Needed by most (not all) organisms for cellular respiration. Released by plants and algae as a waste product of photosynthesis. Aerobic respiration: Process that uses oxygen to extract energy from glucose (sugar). Used by most organisms. Anaerobic respiration: Process that extracts energy from glucose without using oxygen. Gives less energy, so only used by some simple organisms (some bacteria, yeast). These organisms do not need to breathe in oxygen. Inorganic Chemicals: C.__________________________ (_____): C. Carbon Dioxide (CO2) With water, used by plants to make glucose (photosynthesis). Waste product of aerobic respiration. Inorganic Chemicals: D.____________________________ (___): D. Nitrogen (N2) Most common gas in air (70%) Needed to make protein. Converted into nitrates by soil bacteria. Nitrates are absorbed by plants and then eaten by animals. Excreted as waste in urine. Inorganic Chemicals: E. Acids and Bases: Measured by the ________ Measured by the pH scale Very high and very low pHs are usually____________. Very high and very low pHs are usually lethal. pH can affect _______________ of chemical reactions; pH can affect rates of chemical reactions for example, digestive enzymes work fastest in acidic environments, which is why we make stomach acid (hydrochloric acid, or HCl). Organic Compounds Larger, more complex chemicals. Always contain the elements carbon (C)and hydrogen (H). Synthesized from simpler substances (building blocks). Organic Compounds A.____________________________________: Sugars and starches A. Carbohydrates: Sugars and starches Building blocks: ____________________________________ Building blocks: Simple sugars Functions: ____________________________________ Provides energy Stores energy in plants (starch) Organic Compounds B.____________________________________: Fats, oils and waxes B. Lipids: Fats, oils and waxes Building blocks: ________________ Building blocks: fatty acids Functions: Stores energy (animal fat) Insulation Water proofing Cell membrane ____________________________________ ___________________________________ ____________________________________ A starch (A) is broken down by an enzyme (B) into two simple sugars (C, D). This is also a good example of the lock and key model. Organic Compounds C.___________________________________: Complex compounds that carry out all the body’s activities. C. Proteins: Complex compounds that carry out all the body’s activities. Building blocks: ___________ Building blocks: Amino acids Have many different functions as determined by their Shape. ____________________________________. Lock and Key Model: Proteins must have the right ___________to “fit” with other molecules. Lock and Key Model: Proteins must have the right shape to “fit” with other molecules. Changing the ____________________________________ of a protein will change what it can interact with its ____________________________________. Changing the shape of a protein will change what it can interact with its function. Organic Compounds Important types of proteins: ______________________ and ___________________ Hormones and neurotransmitters –carry messages through the body. ____________________________________ Cell receptors – in cell membrane; receive hormones and neurotransmitters. ____________________________________ Antibodies – attack foreign pathogens ____________________________________ Enzymes - act as catalysts, controlling all chemical reactions in the body. High temperatures will cause enzymes to denature (lose their _____________) and stop _________________________. High temperatures will cause enzymes to denature (lose their shape) and stop functioning. This is why high fevers are dangerous. Organic Compounds D.____________________________________ (DNA and RNA): Make up genes and chromosomes. D. Nucleic Acid (DNA and RNA): Make up genes and chromosomes. Building blocks: Nucleotides; molecular bases (ATCGU)