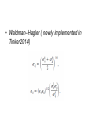* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download van der Waals` forces in molecular modeling
Eigenstate thermalization hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Monte Carlo methods for electron transport wikipedia , lookup
Quantum potential wikipedia , lookup
Biology Monte Carlo method wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Density of states wikipedia , lookup
Entropy of mixing wikipedia , lookup
Rotational spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear force wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear structure wikipedia , lookup
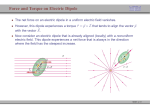
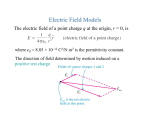
van der Waals' forces in molecular modeling "[There were] only two fundamental forces to account for all natural phenomena. One was Love, the other was Hate. The first brought things together while the second caused them to part." Empedocles ~450 BC Topics • vdW: – Dipersion(attraction) – Repulsion • Mixing Rules Van der Waals Interaction • The attractive or repulsive forces between molecular entities other than those due to bond formation or to the electrostatic interaction • includes: dipole–dipole, dipole-induced dipole and London (instantaneous induced dipole-induced dipole) forces Attraction1: Dipole-dipole interaction • Dipole: a separation of positive and negative charge • Dipole-dipole interaction: Attraction 2: Dipole-induced dipole interaction • Polarizability (α0) • The ease of distortion of the electron cloud of a molecular entity by an electric field (such as that due to the proximity of a charged reagent). It is experimentally measured as the ratio of induced dipole moment (uind) to the field E which induces it: A dipole near a polarizable molecule induces a dipole (charge dislocation) in the neutral molecule leading to an attractive interaction, the corresponding potential energy is referred to as Debye energy. Angle-averaged interaction (Debye interaction or inductive interaction) becomes: Attraction 3: Induced dipole-induced dipole interaction (dispersion) • Random fluctuations in a polarizable molecule lead to a temporary dipole which induces a corresponding dipole in a nearby molecule, leading to attractive dispersion interactions. The involved potential energy is called the London dispersion energy. London Dispesion Attractive + repulsive potentials • Lennard - Jones • • • • • ε :depth of the potential well σ : where inter-particle potential is zero R : dist. between the particles Rm: dist. at which the potential reaches its minimum (- ε). Repulsive forces: (orientation dependent) reflect the shape of molecules, which determines the melting point. Attractive forces : Heat of vaporizations are closedly associated with the cohesive energies in solids and liquids • Born-Mayer potential – Exponential dependence on distances, to account the overlap between the wavefunctions: • Buckingham potential – Combined with London formula for dispersion: Why damping • Deficiency: Damping functions • Hartree-Fock-dispersion(1975) • Koide et al(1981) Tang-Toennies(1984) • widely used damping functions: b : distance scaling factor, usually = B in the Born–Mayer repulsion, on the grounds that both the repulsion and the dispersion damping are consequences of wavefunction overlap. Other forms • Mooij et al • Fermi • In tinker proposed (Rm -> Rmin, mixed vdw) radii) Repulsion(Pauli-principle) • Van der Waals Radii – The Van der Waals radius of a given atom is the halve of the shortest distance observed in crystals betweeen the nuclei of atoms of the same nature belonging to different molecules. Hard Sphere Potential Soft Sphere Potential - Power-law potential typically 9 < n < 12 -Exponential potential -Dham et al. (1989): - Mixing Rules • For N types of interaction sites, one needs to define ½ N(N +1) interaction parameter sets. • In matrix form, the following array depicts these concepts for an N site case, where bold face denotes the vector of parameter sets involved. The boxed elements are the elements that require specification when using mixing rules. Reference :A Generating Equation for Mixing Rules and Two New Mixing Rules for Interatomic Potential Energy Parameters. ALI KHALAF et al. 2003 Theoretical Rules – Based on some quantum mechanical derivation – Requisites additional parameter sets, disabey mixing rules – Most successful equation of this group is the Tang–Toennies Empirical Rules • Lorentz–Berthelot • Halgren HHG: implement weights • Waldman–Hagler ( newly implemented in Tinker2014)