* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Dynamic Notes
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
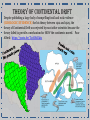
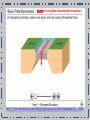
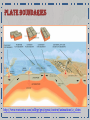
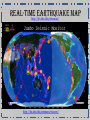
Dynamic Earth Ms. Susinno • In 1915, the German geologist and meteorologist Alfred Wegener first proposed the theory of continental drift which stated that continents were all connected at one point in Earth’s history. • The theory of Continental drift led to the currently accepted theory of plate tectonics. * The continents never actually looked like a chicken, but it’s funny! Theory of Continental Drift Despite publishing a large body of compelling fossil and rock evidence (GEOLOGIC EVIDENCE) for his theory between 1912 and 1929, the theory of Continental Drift was rejected by most other scientists because the theory failed to provide a mechanism for HOW the continents moved. Poor Alfred: https://youtu.be/T1-cES1Ekto Plate Tectonics: The theory that the outer rigid layer of the earth (the lithosphere) is divided into a couple of dozen "plates" that move around across the earth's surface relative to each other. Evidence suggests that the plates are moving atop convection cells in the asthenosphere. Click to see plate boundaries in action! http://www.wwnorton.com/college/geo/egeo2/content/animations/2_1.htm Earth’s layers • The properties of the inner Earth are inferred with evidence from Earthquake waves • We have never penetrated the crust so we have very little direct evidence of the Earth’s interior! https://youtu.be/ZkaDvzGGspM http://www.regentsearth.com/Illustrated%20ESRT/Page%2010%20(Earth's%20Interior)/Page%2010%20index.ht m Earth’s layErs: The asthenosphere is the layer of the Earth that lies below the lithosphere. This Plastic Mantle contains rock that is partially melted and slowly moving below the lithospheric plates. This allows the tectonic plates of the lithosphere to move around on the Earth's surface by “riding" on the convection cells in the asthenosphere! https://ees.as.uky.edu/sites/default/files/elearning/module06swf.swf Marie Tharp (July 30, 1920 - August 23, 2006) created the first scientific map of the entire ocean floor. The Sea Floor Harry Hess (May 24, 1906 – August 25, 1969) considered a founding father of Plate Tectonics, found evidence for sea floor spreading Mid ocean ridges A mid-ocean ridge is a type underwater, volcanic mountain ridge. This uplifting of the ocean floor occurs when convection currents rise in the mantle beneath the oceanic crust. Lava cools to magma and creates a ridge where two plates diverge. The sea floor is made of basalt. http://earthguide.ucsd.edu/eoc/teachers/t_tectonics/p_seafloorspreading.html Sea floor Spreading • Iron in the sea floor lines up with Magnetic North. • Magnetic North changes throughout Earth’s History • The ocean floor keeps a tangible record of polarity Sea Floor SpreadingEvidence that provided the mechanism (convection cells in the asthenosphere) for plate tectonics that Wegener was lacking in his theory. http://study.com/academy/lesson/sea-floor-spreading-and-polar-reversal.html Plate boundaries http://www.wwnorton.com/college/geo/egeo2/content/animations/2_1.htm Types of Faults Hanging wall Hanging Wall Foot Wall Foot Wall Earthquake Waves P Waves- Primary Wavestravel the fastest, first to arrive. Also called push-pull waves because this describes the grounds motion as the waves pass. Travel through solids, liquids or gas. S Waves- Secondary WavesTravel slower than P waves. Also called Side to Side waves because this describes their motion. Only travel through solids. Surface Waves- includes both push-pull motion and side to side motion. Cause the most damage because they travel along the surface. Seismometers are instruments that measure motion of the ground, including those of seismic waves generated by earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and other ground shaking events Seismogram: The Richter magnitude scale (often shortened to Richter scale) is the most common standard of measurement for earthquakes. It was invented in 1935 by Charles F. Richter of the California Institute of Technology as a mathematical device to compare the size of earthquakes. The Richter scale is used to rate the magnitude of an earthquake, that is the amount of energy released during an earthquake. The Richter scale doesn't measure quake damage The Mercalli intensity scale is a seismic scale used for measuring the intensity of an earthquake by taking into account, the damage reported at each location Identify the earthquake intensity of each observation made at different locations. The shadow zone is the area of the earth from angular distances of 104 to 140 degrees from a given earthquake that does not receive any direct P waves. The shadow zone results from S waves being stopped entirely by the liquid core and P waves being bent (refracted) by the liquid core. http://www.classzone.com/books/earth_science/terc/content/visualizations/es1009/es1009page01.cfm Real-Time Earthquake Map http://ds.iris.edu/seismon/ http://ds.iris.edu/seismon/swaves/ Earthquake safety The End Up Next locating an epicenter