* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Problems
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Weightlessness wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Casimir effect wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Electron mobility wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
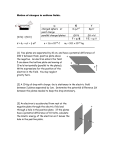
Chapter Seventeen: Problems Note: These problems come from "Fundamentals of Senior Physics" by Parham and Webber. 1. A positive charge of 3×10-6 coulomb is placed in a uniform electric field of 100 newtons per coulomb. What is the force on the charged object? The object moves in the direction of the field for a distance of 2m from A to B. Calculate: (a) the work done on the charge by the electric force. (b) the electric potential difference between A and B. 2. A charge of 5×10-5 coulomb moves through a potential difference of 6 volts. How much work is done on the charge by the electric force? 3. To move a charge of 4×10-7 coulomb from one point A to another point B, 8×10-5 joules of work are required. What is the potential difference between A and B? 4. The potential difference between two points in an electric field is 45 volts. 9 joules of work is required to move a small charged object from one point to the other. What is the magnitude of the charge on the object? 5. If all points in a given region of space are at the same electric potential, what can you say about the electric field in that region? Explain your answer. 6. What is the electric field strength between two oppositely charged metal plates if they are 8 cm apart and have a difference in potential of 240 volts between them? Sketch the field. 7. A spark-plug of a motor car has two insulated pieces of wire connected to an ignition coil. At the time of firing, the coil provides a high potential difference across the gap between the two wires.What is the electric field in a gap of 0.5mm if the potential difference supplied by the coil is 500 volts? 8. Two parallel metal plates are oppositely charged so that they have a difference in potential of 104 volts between them. (a) How much work in electron volts is done on an electron by the electric force when the electron moves from the negative to the positive plate? How many joules does this represent? (b) If the electron were released from rest at the negative plate, what would be its kinetic energy when it reached the positive plate? 9. An electron having a kinetic energy of 225 eV is projected directly through a small hole in the positive plate of a parallel plate capacitor. The two plates are 2.5cm apart and have a potential difference of 250V between them. Describe the motion of the electron after it enters parallel to the electric field between the plates, assuming the space to be a vacuum. Does the electron reach the negative plate? If not, how close does it get? 10. What is the electric potential, in air, at a point 10.0cm from an isolated point charge of 5.0×10-8 coulombs? 1 11. A hollow conducting sphere of radius 15cm has a positive charge of 2.0×10-6 coulombs placed on it. What is: (a) the electric field strength, and (i) at the surface of the sphere, (ii) 10cm away from the surface of the sphere, (b) the electric potential: (i) at the surface of the sphere, (ii) 10cm away from the surface of the sphere, (a+b) (iii) 10cm inside the surface of the sphere? Extra Questions 12. Two point charges of 50 picocoulombs and -144 picocoulombs are placed 13.0 cm apart in air. 5.0cm away from the positive charge and 12.0cm from the negative charge is a point P. Find, at P, (a) the electric potential (b) the electric field strength. 13. These questions relate to electric potential. (a) If the electric field E is zero at a given point, is the electric potential V also zero? Give an example. (b) If you know the value of the electric field E at a given point, can you determine the value of the electric potential V at the point? If not, what further information do you need? Chapter Seventeen: Motion of charged particles in Electric Field. Note: These problems come from "Fundamentals of Senior Physics" by Parham and Webber. 14. A stone is thrown vertically upwards with a velocity of 49 ms-1 in the gravitational field near the Earth’s surface (g = 9.8 Nkg-1). Calculate: (a) the time for the stone to reach its peak height. (b) the height to which it rises. (c) its acceleration at the top of its flight. (c) its velocity after 8 seconds. 15. A projectile is fired at an angle of 30° to the horizontal with a velocity of 980ms-1 in the gravitational field of the Earth. Calculate: (a) the time for the projectile to reach its peak height. (b) the height to which it rises. (c) its acceleration at the top of its flight. (d) its velocity after 8 seconds. 16. Two objects A and B each of mass 10kg are released from a 100m high tower in the gravitational field near the sruface of the Earth. What is the force on each object if the strength of the field is take as 10Nkg-1? Object A is allowed to fall, while object B is thrown downwards with an initial velocity of 20ms-1. What is the kinetic energy gained by each object in falling the 100m? What is the kinetic energy of each object as it hits the ground? Hence, calculate: (a) the final velocity of each object as it hits the ground. (b) the difference in the times take for the objects to hit the ground. 2 17. In a television tube electrons may be accelerated by 20000 volts on their way to the screen. (a) (b) (c) What is the gain in energy of each electron (in eV and joules)? With what speed do they hit the screen? If the acceleration is achieved over 5.0cm, what is the average force on the electrons as they are being accelerated? 18. The potential difference between two parallel plates 0.01m apart is 300V. What is the electric field strength between the plates? An electron initially at rest moves from the plate of lower to the plate of higher potential. What is the force on the electron in the electric field? Calculate: (a) (b) (d) the acceleration of the electron. the final velocity of the electron as it hits the second plate the gain in kinetic energy of the electron? Can you suggest an alternative way of calculating the gain in energy? Use this second method to check your answer for (c). 19. A stream of electrons is shot by an electron gun at right angles to an electric field between two parallel deflecting plates of length 5.0cm. The electrons are accelerated in the electron gun by a potential difference of 5000V. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) What is the energy supplied to each electron? What velocity does each electron acquire before it enters the deflecting plates? How long do the electrons take to pass through the length of the deflecting plates? The electric field strength between the plates is 104 volts per metre, so that as the electrons pass through the plates they acquire a sideways velocity. What is the sideways force on each electron? What is the acceleration of each electron? What is the sideways velocity that the electron acquires on passing through the plates? How far is the electron displaced by the electric field within the plates? 20. A uniform electric field is set up between two large parallel plates 5.0cm apart in air, with a potential difference of 400volts between the plates. Calculate: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) the electric field strength the force on an electron in the field the work done as the electron moves from the negative to the positive plate the gain in kinetic energy of the electron. the acceleration of the electron in the field. the velocity of the electron as it reaches the positive plate, assuming it starts from rest at the negative plate. 21. An electron gun in a cathode ray tube has a potential difference of 100volts applied between the accelerating electrodes. The electron beam produces passes between two parallel metal plates 10.0cm long and 1.0cm apart. A potential difference of 10.0volts is maintained between the two plates. Determine: (a) the speed of the electrons from the gun (b) the electric field strength between the plates (c) the force on each electron in the field (d) the time taken by an electron to pass through the field (e) the sideways velocity gained by each electron in the field (f) the angular deflection of the beam of electrons as it passes through the field. 3