* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download STI/HIV
Herpes simplex wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Cryptosporidiosis wikipedia , lookup
Plasmodium falciparum wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Ebola virus disease wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Antiviral drug wikipedia , lookup
Epidemiology of HIV/AIDS wikipedia , lookup
Microbicides for sexually transmitted diseases wikipedia , lookup
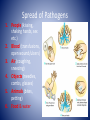
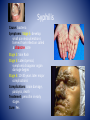
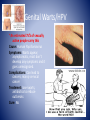
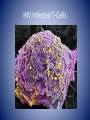
MYTH or FACT • You are able to get some STI’s more than once. • Answer: FACT MYTH or FACT • If you get checked and you’re STI free, your partner doesn’t need to get checked as well. • Answer: MYTH MYTH or FACT • You can’t get an STI if your partner is a virgin • Answer: Myth MYTH or FACT • Skin to skin contact isn’t enough. You can only get an STI from semen. • Answer: MYTH MYTH or FACT • The only way to 100% avoid STI’s is to not have sexual contact. • Answer: FACT STI’s REDUCING YOUR RISK!! STIs • Sexually Transmitted Infections – are infectious diseases spread from person to person through sexual contact. • A person can have an infection and pass it on to others with out actually knowing they have the disease. STIs are caused by pathogens (a disease causing agent; bacteria or virus) Spread of Pathogens 1. People (kissing, shaking hands, sex etc.) 2. Blood (transfusions, open wound/ulcers) 3. Air (coughing, sneezing) 4. Objects (needles, combs, glasses) 5. Animals (bites, petting) 6. Food & water Immune System and Your Body Exterior Defense 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Skin Perspiration Body Oil Tears Mucus Hair Saliva Stomach Acids Immune System and Your Body Interior Defense Lymphocytes (type of white blood cells) 2 Types – 1. Helper T Cells – signal B cells 2. B Cells – makes infection susceptible to macrophages (killer cells) Check for Understanding • Situation: You and your friends decide to go to a tattoo parlor to get a tattoo. • Explain how it is possible for you to contract a STI pathogen. STI Pathogens 1. Bacteria - 1,000 types - release toxins 2. Virus - smallest pathogen - invades cell *As a general rule in regards to STI’s – Bacteria = cure Virus = no cure Risky Behaviors are actions that can lead to the contraction of STIs • Sex with more than one person • Unprotected sex • Having high risk partners (partners that are sexually active with multiple people) • Using alcohol or other drugs – How might this increase your chances of contracting an STI? What are the two types of pathogens that cause a STI? Chlamydia *#1 STD in America Cause: bacteria affecting reproductive organs of both males and females Symptoms: – asymptomatic: no visible symptoms in 75% of cases Discharge (white)burning during urination Complications: sterility and PID in females Treatment: antibiotic Cure: Yes Syphilis Cause: bacteria Symptoms: Stage 1: develop small painless ulcerations formed from infection called a chancre sore Stage 2: Skin Rash Stage 3: Latent period, symptoms disappear organ damage begins Stage 4: 10-30 years later major complications Complications: brain damage, paralysis, death Treatment: penicillin in early stages Cure: Yes Genital Warts/HPV *An estimated 75% of sexually active people carry this Cause: Human Papillomavirus Symptoms: Warts appear; asymptomatic, most don’t develop any symptoms and it goes unrecognized. Complications: Can lead to cancers, mainly cervical cancer Treatment: laser warts, antibiotics to reduce outbreaks Cure: No Herpes Cause: simplex virus (Type 1 – cold sores, Type 2 – genital sores) Symptoms: Sores may appear after 2 weeks. May be asymptomatic or have flu-like symptoms Complications: painful outbreaks, possible transmission the baby, and more susceptible to HIV Treatment: antibiotics to reduce outbreaks Cure: NO Gonorrhea Cause: bacteria - attacks mucus membranes Symptoms: males- discharge yellow or white / burning during testicle Female- yellow discharge / burning during urination Treatment: antibiotics Complications: PID Males infertility Late - Both spreads to bloodstream can hurt joints, hrt valve, and brain urination. Swollen Pubic Lice Cause: crab lice invade pubic hair TOILET SEAT, SHEETS 24 hours Symptoms: itching PUBIC LICE Treatment: OTC shampoo to get rid of lice HEAD Complications: discomfort LICE HIV & AIDS HIV- Human Immunodeficiency Virus- virus destroys body’s T-Cells (destroys immune system) AIDS- Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome- HIV turns into AIDS when • 200 or fewer T-cells • Person gets opportunistic infection Opportunistic infection- infection that develops in a person w/ weak immune system HIV Infected T-Cells How HIV Transmitted • • • • Blood Semen Vaginal secretions Breast milk Risk Behavior - Unprotected sex - Sharing needles - Blood transfusion (organs) - Fluids in open wounds - May pass from mother to baby Bryan Jackson video How HIV NOT transmitted Any other casual contact Hugging Shaking hands Insects Coughing Donating blood World Aids Day HIV tests EIA- 1st test given screens for HIV antibodies in blood Two Positive Results Western Blot – confirms EIA test – Get Western Blot Test detects HIV antibodies Positive Result – HIV Antibodies in blood Negative result – no HIV antibodies * Does not mean not infected can take up to 6 months for antibodies to show up 3-2-1 Summarizer • 3- Name 3 examples of Risky behaviors • 2- Give 2 differences between viral and bacterial STI’s • 1- Write 1 STI and give a fact or symptom of that STI