* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name___________________ Anatomy II Respiration Part I
Survey
Document related concepts
Social history of viruses wikipedia , lookup
Human microbiota wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial morphological plasticity wikipedia , lookup
History of virology wikipedia , lookup
Marine microorganism wikipedia , lookup
Urinary tract infection wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
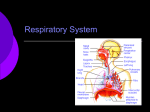
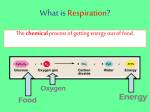
Name___________________ Anatomy II Respiration Part I: Matching ____ 1. Tiny sacs where gases are exchanged A. Diaphragm ____ 2. Ridged bones in the nasal cavity that B. Lungs C. Trachea D. Bronchioles E. Turbinates F. Ribs G. Bronchi H. Alveoli I. Pharynx J. Intercostals K. Visceral pleura oral cavities with the trachea L. Parietal pleura ____ 9. The sheet of muscle which separates M. Goblet cells the thoracic and abdominal cavities and is used in breathing N. Cilia O. Pleurisy P. Epiglottis Q. Nostrils R. Larynx increase the warming, cleaning and moistening of incoming air ____ 3. Muscles that raise the ribs ____ 4. Tubes that branch off from the trachea ____ 5. The membrane that surrounds and touches the lungs ____ 6. The membrane that surrounds but does not touch the lungs ____ 7. The name of the cells that line the trachea and produce mucus ____ 8. The tube that connects the nasal and ____10. The structure in which the vocal cords are found ____11. Tubes which connect the bronchi to the alveoli ____12. The name of the hairs that help to clean air as it is inhaled ____13. The condition that results from inflammation of the pleura ____14. The flap at the top of the trachea that opens during breathing and closes during swallowing Disorders of the Respiratory System o Sinusitis (sinus infection) I. Disorders of the Upper Respiratory Tract (head and neck) o The Common Cold Infection of the cranial sinuses Nasal congestion blocks sinus openings • Symptoms include postnasal discharge, headache, and facial pain Caused by viruses • Sneezing, runny nose, mild fever • Last a few days to a week Antibiotics are ineffective against viral infections o Otis Media (ear ache) Inflammation of the middle ear Nasal infections spread to the ear by way of the Eustachian tubes Antibiotics are usually an effective treatment o Tonsillitis Inflammation of the tonsils II. Disorders of the Lower Respiratory Tract (chest) o Pharyngitis (sore throat) Inflammation of the throat caused by viruses, bacteria or injury May be caused by Streptococcus pyogenes (Strep throat) • Severe sore throat, high fever, white patches in throat region o Acute bronchitis • Infection of the bronchi and/or bronchioles • Usually it is caused first by a viral infection and then followed by a secondary bacterial infection • Bronchioles are inflamed and constricted • Mucus production increases in an attempt to o Laryngitis Inflammation of the larynx • Causes hoarseness of voice • Persistent laryngitis is one warning sign of cancer clear the infection o Chronic bronchitis • Airways are in a state of constant inflammation and are always narrowed and filled with mucus •Bronchi undergo degenerative change including the loss of cilia • Smoking or exposure to other air pollution is the most common cause o Choking Obstruction of the trachea Heimlich maneuver may expel blockage A tracheostomy may be required - the insertion of a breathing tube into the trachea o Emphysema • The walls of the alveoli become inelastic and brittle • Eventually alveoli pop • A chronic and incurable disease o Asthma • Smoking is the major cause of this disease • The bronchi and bronchioles are super • Symptoms are shortness of breath and sensitive to specific irritants called allergens increased breathing rate o Symptoms are wheezing, breathlessness, coughing o Bronchioles are inflamed and produce excess mucus • Incurable but can be treatable with medicines o Pleurisy • Inflammation of the pleura o Symptoms include chest pain and fever o May result in lung collapse o Pneumonia • Infection with virus, bacterial or mold • Bronchioles or alveoli fill with fluid and become inflamed • High fever, chest pain and headache o Cystic fibrosis (CF) • Genetic (a defective recessive gene is passed on by each parent) • Mucus in the lungs (and elsewhere) becomes very thick and sticky • The mucus is hard to cough up and makes a o Tuberculosis (pulmonary) • Caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis • Cells build a protective capsule (tubercle) around the bacteria • Symptoms include fatigue, fever and coughed up blood • High death rate, especially in infants • This communicable disease can cause mental illness if not treated great place to host frequent infections by bacteria and viruses o Lung Cancer • Tumors grow due to the uncontrolled reproduction of cells, causing thickening and callusing of bronchi/bronchiole walls • Caused by smoking (including secondhand smoke) and other air pollutants • Cancer cells may break away from the tumor and move to other parts of the body III. Other Respiratory Disorders o Hypoxia • A state of oxygen deficiency o The Bends • May affect scuba divers if they stay under pressure too long and then rise to the surface too quickly • Respiratory gases dissolved in the blood will come out of solution and cause bubbles • Dizziness, nausea, muscle and joint pains • May cause death • Treatment involves spending time in a decompression chamber o Respiratory Acidosis • When there is insufficient exhalation, too much Carbon Dioxide is left floating around in the blood stream, causing the blood to become • Symptoms are drowsiness and mental fatigue, sometimes headache or euphoria o Hyperventilation • Taking very deep and fast breaths while at rest • Results in a lowered Carbon dioxide content of the blood o Hiccups • Misfiring of nerves causes irregular contractions of the diaphragm, interrupting the normal rhythm of breathing • The brain tries to correct this, and tells the epiglottis to close off the trachea – this causes acidic (from carbonic acid) the “hic” sound • Insufficient exhalation can be a result of • Things that trigger hiccups include hot liquids, pneumonia or emphysema carbonated drinks and uncontrolled laughter o Respiratory Alkalosis • If more than the usual amount of carbon dioxide is exhaled, the blood will become basic • Hyperventilation can cause this to occur o Carbon Monoxide Poisoning • Occurs when you inhale Carbon Monoxide. • Carbon Monoxide outcompetes oxygen. • Skin goes blue, lips cherry red. Death will occur quickly Part II: Respiratory Disorders Worksheet 16. This disease results in loss of alveolar elasticity and caused by smoking ______________ 1. Inflammation of the pleura is called ___________________________ 2. Chemicals in inhaled smoke causes paralysis of __________________________ 3. Pneumonia can be caused by an infection with bacteria, viruses or __________ 4. Type of Bronchitis caused by pollutants_________________ 5. Type of Bronchitis caused by viruses or bacteria _____________ 6. A state of oxygen deficiency is called ______________ 7. Caused by irregular contractions of the diaphragm _____________ 8. A communicable disease that could lead to mental illness ______________________ 9. Something scuba divers could get if they rise to the surface quickly ______________ 10. Caused by the uncontrolled reproduction of lung tissues _______________________ 11. A series of rapid exhalations that results in lowered CO2 levels __________________ 12. Another name for an inflamed larynx ___________________ 13. The condition that results from high levels of CO2 in the blood __________________ 14. Antibiotics will kill bacteria but not ________________ 15. Another name for Otis Media __________________ 17. The bronchi and bronchioles are super sensitive in this disease _______________ 18. A type of gas that outcompetes oxygen when inhaled __________________________ 19. Inflammation of the tonsils is called ________________________ 20. Another name for a sore throat is _____________________________