* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download electromagnetic spectrum
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Computational electromagnetics wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic compatibility wikipedia , lookup
Waveguide (electromagnetism) wikipedia , lookup
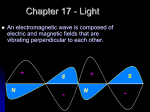
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
ELECTROMAGNETIC
SPECTRUM
Song
• The electromagnetic spectrum song
Brief review:
Water and sound waves transfer energy
from one place to another- they require a
medium through which to travel. They are
mechanical waves.
Electric field-region in which charged
particles can be pushed or pulled.
• The theory of electromagnetism explains
that electricity and magnetism are closely
related.
• Electric charges are the source of electric
fields.
• Moving charges generate magnetic fields.
• Waves are the propagation of a
disturbance.
• They transport energy and momentum but
do not transport matter.
Video
• The electromagnetic spectrum 2 video
Nature of Electromagnetic Waves
• They are Transverse waves without a medium. (They
can travel through empty space)
• Transverse means perpendicular to the direction of the
wave. (No actual displacement of matter).
• They travel as vibrations in electrical and magnetic
fields.
• Have some magnetic and some electrical properties to
them.
• Speed of electromagnetic waves = 300,000,000
meters/second (Takes light 8 minutes to move from the
sun to earth {150 million miles} at this speed.)
• When an electric field changes, so does the
magnetic field. The changing magnetic field causes
the electric field to change. When one field
vibrates—so does the other.
• RESULT-An electromagnetic wave.
• Click here Animation: Interaction of vibrating
charges
Waves or Particles
• Electromagnetic radiation has properties of waves but
also can be thought of as a stream of particles.
• Example: Light
• Light as a wave: Light behaves as a transverse wave
which we can filter using polarized lenses.
•
Light as particles (photons)
•
When directed at a substance light can knock electrons
off of a substance (Photoelectric effect)
DVD Video
• Earthquake DVD
– Write down 3 things that you did not know.
Earthquake video notes
•
•
•
•
P waves – primary (first waves)
S waves – secondary (second + waves)
Most damaged caused by S waves
Liquefaction – ground below turns to quick
sand due to vibrations and water
underground.
Video
• Eureka Episode 30
Eureka Notes
• What is white light made of? All the colors
combined plus IR (Infrared)
• White – reflecting all the colors and IR
• Black – absorbs all the colors and IR
• What determines what color something is?
Which colors it absorbs and which it
reflects. (It shows what is reflected)
B. Waves of the Electromagnetic Spectrum
• Electromagnetic Spectrum—name for the range of
electromagnetic waves when placed in order of increasing frequency
• Click here (Animation—Size of EMwaves)
RADIO
WAVES
INFRARED
RAYS
MICROWAVES
ULTRAVIOLET
RAYS
VISIBLE LIGHT
GAMMA
RAYS
X-RAYS
RADIO WAVES
• A. Have the longest wavelengths and lowest
frequencies of all the electromagnetic waves.
• B. A radio picks up radio waves through an antenna and
converts it to sound waves.
• C. Each radio station in an area broadcasts at a different
frequency. # on radio dial tells frequency.
• D. MRI (MAGNETIC RESONACE IMAGING)
– Uses Short wave radio waves with a magnet to create an
image
MRI of the Brain
Video
• The electromagnetic spectrum – radio
waves
– What are three ways that radio waves are used?
AM=Amplitude modulation—waves bounce off ionosphere can
pick up stations from different cities.
(535kHz-1605kHz= vibrate at 535 to 1605 thousand times/second)
+
FM=Frequency modulation—waves travel in a straight line &
through the ionosphere--lose reception when you travel out of range.
(88MHz-108MHz = vibrate at 88million to 108million times/second)
+
Bands of Radio/TV/Microwaves
AM Spectrum used in Broadcasting and Wirelass
Some common frequency bands
AM radio
Short wave radio
Citizens band (CB) radio
535 kilohertz to 1.7
megahertz
5.9 megahertz to 26.1
megahertz
26.96 megahertz to 27.41
megahertz
Television stations,
channels 2 through 6
54 to 88megahertz
FM radio
88 megahertz to 108
megahertz
Television stations,
channels 7 through 13
174 to 220 megahertz
XM Satellite Radio uses microwaves
DVD
• Mapping the Earth’s surface DVD
– What part of the electromagnetic spectrum do
GPS use?
• GPS use radio waves in the microwave part of the
electromagnetic spectrum.
MICROWAVES
• Microwaves—have the shortest wavelengths and
the highest frequency of the radio waves.
– Used in microwave ovens.
• Waves transfer energy to the water in the food causing them
to vibrate which in turn transfers energy in the form of heat to
the food.
– Used by cell phones and pagers.
– RADAR (Radio Detection and Ranging)
• Used to find the speed of an object by sending out radio
waves and measuring the time it takes them to return.
Video
• The electromagnetic spectrum –
microwaves
• Seeing where the microwaves are… video
INFRARED RAYS
• Infrared= below red
• Shorter wavelength and higher frequency than
microwaves.
• You can feel the longest ones as warmth on your skin
• Heat lamps give off infrared waves.
• Warm objects give off more heat energy than cool objects.
• Thermogram—a picture that shows regions of different
temperatures in the body. Temperatures are calculated by
the amount of infrared radiation given off. Therefore
people give off infrared rays.
VISIBLE LIGHT
• Shorter wavelength and higher frequency than
infrared rays.
• Electromagnetic waves we can see.
• Longest wavelength= red light
• Shortest wavelength= violet (purple) light
• When light enters a new medium it bends
(refracts). Each wavelength bends a different
amount allowing white light to separate into it’s
various colors ROYGBIV.
Video
• The electromagnetic spectrum video
ULTRAVIOLET RAYS
• Shorter wavelength and higher frequency than
visible light
• Carry more energy than visible light
• Used to kill bacteria. (Sterilization of equipment)
• Causes your skin to produce vitamin D (good for
teeth and bones)
• Used to treat jaundice ( in some new born babies.
• Too much can cause skin cancer.
• Use sun block to protect against (UV rays)
– Sunburn can cause skin cancer
X- RAYS
•
•
•
•
Shorter wavelength and higher frequency than UV-rays
Carry a great amount of energy
Can penetrate most matter.
Bones and teeth absorb x-rays. (The light part of an xray image indicates a place where the x-ray was absorbed)
• Too much exposure can cause cancer
– (lead vest at dentist protects organs from unnecessary exposure)
• Used by engineers to check for tiny cracks in structures.
– The rays pass through the cracks and the cracks appear dark on
film.
Video
• How x-rays work video
GAMMA RAYS
• Shorter wavelength and higher frequency than Xrays
• Carry the greatest amount of energy and
penetrate the most.
• Used in radiation treatment to kill cancer cells.
• Can be very harmful if not used correctly.
Bone Scan
Using the EM waves to view the Sun
Animation—View a Galaxy at different wavelengths
• Brief SUMMARY
• A. All electromagnetic waves travel at the
same speed. (300,000,000 meters/second in a
vacuum.
• B. They all have different wavelength and
different frequencies.
– Long wavelength-lowest frequency
– Short wavelength highest frequency
– The higher the frequency the higher the energy.
Video
• How do your mobile phones work video
DVD
• Characteristics of waves and ocean motion of waves DVD
Video
•
•
•
•
Plate tectonics video
Earthquakes Ring of Fire video
Japan 2011 Earthquake (Youtube)
2004 Boxing Day Tsunami (Youtube)