* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 10 Student Guided Notes Heart -Introduction Parts of the Heart
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
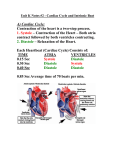
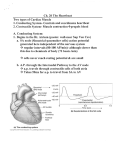
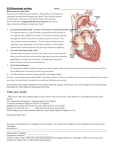
Unit 10 Student Guided Notes Heart -Introduction Parts of the Heart Left and Right Atria - ________________________________ Right: _________________________________________________. Left: Collects blood from ______________________________________. Left and Right Ventricles - ______________ Right: Sends blood to the _____________ via the Pulmonary Trunk. Left: Sends blood to the __________ via the Aorta Atrioventricular Valves - Valves between the _________________________. Prevent _______________________ of blood Right hand side "_______________________ cusps, or flaps Left hands side "__________________" - two cusps Chordae Tendineae - Strong, Fibrous strings that support the _________ Valve. Keeps the valves from _________________ with the force of blood flow. Semi-Lunar Valves - Between the ____________________________. Between the ventricles and the __________________________. Pulmonary Trunk - Branches off to form the ______________________________. _____________________________ from the right ventricle. Septum - The wall of the ______________. Separates the __________ and _____________ sides of the Heart Click on the following link for detailed information and video on heart structure/function: http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/hhw/contraction.html Cardiac Cycle and Intrinsic Beat Contraction of the heart is ____________________ process. _____________ - Contraction of the Heart _____________ - Relaxation of the Heart Each Heartbeat (Cardiac Cycle) Consists of: TIME 0.15 Sec 0.30 Sec 0.40 Sec =0.85 Sec ATRIA Systole Diastole Diastole VENTRICLES Diastole Systole Diastole Average rate of 70 beats per min The __________________ have a _______________________________ contraction because blood must be pumped throughout the body. The _________________ sound of the heart is due to the closing of the valves: First the _______________________________, then the semi-lunar. The beat of the heart is said to be intrinsic. It will beat ________________________________. (It can be removed from the body and still continue beating) The beat is controlled by a special type of tissue called ____________________, which has both _______________ and ___________________ tissue characteristics There are two locations of Nodal Tissue in the Heart: 1. SA Node (____________________ Node) Found in the upper wall of the _________________________. 2. AV Node (____________________________) Found at the bottom of the _____________________ near the Septum The SA Node (also called the _______________) initiates the heartbeat and sends out an __________________________ every 0.85 seconds. The impulse causes both Atria to _____________. The impulses are sent to the AV Node Via the __________________________. When the impluse reaches the AV Node, an impulse is sent from the AV Node, down the Purkinje Fibers (found in the walls of the ventricles and the septum) which stimulates both __________________ to contract. An __________________ registers the _____________ changes across the surface of the heart as it ________. The letters _______________ are the standard labels used to identify the parts of the ______________. The P Curve records the ________________________ _______________ of the __________ as they drive the blood out into their ventricles. The QRS is the _____________________________________ as they drive the blood out into their respective arteries. Note the much higher peak of the QRS phase of the cardiac cycle in the picture to the right. This is due to the much longer stronger contraction of the ventricles pushing blood out of the heart. The T marks the ______________ of the Ventricles (restoration of the normal electical condition, preparing them for the next contraction). http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/dci/Diseases/hhw/hhw_electrical.htm Autonomic Control of the Heart The rate of the heart can also be controlled by the __________________________. The heart rate center is located in the __________ ________________ of the brain. The SA Node is connected to the brain by the Vagus nerve (cranial nerve #10). This nerve pathway called the ____________________________________ (not under conscious control) has two system that affect the Heart Rate: 1. Parasympathetic System - _________________________________________. 2. Sympathetic System - Causes the heart beat to ______________ during times of stress. Factors such as need for _____________ or the blood pressure level determine which of these systems become active. When the brain perceives that the blood is getting delivered to the tissues too slowly, or if blood pressure is low, the brain will signal the _____________________________________ _________________________________. Blood Pressure Ventricles pump a volume of blood (__________________) each time they contract. The arteries must have __________________________________ to withstand this pressure. The Force of blood against the blood vessel walls is simply known as _______________________. Blood pressure is not constant. The term Systolic pressure (or Systole) refers to the _________________________________ _______________________. This is the highest blood pressure reading. The term diastolic pressure (diastole) refers to the blood pressure when _________________________________________. This is the lowest blood pressure reading. Pulse: As blood is pumped through arteries, the _____________ ____________________, and then recoil. This swelling can be felt in any artery that runs close to the surface. Blood pressure is normally measured along the _______________________________ of the arm. A reading of ______________ is quite normal. 120 - Systolic Reading as ventricles contract 80 - Diastolic Reading as the ventricles relax A number of things can affect the blood pressure. Hypertension - _____________________________ Example: 140/90 or 125/90 Diet and lifestyle are often to blame for elevated blood pressure Reasons: Stress Plaques - ______________________________ _______________________________________ _______________________________________ _______________________________________ __________________. (Arteriosclerosis) (Strokes, heart attacks...) High Salt intake - retain water - _____________ _______________________________________. Smoking Stimulants Lack of exercise Diet - amount and type Working too hard Age, Sex, Race Hypotension - _________________________________ _______________________________________ ______________________________________ o Example: 110/70 Reasons: ________________________________________________ _________________ _________________ Proper kidney function can only be maintained if there is a sufficient _______________ for filtration. Luckily the body can adjust blood pressure. Monitored by the _____________________ (part of the brain), the body can dilate (widen) arterioles thus ____________________________ pressure in them, or constrict (narrow) them to _____________________________________ _____________________. Review Finish the following statements or answer the question: 1. The SA node is found 2. The SA node is also called the ______________ of the heart and causes 3. The AV node is found 4. The AV node stimulates the __________ which are found in the___________and cause