* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download P4 – Explaining Motion
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Woodward effect wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Negative mass wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
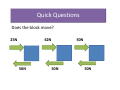
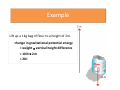
P4 – Explaining Motion Mechanics Force • Forces must always act in pairs! • An object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. • So remember only if the object is speeding up or slowing down is one force bigger than another!!! Quick force pairs Quick force pairs Getting moving • Draw both force arrows • Write what the force is doing – Eg. The foot pushes on the ground Definitions • Displacement – Distance moved in a stated direction • Speed – Distance per unit time • Velocity – Displacement per unit time • Instantaneous speed – Speed at a given instant of time • Acceleration – Is the rate of change of velocity Equations • Average speed = Distance Time Example Equations • Average acceleration (a) = increase in velocity Time Remember that an increase in velocity can be negative, this means you have a negative acceleration (deceleration) What causes friction? • Friction is caused by irregular surfaces • All surfaces are slightly irregular (except ice or frictionless Remember we need friction • Without it we can’t push the ground Backwards. But it stops us • But is stops us doing other thing Quick Questions Does the block move? 25N 62N 50N 50N 50N 50N Momentum • Momentum = mass x velocity • Change in momentum = Force x Time • Think of momentum as a property of a moving object. Reducing force Safety Questions Force = Change in momentum ÷ Time If we want to reduce the force and you CANNOT change the change in momentum, what can you do? 6 Mark question • Explain how seat belts reduce the injuries caused in a car crash? [6 marks] Steady State of motion What does a steady state mean? “A steady state is when an object travelling at a constant velocity, the resultant force on the object is zero” This means that the forward force is balanced with the forces stopping the motion Energy • Energy is measured in – joules, J • Energy CANNOT be created or destroyed ONLY transferred Different equations depending on type Work Done • Definition – Work is done whenever a force makes and object move. It is the energy transferred to move the object Work done = Force x Distance moved Work done = Fd Energy transfers Example Lift up a 1kg bag of flour to a height of 2m. change in gravitational potential energy = weight vertical height difference = 10N 2m = 20J Example All of the energy is transferred to kinetic kinetic energy = 20 J ½ mass speed2 mass speed2 speed2 speed speed = 20J = 40 = 40(m/s) = √40m/s = 6.32m/s First drop is the tallest • When doing maths questions in GCSE physics we imagine an ideal world. • When explaining in a 6 mark question we explain the world how it actually is. Big question A rollercoaster will have a large drop at the start of the ride. Explain why will no other point on the roller coaster be as tall as the start of the first drop? [6 marks] Answering this question is all about loses. Key steps • Why is there a big lift, what is the car gaining? • How is the energy transferred in the drop? • Why is all of this energy not transferred? – What are the loses • Remember to use key words, they are on the wall if needed. Kinetic Energy • Definition – The energy that something has owing to its motion – The movement energy it has to keep moving Kinetic Energy = ½ x mass x velocity2 KE = 1/2mv2 Gravitational Potential • Definition – The energy stored when an object is raised to a higher point in the Earth’s gravitational field Gravitational Potential = Mass x gravity x height GPE = mgh