* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Parts of a Sentence
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ukrainian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Relative clause wikipedia , lookup
Comparison (grammar) wikipedia , lookup
Lexical semantics wikipedia , lookup
Sloppy identity wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
American Sign Language grammar wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Italian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Icelandic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Turkish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
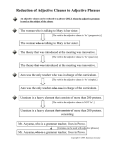
Parts of a Sentence Review Define each of the following: Adjective Modifies a noun Adverb Modifies a verb, adverb, and adjective Subject Who or what the sentence is about. Direct object Receives the action of the verb Define each of the following: Indirect object The person who receives the object that is being transferred. Object of the preposition Answers what after a preposition Transitive Sentence The action verb transfers action to the direct object. Label the direct object. The plane flew passengers across the Atlantic. The student brought the teacher chocolate. Jan opened the door. Bob threw me the ball. The dog chased the fly. The dog brought me the bone. Label the direct object. The plane flew passengers across the Atlantic. The student brought the teacher chocolate. Jan opened the door. Bob threw me the ball. The dog chased the fly. The dog brought me the bone. Label the indirect object. The plane flew passengers across the Atlantic. The student brought the teacher chocolate. Jan opened the door. Bob threw me the ball. The dog chased the fly. The dog brought me the bone. Label the indirect object. The plane flew passengers across the Atlantic. The student brought the teacher chocolate. Jan opened the door. Bob threw me the ball. The dog chased the fly. The dog brought me the bone. Diagram and label the following: Johnny walked over the hill and into the park. I looked for the jacket in the house and the car. Scott jogged quickly and quietly onto the soccer field. Mark is running, but had been walking. Mrs. Caple gave her students tawdry stars for a reward. Friday, Mrs. Caple gave the students chocolate. Recall Linking verb Links the subject to the verb Predicate Adjective Describes the subject Predicate Noun Renames the subject Intransitive sentence Linking verb does NOT transfer action. List the linking verbs. all "to be" verbs be, am, is, are, was, were, and been, plus the following are linking verbs: appear, become, feel, grow, look, seem, remain, smell, sound, stay, taste, and turn. Circle the predicate adjectives The teacher is nice. My neighbor is a chef. The cookies taste and smell delicious. The baby is a boy. The instructor is a professional musician. The students are loquacious today. Underline the predicate nouns The teacher is nice. My neighbor is a chef. The cookies taste and smell delicious. The baby is a boy. The instructor is a professional musician. The students are loquacious today. Italics – PA Underline - PN The teacher is nice. My neighbor is a chef. The cookies taste and smell delicious. The baby is a boy. The instructor is a professional musician. The students are loquacious today. Diagram and label The little girl is so sweet and kind. The little dog is a Miniature Poodle. The family dog is so friendly to guests. The beautiful flowers are pansies. The back yard is spacious. Types of Sentences What is the difference between transitive sentences and intransitive sentences? Indicate Transitive or Intransitive Johnny walked over the hill and into the park. The teacher is nice. Friday, Mrs. Caple gave the students chocolate. The cookies taste and smell delicious. The students are loquacious today. I looked for the jacket in the house and the car. Compose your own Create and write your own transitive sentence. Create and write your own intransitive sentence. Create a new sentence using a predicate noun. Create a new sentence using a predicate adjective. Create a new sentence using a direct object Create a sentence using an indirect and direct object. Justify Share your sentences with your tablemate and justify why each sentences are correct. Define each of the following: Clause Is a group of words with a subject and a verb. Two Types of Clauses Independent – express a complete thought and can stand alone. Example: I tied my shoes Dependent – do not express a complete thought; they must be connected to an independent clause to make sense. Example: because I tied my shoes. Dependent Clauses act as single parts of speech such as adverbs, adjectives or nouns. Define Adverb Clause It is a dependent clause that acts as an adverb. Words that introduce Adverb clauses are called subordinating conjunctions Subordinating Conjunctions Examples: although, as, because, before, if, until since, and when Example Sentence: My mom smiled when I made dinner. Independent Clause: My mom smiled. Dependent Adverb Clause when I made dinner (modifying smiled) Subordinating Conjunction when Example Sentence: If you don’t clean your room, you can’t have a cookie. Independent Clause: You can’t have a cookie Dependent Adverb Clause If you don’t clean your room (modifying can have) Subordinating Conjunction If Example Sentence: You should brush your teeth before you go to sleep. Independent Clause: You should brush your teeth Dependent Adverb Clause before you go to sleep. Subordinating Conjunction before Example of Diagram My mom smiled when I made dinner. Diagram and label the following. Adjective Clause Adjective Clause Adjective Clause Adjective Clause Adjective Clause Adjective Clause Adjective Clause Adjective Clause Adjective Clause