* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Energy - Gyanpedia
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Gibbs free energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
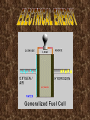
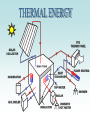
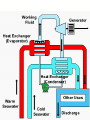
The ability to do work Energy, capacity of a physical system to perform work. Matter possesses energy as the result of its motion or its position in relation to forces acting on it. Energy associated with motion is known as kinetic energy and energy related to position is called potential energy. Kinetic Energy -- Energy possessed by an object, as a result of its motion. The magnitude of the kinetic energy depends on both the mass and the speed of the object according to the equation E =1/2 mv2 Potential Energy -- Stored energy possessed by a system as a result of the relative positions of the components of that system. For example, if a ball is held above the ground, the ball has a certain amount of potential energy; lifting the ball higher increases the amount of potential energy the system possesses. If two equally and oppositely charged bodies are connected by a metallic conductor such as a wire, the charges neutralize each other. This neutralization is accomplished by means of a flow of electrons through the conductor from the negatively charged body to the positively charged one.. In any continuous system of conductors, electrons will flow from the point of lowest potential to the point of highest potential. A system of this kind is called an electric circuit. Charges between clouds or between a cloud and the ground produce atmospheric electrical discharges—lightning. The flow of electricity from one discharge point to another also produces a sound wave heard as thunder. Nuclear Energy - Energy released during the splitting or fusing of atomic nuclei. The quantities of energy that can be obtained from the nucleus far exceed those that can be obtained from chemical processes, which involve only the outer regions of the atom. Nuclear energy can be released in two different ways: by fission (splitting) of a heavy nucleus, or by fusion (combining) of two light nuclei. The energy due to the heat of the body. The energy due to the chemical reaction (involved with electrons in the orbits). e.g., dry cell. All forms of energy are interconvertible by appropriate processes. In the process of transformation either kinetic or potential energy may be lost or gained, but the sum total of the two always remains the same.