* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download color - Richard G. Howe
Indra's Net (book) wikipedia , lookup
Bhagavata Purana wikipedia , lookup
History of Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
Rajan Zed prayer protest wikipedia , lookup
Hindu–Islamic relations wikipedia , lookup
International Society for Krishna Consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Vishnu sahasranama wikipedia , lookup
Vaishnavism wikipedia , lookup
Svayam Bhagavan wikipedia , lookup
Hindu views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
LGBT themes in Hindu mythology wikipedia , lookup
Karma in Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
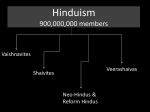
Hinduism Richard G. Howe, Ph.D. based on Corduan, Winfried. Neighboring Faiths: A Christian Introduction to World Religions. 2nd ed. Downers Grove: InterVarsity, 2012. What Makes Something Hindu? 1 In order to qualify as "Hindu," a religion has to: 1) regard the Vedas (the early sacred writings) as divinely inspired and authoritative. 2) accept the caste system. 3) respect the veneration of the various levels of deities and spirits, including the protection of cows. The Three Ways: The Three Major Phases of Hinduism 2 The Way of Works The Way of Knowledge The Way of Devotion The Way of Works 3 Aryan Origins Hinduism Zoroastrianism devas - good gods deavas -evil gods asuras -evil gods ahuras - good gods 4 The Four Vedas The Rig Veda (rig = "verses") The Yajur Veda The Sama Veda The Atharva Veda 5 The Vedic Gods Dyaus Pitar the original sky god 6 Varuna the god of the sky and the celestial waters Indra the "King of Heaven" 7 Mitra a sun god Rita a god of truth and right 8 Vishnu a minor god in the Vedas Rudra a capricious, sometimes malicious mountain god 9 Agni the god of fire Soma the god of the sacred drink 10 Brahmanaspati the word spoken at the sacrifice Variations of the word Brahman 11 Brahman the impersonal and pantheistic form of God Brahma the personal creator god Brahmin the priests and the priestly caste Brahmanas priestly commentaries on the Vedas Writings Subsequent to the Vedas 12 The Sutras The Brahmanas The Code of Manu The Caste Sytstem 13 The Brahmins The Kshatriyas The Vaishyas "Twice-Born" The Brahmins The Kshatriyas The Vaishyas The Shudras 14 Reincarnation Reincarnation, Karma, and Galatians 6:7 15 Reincarnation is called samsara, which literally means "wanderings." It is also called transmigration and metempsychosis What level of being one returns as is determined by the law of karma. Karma is best translated as "cause and effect." 16 Samasara and karma became the primary support for the caste system. The goal of Hinduism became finding release from samsara. The word for release is moksha, which can sometimes be translated as "redemption" 17 [Clarifying Karma] Karma is not fate. Karma is not judgment. Karma is not sin. [Karma and Gal. 6:7] 18 [Karma and Gal. 6:7] Do not be deceived, God is not mocked; for whatever a man sows, that he will also reap. Does the Bible Teach Reincarnation? 19 The Way of Knowledge 20 Upanishads Maya Atman is Brahman The Way of Devotion 21 Bhakti The roots of Bhakti Hinduism go back as least as far as the poem, the Bhagavad Gita, which forms a part of the lengthy epic, the Mahabharata, and which was composed roughly around 200 BC. 22 The Trimurti Brahma the Creator 23 Vishnu the Preserver Shiva the Destroyer 24 The roots of Bhakti Hinduism go back as least as far as the poem, the Bhagavad Gita, which forms a part of the lengthy epic, the Mahabharata, and which was composed roughly around 200 BC. 25 Three Schools of Bhakti Hinduism Vaishnavite recognizes Vishnu as the highest god Shaivite worships Shiva as highest god Shaktite primary allegiance is to a goddess 26 27 Some Main Deities and Their Shaktis Brahma and Sarasvati 28 Vishnu and Lakshmi The Ten Avatars of Vishnu 29 Matsya (fish) Kurma (turtle) 30 Varaha (boar) Narasimha (man-lion) 31 Vamana (dwarf) Parashu-Rama (Rama with axe) 32 Rama (the hero of the Ramayana epic) Krishna (the speaker of the Bhagavad Gita) 33 A. C. Bhaktivedanta [Swami] Prabhupada A. C. Bhaktivedanta [Swami] Prabhupada 34 A. C. Bhaktivedanta [Swami] Prabhupada Krishna is the supreme form of personal god. Salvation can be obtained by constant chanting of the Krishna mantra (Hare Krishna, Hare Krishna, etc.). The Bhagavad Gita is inspired scripture. The devotees must observe a life of pure devotion to Krishna. The distribution of literature disseminating the message of Krishna consciousness is an important aspect of the mission of this group. Buddha (the founder of Buddhism) 35 Balarama (Krishna's brother) Kalki (horse, yet to come) 36 Shiva and His Family Modern Developments in Hinduism 37 Ramakrishna (1836-1886) Swami Vivekananda (1863-1902) 38 Sai Baba (1863-1902) 39 Sathya Sai Baba (1926-2011) Tal Brooke 40 Rabi R. Maharaj 41