* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hypothyroidism
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
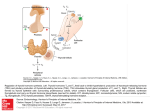
m s i d i o r y h t o p y H 016 2 t s u g Au According to the American Thyroid Association, more than 12% of the U.S. population will develop a thyroid condition during their lifetime. The Thyroid Gland The thyroid gland is located in the lower part of the neck, wrapped around the windpipe. This gland makes, stores, and releases several different hormones that are essential to the function of all organs in the body. Contact Information ProAct, Inc. 6333 Route 298, Suite 210 East Syracuse, NY 13057 Syracuse, Newark, Orlando, Houston, Chicago, New York, Minneapolis Hypothyroidism or under-active thyroid disease, is a common disorder. Hypothyroidism means that the thyroid gland cannot make enough of the thyroid hormone to keep the body functioning properly. The thyroid gland is located in the front lower part of your neck. The hormones that the thyroid releases travels through the bloodstream and can affect nearly every part of the body. The thyroid controls how an individual’s body cells use energy from food through the process of metabolism. Your metabolism affects your heartbeat, how you burn calories and your body temperature. If the body does not have enough of this hormone, the body starts to slow down, lose energy and your metabolism becomes sluggish. Causes There are numerous factors that can cause hypothyroidism. The most common cause is Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis. This is an inflammation of the thyroid gland, which is considered an autoimmune disorder. With this disorder, the body will produce antibodies that will attack and destroy the thyroid gland. Other causes of hypothyroidism are: • Radiation therapy to the neck area will damage the thyroid which in turn makes it harder for the gland to produce hormone. • Radioactive iodine treatment. • Use of certain heart, psychiatric or cancer medications. • Thyroid surgery. • Too little iodine in the diet. • Pregnancy. Hypothyroidism is more likely to develop in women and in those individuals where a close family member has an autoimmune disease. Symptoms and Diagnosis Hypothyroidism symptoms vary and can be vague and mimic other conditions. Symptoms include but are not limited to the following: • Depression • Dry hair and skin • Fatigue • Slow heart rate • Carpal tunnel syndrome • Unexplained weight gain or difficulty losing weight • Sensitivity to cold • Low body temperature Be sure to contact your physician if you or someone you know has the above symptoms. It is very important to remember that many, if not all, of these symptoms can be caused by other medical conditions, therefore seeing your doctor is the best solution. If you have these symptoms and your doctor feels it may be related to hypothyroidism, he/she will order a blood test to check your hormone levels. Some of the levels tested are the Thyroid-stimulating hormone, and T4 (thyroxine). If the blood test or physical exam of the thyroid comes back abnormal, a thyroid ultrasound or scan could be next to check for inflammation. Treatment If an individual is diagnosed with hypothyroidism, their doctor will prescribe them a synthetic thyroid hormone that is to be taken daily. Regular blood tests to check the thyroid hormone levels will be needed to adjust medication dose if needed. It is extremely important to keep hypothyroidism under control as it can result in myxedema, a very severe case of the disease that can cause loss of consciousness or death. Medications • Synthroid (Levothyroxine): Levothyroxine is a synthetically prepared isomer of thyroxine (T4), which is a hormone secreted by the thyroid gland. Levothyroxine is indicated for the treatment of primary, secondary, and tertiary hypothyroidism. It is the preferred treatment option because the hormonal content is standardized and the effects of the drug are more predictable. • Cytomel (Liothyronine): Liothyronine is a synthetic version of triiodothyronine (T3). Liothyronine has a much faster onset of action than levothyroxine due to the fact that it is already in its active form and does not need to be converted. Levothyroxine needs to be converted from T4 to its active T3 form to elicit an effect. • Armour Thyroid, Nature Thyroid, Westhroid (Desiccated Thyroid): Desiccated thyroid is a naturally occurring thyroid hormone derived from the thyroid glands of pigs. Unlike synthetic versions, desiccated thyroid contains both T3 and T4. There are also larger variations in the T3 and T4 content compared to the available synthetic versions.