* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download NAME: ____________ DATE: BLOCK: ___ GASTROINTESTINAL
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
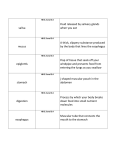
NAME: _____________________________________________________ DATE: _______________ BLOCK: ___ GASTROINTESTINAL (GI) TRACT • GI or alimentary canal – continuous, coiled, hollow tube that winds through ventral body cavity from mouth to anus – Entire GI is ~30 feet in cadaver, but shorter in living person due to muscle contractions – Includes mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and ends at the anus – Other accessory organs include salivary glands, pancreas, liver, gall bladder FUNCTIONS OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1. Ingestion – putting food into mouth 2. Propulsion – moving food from one organ to the next 3. Mechanical digestion – breaks down food _______________________ into smaller pieces 4. Chemical digestion – large _________________ are broken down into their building blocks by ____________________ 5. Absorption – transport of digested end products from the GI tract to the blood or lymph 6. Defecation – elimination of indigestible food that leaves through the anus in the form of feces ACTIVITIES OF MOUTH, PHARYNX, AND ESOPHAGUS • Mouth – Chewing begins mechanical breakdown of food • Pharynx – Propels food into esophagus by _____________________ (involuntary smooth muscle contractions) • Epiglottis covers windpipe (trachea) to prevent food from moving down into lungs • Esophagus – ____________________ food into stomach via peristalsis ACTIVITIES OF STOMACH • Stomach – a storage tank – C-shaped sac with sphincters at each end • __________________________ or esophageal sphincter prevents food from going back into esophagus • _______________________________ opens to allow food to move into the small intestine – Physical digestion occurs as stomach grinds and churns food – Chyme - partially digested food that leaves the stomach – Chemical digestion occurs with enzymes • Gastric glands – in stomach lining; release ________________________ – Gastric juice – includes digestive enzymes, intrinsic factor, hydrochloric acid (HCl), and mucus » Intrinsic factor helps absorb vitamin B12 • ____________________ – enzyme that breaks down protein (activated by HCl) ACTIVITIES OF THE SMALL INTESTINE • A tube that is 8 – 18 feet long and twisted into coils • The major digestive organ • Three subdivisions – ____________________________ (5% of total length) – ____________________________(40% of total length) – ____________________________ (almost 60% of total length) • Nearly all food absorption occurs in the small intestine! • Duodenum – Pancreatic ducts dump _____________________________________ into duodenum – Bile duct (joins with pancreatic ducts) dumps bile from liver into duodenum • Jejunum and ileum - primary function is absorption – Intestinal ___________________ tiny projections of inner wall of small intestine; greatly increase surface area for absorption – Each villus contains blood capillaries and a lacteal into which foodstuffs are absorbed • _____________________________ – opens to let chyme pass into large intestine ACTIVITIES OF THE LARGE INTESTINE • Larger in diameter than the small intestine, but not nearly as long (~5 feet) • Major function is to dry out indigestible food residues by absorbing water and then eliminate them as feces • Subdivisions: cecum, appendix, colon, rectum, and anal canal • ______________________ – first part of large intestine; sac-like with worm-like appendage called appendix • Colon – parts in order are: ______________________ (travels up), ______________________ (travels across), descending (travels down), and then ______________________ (S-shaped) • Rectum – stores feces and leads to anal canal • Anus – ending of GI; voluntary sphincter opens to release feces ACTIVITIES OF ACCESSORY ORGANS • Teeth – breakdown, grind, and tear food into smaller pieces • Salivary glands release saliva; contain mucus to soften food and salivary amylase, which begins carbohydrate digestion – ______________________– largest, lie anterior and somewhat inferior to each ear – Sublingual gland – smallest; lie on floor of mouth inferior to tongue – ______________________– lie in floor of mouth on inside surface of lower jaw • Pancreas – soft, pink, triangular gland; secretes pancreatic juice – Pancreatic duct – tube that carries pancreatic juice to duodenum – Pancreatic juice contains the following: • ______________________ - neutralizes acidic chyme coming from stomach • amylase - enzyme that breaks down carbohydrates • lipase - enzyme that breaks down ______________________ • trypsin, chymotrypsin, and carboxypeptidase - enzymes that breakdown proteins • ______________________ – enzyme that breaks down nucleic acids • Liver – largest gland in the body; digestive function is to produce bile • – ___________________ – leaves liver through the hepatic duct and enters duodenum through bile duct • Yellowish-green liquid containing bile salts, bile pigments (bilirubin), cholesterol, electrolytes, and lipids (no enzymes) • Only the bile salts and lipids help with digestion • ______________________emulsify fats by physically breaking large fat globules into smaller ones ______________________– small, green sac under liver that stores bile HOMEOSTATIC IMBALANCES • Gall stones – if bile is stored in gall bladder too long or too much water is removed, the cholesterol in it crystallizes forming gall stones – Can cause blockage of hepatic or bile ducts and bile begins is released into bloodstream instead • Bile in blood and eventually tissues causes jaundice • ______________________ – inflammation of liver; often cause by virus (also called hepatitis) • Cirrhosis – chronic inflammation of liver; can be from drinking too much alcohol • Heartburn – when cardiac sphincter does not close tightly and allows acidic stomach juices to enter esophagus – Hiatal hernia – superior part of stomach protrudes slightly above the diaphragm; which weakens cardiac sphincter • Peptic ulcers – erosion of stomach lining (open sore in membrane), which exposes the lining to acid; often caused by some bacteria (Helicobacteri pylori) • ______________________ – inflammation of pancreas caused by pancreatic enzymes breaking down the pancreatic tissue itself • Diverticulitis – diverticula are formed by the inner layer of the intestine protruding through the large intestine wall; causes inflammation and pain – Caused by not eating enough bulk (fiber); colon narrows and puts more pressure on walls • ______________________ – large intestine does not absorb enough water from feces; loss of electrolytes and fluids can cause severe dehydration • Constipation – too much water is removed from feces; can be caused by low fiber diets • Impacted teeth – teeth that remain embedded in jawbone; can cause pressure and pain; often occurs with wisdom teeth • ______________________ – infected appendix; bacteria can accumulate because its twisted • Hemorrhoids – enlarged and inflamed branches of the rectal vein in the anal canal that cause itching, pain, and sometimes bright red bleeding • Vomiting – complex reflex that empties stomach through esophagus, pharynx, and mouth (vomiting center in medulla oblongata)