* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Using this template - British Hypertension Society
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of beta-blockers wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence wikipedia , lookup
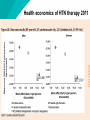
Hypertension Cost effectiveness Mark Caulfield For the British Hypertension Society The William Harvey Research Institute and Barts and The London NIHR Biomedical Research Unit Queen Mary University of London Launch: Wednesday 24th August 2011 NICE clinical guideline 127 The guideline 2004: National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) hypertension guideline 2006: Drug model developed as part of pharmacological update to guideline 2011: Model updated during second guideline update National Collaborating Centre for Chronic Conditions Model overview Population • Patients with essential hypertension seen in primary care • Base case patient: 65-year-old men and women with 2% CVD risk, 1% HF risk and 1.1% diabetes risk Comparators • no intervention (NI) • thiazide-type diuretics (TD) • calcium-channel blockers (CCB) • beta-blockers (BB) • ACE inhibitors/angiotensin-II receptor antagonists (ACE/ARB) Perspective and time horizon • UK NHS perspective, lifetime horizon Model overview: model structure Markov model Health states chosen to represent disease (simplification/data dependant) • Transitions between health states affected by the effectiveness of treatments over time (Cycles) Model inputs: drug effectiveness •Systematic clinical review and meta analysis •Head to head studies off different drug classes reporting various clinical outcomes UA Thiazide-type diuretics (D) 0.893 MI 0.78 0.796 0.855 0.85 Diabetes 0.985 0.808 1.137 0.77 Stroke 0.69 0.656 0.851 0.69 Heart failure 0.53 0.731 0.761 0.65 Death 0.91 0.883 0.939 0.9 Outcome Calcium-channel Betablockers (C) blockers (B) 0.881 0.984 ACEi/ARB (A) 1.01 Studies included in systematic review •ALLHAT 2002 •MRC-0 1992 •ANBP2 2003 •NICS-EH 1999 •ASCOT 2005 •ONTARGET 2008 •CORD 2009 •PHYLLIS 2004 •ELSA 2002 •SHEP-P 1985 •HAPPHY 1987 •SHEP 1991 •INSIGHT 2000 •STOP-H2 1999 •INVEST 2003 •SYST-EUR 2000 •JMIC-B 2004 •Tedesco 2007 •LIFE 2002 •VALUE 2004 •MIDAS 1998 •VHAS 1998 •MRC 1985 Model inputs: drug costs Drug used in model ACEi Ramipril (10mg) ARB Losartan (100mg) BB Atenolol (100mg) CCB Amlodipine (10mg) DD Bendroflumethiazide (2.5mg) UK generic list prices (BNF) 2011 Yearly drug 2006 Yearly drug cost cost (EUR) (EUR) £21 (€26) £30 (€49) £26 (€32) £217 (€287) £13 (€16) £13 (€17) £19 (€24) £70 (€92) £12 (€15) £17 (€22) Interpreting cost effectiveness results •Clinical and cost effectiveness •Cost effectiveness = Costs and health outcomes and getting the most health gain from the resources available •Health is measured in QALYs •Life years x QoL (Utility) = QALY Incremental costeffectiveness ratio (ICER) Difference in costs = = Difference in QALYs Cost per QALY gained Health economics of HTN therapy 2006 Health economics of HTN therapy 2011 Uncertainty - sensitivity analysis •Varying individual parameters to test sensitivity of model results • Risk of CVD events (HF, MI, UA etc...) • Effectiveness of drugs • Cost of drugs and events • Side effects of drugs •Model remained fairly robust to changes •In a few extreme scenario analyses, other drugs became cost effective (mainly diuretics) Interpretation •Treatment of hypertension is highly cost effective •Based on UK, generic drug prices •CCBs are the most cost effective option with an ICER below £2,000 •The results are more robust than in the 2006 model •As commonly used anti-hypertensives become generic it is now cheaper to treat hypertension than to do nothing Acknowledgements Kate Lovibond Ralph Hughes Prof Bryan Williams Leo Nherera Joanne Lord 2006 hypertension (update) GDG members 2011 hypertension (update) GDGmembers British Hypertension Society National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence

















![[ Insert Title Here ]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008479268_1-03ff748536c27aeae665c17a72e89ec4-150x150.png)





