* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download HCB Objectives 13
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
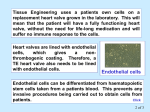
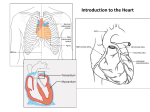
HCB Objectives 13 1. Elastic artery: Large vein: Muscular artery: Medium/small vein: Arteriole: Venule: 2. Types of capillaries: a. Continuous: endothelial cells sealed with tight junctions, no perforations, surrounded by complete basal lamina, transport across membrane is transcytosis (pinocytosis). Found in CNS, lungs, muscles, and CT b. Fenestrated: endothelial cells sealed with tight junctions, pierced by fenestrae, surrounded by complete basal lamina. Found in choroid plexus, gall bladder, intestine, and endocrine glands c. Sinusoidal: endothelial cells with gaps to permit direct exchange, pierced by fenestrae without diaphragms, basal lamina is missing at pore areas. Found in liver, lymph nodes, and adrenal cortex. 3. Function of arteriovenous anastomoses: direct connection of arteries and veins (bypassing capillaries). When anastomoses are open, blood is shunted from capillaries back to the cardiovascular system; therefore, arteriovenous anastomoses takes blood to the areas where it is needed most and away from where it isn’t immediately needed (fight/flight AV anastomoses close in skeletal muscle to provide blood to muscle; AV anastomoses open in gut to shunt blood away) 4. Histological organization of the heart: a. Pericardium: tissue surrounding the heart, used to protect and support the heart b. Epicardium: collagenous CT with elastic fibers, fat cells, nerves, ganglia, lymphatic vessels, and blood vessels. Externally covered by simple squamous epithelium (mesothelium). Borders the visceral pericardium. c. Myocardium: cardiac muscle cells, thickest part of the heart. d. Endocardium: collagenous CT with elastic fibers and smooth muscles covered by an endothelial layer with a continuous basement membrane. Where Purkinje fibers reside. Note: Heart valves are endocardium, and are made of dense fibrous CT bordered by endothelial layers. Valve bases attach to fibrous skeleton rings which are attached to myocardium to allow electrical conduction of valves. Structure as a modified blood vessel: Epicardium = Tunica Adventitia, Myocardium = Tunica Media, Endocardium = Tunica Intima 5. Lymphatic vessel cross-section: Lymph flow from tissues to blood: Lymphatic capillaries → lymphatic vessels → lymphatic ducts → veins