* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
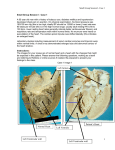
3. Be able to identify and describe the purkinjie fibres, purkinjie cells and myocardial cells. Purkinjie fibres are modified cardiac muscle fibers in the subendothelial tissue, concerned with conducting impulses through the heart. The role of this fibre is to conduct electrochemical signals through the heart in order to signal the contraction of myocardial muscles. An image of a Purkinjie fibre compared to cardiac muscle. The Purkinjie fibre looks much larger with a larger nucleus in comparison to the cardiac muscle Purkinjie cells are neuronal cell bodies in the middle layer of the cerebellar cortex; characterized by a large, globose body and massive, branching dendrites but a single, slender axon. Image of a Purkinjie Cell (Neuron) Note that the Purkinjie cell and fibre share the name of the person who discovered them, anatomist Jan Evangelista Purkinje. They are related in the fact that they both conduct electrochemical signals, however they are found in two anatomically different areas of the body. Myocardial cells are the specialized cells of the heart. They are smooth muscle cells with acquired features and properties similar to those of skeletal muscles. In turn, they appear “hybrid looking” between smooth and skeletal muscles. 4. Know the cardiac layers and identify the histological features of each layer. The heart has three layers; the endocardium, myocardium and epicardium. These three layers correlate with the three layers of the vessels and reflects the nature of which the heart was embryologically formed (as folds of the vessels): Endocardium – Tunica Intima Myocardium – Tunica Media Epicardium – Tunica Adventitia The Endocardium is the inner layer of the heart and consists of epithelial tissue and connective tissue. This is also the layer which Purjinkie cells are present. It serves as the inner lining f the heart, covering all the inner cavities and the valves. The Myocardium is the middle layer of the heart and consists of cardiac muscle fibres which provide the heart with its pumping action. The cardiac muscles receive electrical signals to contract in an organized manner (also to relax at the absence of the signal). The Epicardium is the outer wall of the heart and consists of connective tissue covered by an epithelium. This layer of the heart provides physical protection and is also known as the visceral pericardium. The Endocardium and Myocardium of the heart. Note that the majority of the heart’s bulk consists of Myocardium. The Myocardium (dark) and the Epicardium (light) of the heart.