* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Heart
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiothoracic surgery wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac arrest wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
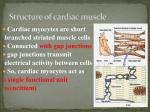
13.0 HEART Upon completion of this lecture, students will be able to: a) Define and use properly the following words: Heart, Endocardium, Endothelium, Subendocardium, Myocardium, Epicardium, Pericardium, Atria, Ventricle, Mesothelium, Fibroelastic, Cardiac skeleton, Fibrous rings, annulus fibrosi, Trigone, Cardiac valves, Cardiac conduction, Chordae tendinea, Purkinje fibers, Glycogen, Intercalated discs, Sinoatrial node, Atrioventricular node, Atrioventricular bundle, Bundle of His. a) Describe and associate basic structure/function for the following: all structures listed above; why Purkinje fibers appear as they do in histology sections, the cardiac conduction system, compare endocardium and myocardium in the atria versus the ventricles b) Identify by microscopy: Heart, Endocardium, Endothelium, Subendocardium, Myocardium, Epicardium, Pericardium, Atria, Ventricle, Mesothelium, Fibroelastic, Cardiac skeleton, Fibrous rings, annulus fibrosi, Trigone, Cardiac valves, Chordae tendinea, Purkinje fibers, Glycogen, Intercalated discs. 1 HEART I. LAYERS OF THE HEART (T.intima; T. media; T. adventitia) A. ENDOCARDIUM (T. intima) 1. Location: Inner surface 2. Structure: Endothelium + dense connective tissue (CT) (fibroelastic) 3. Relative thickness: thinner than myocardium; Thicker in atria than ventricles 4. Subendocardium: blood & lymph vessels, nerves, conducting system B. MYOCARDIUM (T. media) 1. Structure: Cardiac muscle + CT 2. Relative thickness: Thickest layer but thinner in atria C. EPICARDIUM (T. adventitia) 1. Visceral pericardium: 2. Structure: Mesothelium + fibroelastic CT 3. blood vessels, autonomic nerves, fat II. CARDIAC SKELETON A. The fibrous connective tissue base onto which the atrial and ventricular musculature and the cardiac valves insert. B. Consists of: Four dense FIBROUS RINGS 1. CT (annulus fibrosi) 2. surrounding the atrioventricular openings 3. and the origins of the aorta and pulmonary artery 4. The interventricular septum consists of collagen fibers C. TRIGONE 1. dense connective tissue between the AV opening and the base of the aorta 2. continuous with the fibrous rings. D. Species variation 1. 2. 3. 4. III. Pig & cat: dense irregular CT Dog: fibrocartilage Horse: hyaline cartilage Young Ruminants: bone CARDIAC VALVES A. Structure: 1. fold of endocardium; 2. core of dense CT (with elastin); 3. continuous with fibrous rings B. Chordae tendinea continuous with the endocardium of the cardiac valves 2 IV. CARDIAC CONDUCTION SYSTEM (Modified cardiac muscle fibers) A. PURKINJE FIBERS 1. Subendocardial connective tissue area 2. fewer myofibrils (more space within each cell) 3. glycogen & mitochondria numerous 4. no intercalated discs; but desmosomes and gap junctions 5. can be bi-nucleate B. Sinoatrial node (SA node) 1. normal pacemaker (Atria to ventricles) C. Atrioventricular node (AV node) 1. receives the impulse from the SA node and sends to ventricles through AV bundles D. Atrioventricular bundle (fibers merge to form "Bundle of His") 1. "Bundle of His" branches to form left & right bundles (Purkinje fibers) along the septum 2. Purkinje fibers are found in subendocardium & extend into the myocardium V. BLOOD SUPPLY A. Coronary arteries 1. thick, often with longitudinal bundles of muscle 2. supply dense capillary network 3. originate with the aortic arch B. Capillary Network 1. supplies myocardium, epicardium, heart skeleton, valves C. Venules and Veins 1. collect blood from capillaries 2. open into the right atrium D. Heart Lymph vessels 1. capillaries in connective tissue (can become very prominent & appear engorged) 2. usually parallel with blood vessels 3. more lymph vessels in epicardium VI. NERVE SUPPLY A. Extensive plexuses in the sinoatrial and atrioventricular nodes B. Sensory fibers in myocardium and epicardium C. Autonomic innervation 1. Parasympathetic supplies only the SA node, atria, & AV node 2. Sympathetic innervation supplies the entire heart 3