* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Test 1 review chapters1-4
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
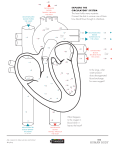
Bio 24 Test 3 review chapters 9-12 These are review questions that I came up with by going through my lecture notes and the answers are found in my lecture notes. Therefore, you should be able to answer these questions if you go through my notes (or the book). On the test, the phrasing of the questions will be different. Therefore, you should test yourself making up your own questions. Also do review problems at the end of the book, and try my practice tests. Lastly, google search practice tests. Make flash cards out of my vocabulary lists. Also try to explain the terms on my vocabulary lists to other people. Standard Disclaimer: This is a partial review list. If a topic was mentioned in class, it is fair game on the test! Chapter 11 What is the function of the circulatory system? Where is the heart located. What surrounds the heart? What are the 4 chambers of the heart? What are the 4 valves? 1. What chambers receive blood? (Blood enters _________ chambers) 2. What chambers pump blood? (Blood is pumped by what chambers) 3. Which chamber receives deoxygenated blood? 4. What 2 main veins return deoxygenated blood from the body? 5. Which chamber pumps deoxygenated blood? 6. What vessel transports deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs? 7. What chamber receives oxygenated blood? 8. What vessel transports oxygenated blood to the heart from the lungs. 9. That chamber pumps oxygenated blood to the body? 10. What vessel does oxygenated blood leave the heart by? 11. What are the 4 valves in the heart? What is their function? Where are they located? 12. Trace a drop of blood through the heart. 13. What vessels take blood away from the heart? 14. Arteries branch into what smaller vessels? 15. Arterioles branch into what smaller vessels? 16. What diffuses out of the blood in the capillaries? 17. What diffuses into the blood in the capillaries? 18. How is excess fluid returned to the circulatory system? (the lymphatic system) 19. Capillaries feed into what larger vessels? 20. Venules branch into what larger vessels? 21. All veins from the body must branch into what vein? (Vena cava) 22. What is the function of the following :SA node, AV node, AV bundle (transmission of the signal) and the purkinje fibers? 23. What is special about cardiac muscle? (Autorythmic, communicate through gap junctions/intercalated disks. So when 1 cell contracts, it causes the ret of the heart to contract. 24. What is the sequence of events for cardiac contraction? 25. What is Systole 26. What is Diastole 27. How are veins equipped to prevent backflow of blood? What happens when they don’t work? 1 Bio 24 Test 3 review chapters 9-12 28. What hormones and neurotransmitters will increase blood pressure? How? 29. What neurotransmitters will slow down heart rate? 30. What is Cardiac output? 31. What is stroke volume? 32. What is heart rate? 33. How are the 3 terms related. 34. What are 2 ways I can increase blood pressure 35. What is the pulmonary circuit 36. What is the systemic circuit? 37. Which circuit has oxygenated blood and which has deoxygenated blood. 38. How is plasma kept in your capillaries? 39. How do you take blood pressure? 40. What makes the Lub and what makes the dub 41. What are the sources of energy for cardiac muscle? 42. Why is cardiac muscle fatigue resistant? 43. What is the body’s response to low blood pressure? 44. What is the body’s response to high blood pressure? 45. Which is the preferable response to reacting to a change in BP Change Stroke volume or heart rate? Why? 46. What controls blood flow into capillary beds? 47. How does fluid return to the heart in veins? In lymphatic tissue? 48. How does the endothelium of capillaries differ from most other endothelium? 49. What are my major lymphatic organs? What do they do? Chapter 12 Lymphatic Lymphatic: What is the function of the lymphatic system? What is the acculumlition of lymphatic fluid in the legs called (edema) What is it called when lymph vessles are blocked by a type of round worm? (Elephantitus) Chapter 12b the Immune System (related to blood) 1. What are the 2 general types of immunity? 2. In general, what is non specific immunity? a. What are the 2 aspects of non specific immunity? 3. In general, what is specific immunity? 4. What immune function does the skin provide? 5. How do the following things help the skin’s immune function a. Poor in nutrients b. Physical barrier c. Oil from Sebaceous glands d. Lactic acid/uric acid from sweat glands e. Constantly falling off. 6. What are mucus membranes? 7. Where would I find mucus membranes 8. What is the function of mucus membranes? 9. What are phagocytes? What do they do? 10. How does nuturphil destroy invading cells? (Think of the movie psycho) 2 Bio 24 Test 3 review chapters 9-12 11. What are macrophages? What are monocytes? Where would I find them? 12. How does the heat and swelling of an inflammation help protect you? 13. What is specific immunity? 14. What is an antigen? What is an antibody? 15. How many invaders will each antibody look for ? 16. What happens when a lymphocyte first finds its antigen? 17. What is a memory cell, what is its function? 18. What do helper T cells do? 19. What are natural Killer cells? What do they do? 20. What causes an allergy? 21. What is Humoral immunity? What cells are involved? 22. What is cellular immunity? What cells are involved? 23. A memory B cell finds its antigen? What happens next? 24. How do immunizations work? 25. What do plasma cells do 26. What are 4 things antibodies can do? 27. What cell helps T cells in Cell mediated immunity? How does that cell help? 28. What do cytotoxic T cells (CD8) do? 29. What do helper T cells (CD4) do? 30. What do suppressor T cells do? Respiratory system: About 15 to 20 questions 1. What are the 2 functions of the respiratory system? 2. What is the upper respiratory system? 3. What is the lower respiratory? 4. What are 2 functions of mucus in the nasal cavity? 5. What is the chamber in the back of the mouth (oral cavity) and nasal cavity called? 6. What is the glottis? What is the epiglottis? 7. What structure takes air into the lungs? 8. What immune cell will I find in the alveoli 9. What are alveoli? Where specifically would I find them? 10. What happens in alveoli 11. Why does oxygen diffuse into the blood in the alveoli 12. Why does carbon dioxide diffuse out of the blood in the alveoli 13. Why does oxygen diffuse out of the blood in the capillaries in tissue? 14. Why does carbon dioxide diffuse into the blood in the capillaries found in tissue? 15. What produces the carbon dioxide in our bodies? 16. Why does our body consume oxygen? (The answers are related!) 17. What transports oxygen in our bodies? 18. How is carbon dioxide transported? 19. What waste product is produced by that transport? Why is that waste product dangerous? 20. What is acidosis? What causes it? 21. Which is more critical, blood oxygen or blood carbondioxide levels? Why? 22. How do we inhale? What are the steps? 23. What happens to thoracic cavity pressure (chest) when the diaphragm contracts? 24. What does that low (negative pressure) cause air to do? 3 Bio 24 Test 3 review chapters 9-12 25. What happens to thoracic cavity pressure when the diaphragm relaxes? 26. What is Emphysema 27. What is Chronic Bronchitis 28. What is Asthma 29. What is Sudden Infant Death syndrome (SIDS) Chapter 14 1. What 2 places does mechanical digestion occur? 2. What is chemically digested in the mouth? 3. What enzyme is responsible? 4. What digested in the stomach? 5. What 2 substances are responsible for protein digestion in the stomach? 6. What is the function of the rugae of the stomach? 7. What are peristaltic contractions? 8. What is chyme? 9. What happens in the 2 inches of the small intestine? PANCREATIC juice and bile enter and mix with the chyme. 10. What is in pancreatic juice and the function of each thing. o Peptidases/protidases (digests proteins) o Carbohydrateases (Digests sugars) o Bicarbonate (neutralizes the acid of the stomach) o Lipases (digest fats) 11. What does bile do? 12. What 2 things does the small intestine do. 13. What does the large intestine do? 14. What protects our stomach from stomach acid? 15. Where does stomach acid get neutralized? Where does neutralization occur? 16. What is gastrin? What does gastrin do? 17. Why do we get hungry when we smell or see food that we like? 18. What is the pancreases digestive function? 19. What 2 things are digestion? 20. What is the Alimentary canal? What organs are found on it. 21. What are accessory organs? What do they do? 22. What is motility? 23. What are the functions of saliva? 24. What is the reason why we must chew our food? 25. What is the pharynx? 26. What is the function of the epiglottis? 27. What causes heart burn? 28. What is the function of sphincters? 29. What are the function of villi? 30. Where do proteins and carbohydrates go when they are absorbed? (Capillaries) 31. Where do lipids go? (The lymphatic system) 32. Where must all food go to be processed (The liver) 33. How are carbohydrates and proteins absorbed? 4 Bio 24 Test 3 review chapters 9-12 Organ Does mechanical digestion occur What is chemically digested What is absorbed Mouth Stomach Small intestine Large intestine Chapter 15 1. What are the two main functions of the urinary system? 2. What are considered “wastes” by the urinary system? 3. What does the urinary regulate? 4. How does the urinary system regulate electrolyte balance? Where does this regulation occur? 5. Where does water regulation occur? 6. What is the function of the kidney? Ureters? Urinary Bladder? Urethra? 7. What are the 2 regions of the kidney? 8. How does the cortex differ from the medulla? Why is that important? 9. What is the functional unit called? 10. What happens to the majority of what is filtered by the kidney? 11. What happens in the following structures? a. The glomerular capsule b. The proximal convoluted tubule c. The nephron loop d. The distal convoluted tubule e. And the Collecting duct. 12. Why does plasma/filtrate enter the glomerular capsule? 13. What gets filtered from the blood? What does not get filtered? Why doesn’t it get filtered? 14. What are the 3 steps of renal function? 15. What is reabsorbed where? 16. What is secreted where? 17. How does the descending nephron loop differ from the ascending? 18. Why is there a capillary that has blood flowing (in the opposite direction) of the filtrate in the nephron? 19. What does aldesteron do? ADH? Parathyroid hormone 20. What is the urinary bladder made of? 21. Why can the female bladder hold less urine (especially when she is pregnant) even though it is about the same size as the male? 22. How does urin move through the Urethra and Ureters 23. How does the function of the urethra differ in males than in females? 24. What is acidosis? How does the urinary system deal with acidosis? Chapter 16 This chapter counts as 2 chapters. 1. What is the difference between reproduction and sexual reproduction? (Sexual reproduction requires 2 parents and is just one method of reproduction) 2. How do the chromosomes in eggs differ from the chromosomes in sperm? 3. What is the difference between a sperm and an egg? What is the function of sperm? What is the function of eggs? 5 Bio 24 Test 3 review chapters 9-12 4. 5. 6. 7. What are the primary sex organs of males and females? What are secondary sex characteristics? Why do we have them? What sex do all fetus start out as? How many sets of gonads does an early fetus have? How many duct sets does an early fetus have? 8. What is the SRY region of the Y chromosome? What 2 things does it do? 9. What happens in the absence of this region or if the region doesn’t work right? 10. What does the presence of testosterone with testosterone receptors cause? What does an absence of testosterone or testosterone receptors cause? 11. Where are the testes in a developing embryo? What happens to them? 12. What happens in the seminiferous tubules 13. What happens in the epididymis 14. What is the function of the Ductus Deferens (Vas Deferens) 15. What happens if this is blocked (tied)? 16. How do sperm exit the body? 17. What is the function of the Seminal Vesicles 18. What is the function of the Prostate Gland 19. What is semen? 20. What is the function of the scrotum? 21. What is Spermatogenesis? Why must it happen outside the body? 22. Where does Spermatogenesis occur (be specific)? 23. What is a Spermatogonia? How does it divide? How many cells does it produce by this division? DO they have 46 or 23 chromosomes? 24. How does a Primary spermatocyte divide? How many cells does it produce? Do they have 46 or 23 chromosomes? 25. What are the 3 parts of a sperm? What is the function of each part? 26. What does LH do in males? What does FSH do in males? 27. How many sets of arteries are in the penis? What does each one do? 28. What causes an erection? 29. What receptor types are found in the penis? Where do they lead? 30. What are the 4 stages of the male sexual response? What happens in each? 31. What are the 3 functions of the female (mammal) reproductive system? 32. What happens when a fetus differentiates into a female? 33. What is an ovary? 34. What are the structures of the female reproductive system? What does each structure do? 35. What lines the uterine tubes? 36. What are the structures in an ovary? Explain what each is/does. 37. What are the 4 follicle stages? What happens in each? 38. Why is the clitoris analogous to the penis? 39. What is the difference between a lactating and non-lactating breast? Between a nonlactating female and a male (of normal weight)? 40. What is Oogenesis. How is it the same as Spermatogenesi. How does it differ? 41. When does meiosis 1 begin for women? When does meiosis 2 end? 42. What is a polar body? 43. What does the follicle do during maturation of an oocyte? After? 44. What hormone causes the follicle to mature? 6 Bio 24 Test 3 review chapters 9-12 45. What causes ovulation ? What happens to the remaining follicles? 46. What does a large amount of estrogen do to the body (in non reproductive terms) 47. What does LH do? 48. What are the stages of the female sexual response? What events happen in each stage? 7