* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution and Natural Selection
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
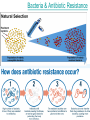
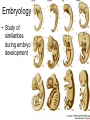
Evolution • = change/time – Change of what? – Inherited characteristics • two types 1. Microevolution – refers to change in the gene pool of a population 2. Macroevolution – refers to speciation Species Concept • What is a species? • Definition = a group of organisms that are capable of mating with one another in nature to produce fertile, viable (living), offspring POPULATION GENETICS • Def: study of changes in the genetic composition of populations • What is a population? • Def: organisms of the same species living together in the same area/environment NOTE: If organisms live in the same region, they experience same environmental pressures from natural selection! Peppered Moth Bacteria & Antibiotic Resistance How does a species develop? • Species develop from other species (ancestor) through variation over time! • Variation = differences within a species – Arise due to mutation, errors in DNA replication, meiosis, etc. Does variation alone lead to a new species? • No Isolation! • When groups separate they change from one another due to different environmental pressures! – What happens when 2 best friends go away to different colleges? Classification We classify based on a Hierarchical System! Big, general Small, specific King Phillip Came Over For Great Spaghetti Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Kingdoms of Life Until recently scientists recognized 5 kingdoms: Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, & Animalia Monera was split into two: archaebacteria and eubacteria Now scientists use a six kingdom model: 1. Eubacteria 2. Archaebacteria 3. Protista 4. Fungi 5. Plantae 6. Animalia Example! • Human Classification • Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species • Animalia Chordata Mammalia Primate Hominidae Homo Sapien Binomial Nomenclature • • • • • • Carolus Linnaeus - Taxonomy Scientific Name vs. Common Name Always written in italics First word is capitalized = genus Second word is lowercase = species Example: White Pine Pinus strobus Dog Canus familaris History of Evolutionary Theory • Jean Baptiste Lamarck – Theory of use & disuse – Individual organisms change in response to their environment and pass this acquired trait to their offspring. History of Evolutionary Theory • Charles Darwin – Early to Mid 1800’s – Age 22 left England aboard the HMS Beagle – Galapagos Islands, South America, Africa, and Australia Darwin’s Theory • • 1859 “On Origin of the Species” Theory of Natural Selection – survival and reproduction of organisms that are best suited to their environment Theory of Natural Selection Main Points 1. Populations tend to grow & overpopulate 2. Resource competition resources are limited 3. Inheritable Variation exists among populations that makes some individuals more “fit” than others. 4. Those individuals with variation that allows them to survive better will reproduce more often. Their genes & traits are passed onto offspring, causing these genes & traits to increase in proportion in the population. Evidence for Evolution • • • • • Fossil Record Comparative Anatomy Molecular Biology Biogeography Embryology Fossil Record • Remains of plants or animals that were once living • Used to: – reveal the existence of species that came before & are now extinct (Life has changed over time!) – Develop relationships – Rate of Evolutionary Change • Incomplete – Why? Comparative Anatomy • Study of different structures used to develop relationships • Homologous, Analogous, Vestigial Molecular Biology • Study differences in DNA & amino acid sequences • Those organisms most closely related have the most similarities. Biogeography • Movement of continents continental drift • Trace species back to splits in populations due to continental drift Embryology • Study of similarities during embryo development What can we conclude from all of this evidence? • Descent with Modification! – New life forms appeared to be modifications of fossil forms found in similar geographic areas. – Implies that modern life forms are descendents of older life forms that have changed slowly over time. Q: What made them change? • Coevolution – Change or Evolution of 1 species affects the evolution of another. – Ex: Predator Prey (arms race) • Convergent Evolution – Occurs when environmental pressures act similarly to unrelated species. – Example: whale & shark • Divergent Evolution – 2 or more related species become increasingly different – Related species are introduced into different environments. Divergent Evolution • Adaptive Radiation – Rapid increase in # of species