* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Physiology of urinary system
Vasopressin wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Hemodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac output wikipedia , lookup
Biofluid dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Countercurrent exchange wikipedia , lookup
Reuse of excreta wikipedia , lookup
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
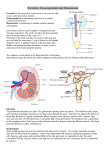
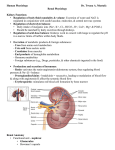
Physiology of urinary system Functions of the Urinary System •Filters waste products from blood metabolites, foreign substances (e.g. drugs..), ammonia, urea etc. •Conserves valuable nutrients e.g. glucose, amino acids are not lost from the urine •Regulates ion levels of EC fluid •Regulates EC fluid pH •Regulates EC fluid volume •Regulates RBC production • Stores and excretes urine •Produces and secretes hormones 1 Parts of nephron •The functional units of the kidneys are called nephrons. •Each kidney is made up of millions of nephrons. Two types of nephrons Cortical nephrons -~85% of all nephrons -Are located in the cortex Juxtamedullary nephrons -Are closer (juxta = next to) the renal medulla -The loops of Henle extend deep into the renal pyramids 2 Process of Urine Formation Urine formatio depends on : - Glomerular filtration - Tubular reabsorption of the substance from the tubular fluid into blood - Tubular secretion of the substance from the blood into the tubular fluid Filtrate Composition Glomerular filtrate is produced from blood The filtrate must pass through: • Pores between endothelial cells of the glomerular capillary • Basement membrane • Filtration slits formed by podocytes Filtrate is similar to plasma except it is essentially protein-free 3 Forces Involved in Glomerular Filtration PGC - glomerular capillary hydrostatic pressure πGC - oncotic pressure of blood PBS - Bowman's space hydrostatic pressure πBS - oncotic pressure of Bowman's space =0 Net Filtration Pressure =(PGC-PBS)+(πGC - πBS ) Measures of Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) The rate of glomerular filtration is a function of the - net filtration pressure, - the permeability of the filtration membrane, - the surface area available for filtration. The measured GFR reflects these factors, and the total number of functioning nephrons. Average GFR is 125 ml/min for a healthy human GFR is directly measured by measuring the inulin clearance or by measuring the creatinine clearance . 4 Regulation of GFR 1. Renal autoregulation renal autoregulation maintains a nearly constant glomerular filtration rate at rest autoregulation mechanisms prevail 2. Neural controls the sympathetic nervous system will override renal autoregulation under stress afferent arterioles constrict filtration is reduced sympathetic nervous system stimulates renin secretion by the juxtaglomerular cells 3. Hormonal mechanism the renin-angiotensin system reduces GFR atrial natriuretic peptide) increases GFR 3. Hormonal regulation of GFR 5 Quantitative description of renal function 1. Extraction ratio (E) E= ( Pa - Pv ) 0<E<1 Pa E: is the amount of compound entering the kidney that got excreted into the final urine Pa Pv Pa is the concentration in renal artery Pv is the concentration in the renal vein Quantitative description of renal function 2. Concept of clearance U*V=P*C -> C = U * V / P (ml / min) C is the virtual volume of plasma cleared from the given substance within 1 min U = urinary concentration V = diuresis (ml / min) P = plasma concentration (Pa) C = clearance (ml / min) Pa Pv Pv can be ignored ! U*V 6 Quantitative description of renal function 3. Relation of C to E Mass of substances entering and leaving the kidney within 1 min (mg/min) Pa * RPF Pv * RPF RPF=Renal Plasma Flow RPF = (U * V) / Pa = (Pa - Pv) / Pa C U*V E U = urinary concentration V = diuresis (ml / min) P = plasma concentration (Pa PV) C = clearance (ml / min) C = RPF * E Quantitative description of renal function 4. Measurement of GFR Amount excreted (E) = filtered (F) - reabsorbed (R) + secreted (S) U*V Pa * GFR no tubular transport Æ U * V = Pa * GFR e.g. inulin, creatinine 7 Quantitative description of renal function 5. Tubular function The main function of tubule is secretion and reabsorption e.g. production of concentrated or diluted urine reabsorption of glucose in proximal tubule secretion of PAH Quantitative description of renal function 6. Definitions RBF (renal blood flow) = 1200 ml / min (20% of CO) RPF (renal plasma flow) = 670 ml / min RPF = RBF * (1 - Htc) GFR (glomerular filtration rate) = 125 ml / min FF (filtration fraction) = 0.2 FF = GFR / RPF 8 Transport in the different parts of tubule Transport in the distal tubule This part performs final tuning of urine by active secretion or absorption Aldosterone dependent movement of Na+ and K+ aldosterone production is stimulated by hyperkalemia and angiotensin II Secretion of K+ and H+ based on body pH Water permeability is regulated by ADH (vasopressin) 9 Effect of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) ADH - is released by posterior pituitary when osmoreceptors of hypothalamus detect an increase in plasma osmolality. - it restores the water permeability of collecting duct. Control of volume and osmosis of urine Building up of osmotic gradient 10 Control of volume and osmosis of urine Formation of concentrated urine Control of volume and osmosis of urine Formation of diluted urine 11 Acid-base balance • Importance of isohydria: enzymes are sensitive to pH • Physiological pH: 7.38 - 7.42 (acidosis - alkalosis) • Defense: immediate: buffer systems long-term regulation: respiration (10-15 min) renal function (hours - days) Acid-base balance pH = pK + log [salt] [acid] Buffer minimizes the change in pH when a base or an acid is added to the solution. Buffers systems consist of a weak acid (releases H+ ions) and a weak base (binds H+ ions) Buffer systems Intracellular buffer systems Phosphate buffer Proteins Extracellular buffer systems Phosphate buffer Proteins Carbonic acid bicarbonate buffer 12 Acid-base balance pH = pK + log [HCO3-] pCO2 Respiratory acidosis pCO2 × e.g. hypoventillation Respiratory alkalosis pCO2 Ø e.g. hyperventillation Metabolic acidosis HCO3- Ø e.g. diarrhea Metabolic alkalosis HCO3- × e.g. vomitus Micturition active and passive incontinance 13 Hemodialysis 14