13 - Coach Eikrem's Website
... Diseases and Disorders of the Urinary System • kidney stones – calcium, magnesium, or uric acid ...
... Diseases and Disorders of the Urinary System • kidney stones – calcium, magnesium, or uric acid ...
Renal Physiology
... Renal Clearance • From previous examples, it can be seen that clearance can be calculated for any substance • Clearance an vary from zero to ~ 600 ml/min depending on the renal handling of the substance • A substance that is not normally filtered across the glomerular capillaries will have a clearan ...
... Renal Clearance • From previous examples, it can be seen that clearance can be calculated for any substance • Clearance an vary from zero to ~ 600 ml/min depending on the renal handling of the substance • A substance that is not normally filtered across the glomerular capillaries will have a clearan ...
Essential Calculations in Renal Physiology
... secretion processes in the epithelial cells that line the nephron. With reabsorption, a substance that was previously filtered is transported from the lumen of the nephron into the peritubular capillary blood. Many substances are reabsorbed, including Na +, Cl-, HCO3-, amino acids, and water. With s ...
... secretion processes in the epithelial cells that line the nephron. With reabsorption, a substance that was previously filtered is transported from the lumen of the nephron into the peritubular capillary blood. Many substances are reabsorbed, including Na +, Cl-, HCO3-, amino acids, and water. With s ...
Slide 1
... • The goal of urine production – Is to maintain homeostasis – By regulating volume and composition of blood – Including excretion of metabolic waste products ...
... • The goal of urine production – Is to maintain homeostasis – By regulating volume and composition of blood – Including excretion of metabolic waste products ...
Renal System Physiology
... Each of the million or so nephrons in each kidney is a microscopic tubule consisting of two major parts: a glomerulus and a renal tubule. The glomerulus is a tangled capillary knot that filters fluid from the blood into the lumen of the renal tubule. The function of the renal tubule is to process th ...
... Each of the million or so nephrons in each kidney is a microscopic tubule consisting of two major parts: a glomerulus and a renal tubule. The glomerulus is a tangled capillary knot that filters fluid from the blood into the lumen of the renal tubule. The function of the renal tubule is to process th ...
UTI - the CVC
... o Risks can be decreased by being careful to perform invasive procedures only when necessary, by performing the procedure as atraumatically as possible, and by removing the catheter or endoscope as soon as possible o Catheter-induced bacterial urinary tract infection o Bacteria migrate along outside ...
... o Risks can be decreased by being careful to perform invasive procedures only when necessary, by performing the procedure as atraumatically as possible, and by removing the catheter or endoscope as soon as possible o Catheter-induced bacterial urinary tract infection o Bacteria migrate along outside ...
What is the anatomy of the urinary bladder?
... peritoneum and is stabilized by the middle umbilical ligament and lateral ligaments • The interior surface of the urinary bladder is thrown into folds called rugae • The ureters enter the bladder through ureteral openings and meets the center of trigone • The center of trigone lies superior to the n ...
... peritoneum and is stabilized by the middle umbilical ligament and lateral ligaments • The interior surface of the urinary bladder is thrown into folds called rugae • The ureters enter the bladder through ureteral openings and meets the center of trigone • The center of trigone lies superior to the n ...
NVCC Bio 212 - gserianne.com
... amino acids, urea, uric acid, creatine, creatinine, Na, Cl, K, HCO3-, PO43-, SO42-. But notice how different the composition of urine is. Additionally, note that protein is not normally present in urine. ...
... amino acids, urea, uric acid, creatine, creatinine, Na, Cl, K, HCO3-, PO43-, SO42-. But notice how different the composition of urine is. Additionally, note that protein is not normally present in urine. ...
Acid – Base Physiology
... Renal Tubular Acidosis: due to a defect in H+ secretion or HCO3 reabsroption. Diarrhea: Excess bicarbonate loss into the feces without time to reabsorb (most common cause). Diabetes mellitus: In the absence of normal glucose metabolism the cells metabolize fats and form acetoacetic acid, reducing pH ...
... Renal Tubular Acidosis: due to a defect in H+ secretion or HCO3 reabsroption. Diarrhea: Excess bicarbonate loss into the feces without time to reabsorb (most common cause). Diabetes mellitus: In the absence of normal glucose metabolism the cells metabolize fats and form acetoacetic acid, reducing pH ...
1 FORM W KEY deducted if you fail to do this!!!!!!
... a) Is a Na+ dependent passive process b) Is a Na+ dependent active process c) Occurs because water osmotically follows Na+ from the tubule to the interstitial fluid d) Both a and c are true e) Both b and c are true 19. Anakin Skywalker, from the planet Tatooine, has a PO2 of 200 mm Hg in his alveoli ...
... a) Is a Na+ dependent passive process b) Is a Na+ dependent active process c) Occurs because water osmotically follows Na+ from the tubule to the interstitial fluid d) Both a and c are true e) Both b and c are true 19. Anakin Skywalker, from the planet Tatooine, has a PO2 of 200 mm Hg in his alveoli ...
B. True or False/Edit
... thick segments of the ascending limbs also contributes to the hypertonicity of the medulla, so that water is reabsorbed by osmosis from the collecting ducts. IV. RENAL PLASMA CLEARANCE As blood passes through the kidneys, some of the constituents of the plasma are removed and excreted in the urine. ...
... thick segments of the ascending limbs also contributes to the hypertonicity of the medulla, so that water is reabsorbed by osmosis from the collecting ducts. IV. RENAL PLASMA CLEARANCE As blood passes through the kidneys, some of the constituents of the plasma are removed and excreted in the urine. ...
The Physiology of the Kidney and Body Fluids EDUCATIONAL
... pressure changes but blood flow (and filtration rate) are nearly constant. Autoregulation is by myogenic and tubulo-glomerular feedback (TGF) mechanisms. It occurs at the afferent arterioles Myogenic autoregulation depends on stretch activated ion channels in vascular smooth muscle that, when stretc ...
... pressure changes but blood flow (and filtration rate) are nearly constant. Autoregulation is by myogenic and tubulo-glomerular feedback (TGF) mechanisms. It occurs at the afferent arterioles Myogenic autoregulation depends on stretch activated ion channels in vascular smooth muscle that, when stretc ...
Chapter 17
... discarded. This ordeal describes home peritoneal dialysis for people whose kidneys do not function properly. Repeated several times each day, this procedure consumes many hours and is very expensive. Filtration of the blood is only part of the work normally done by healthy kidneys. Much of the work ...
... discarded. This ordeal describes home peritoneal dialysis for people whose kidneys do not function properly. Repeated several times each day, this procedure consumes many hours and is very expensive. Filtration of the blood is only part of the work normally done by healthy kidneys. Much of the work ...
جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان
... Tikrit university excreted or held onto. The kidneys help maintain the blood PH mainly by excreting hydrogen ions and reabsorbing bicarbonate ions as needed. Removal of metabolic waste products and foreign substances from the plasma. One of the most important things the kidneys excrete is nitrogenou ...
... Tikrit university excreted or held onto. The kidneys help maintain the blood PH mainly by excreting hydrogen ions and reabsorbing bicarbonate ions as needed. Removal of metabolic waste products and foreign substances from the plasma. One of the most important things the kidneys excrete is nitrogenou ...
Review A REVIEW ON UROLITHIASIS IN DOGS AND CATS
... function is to control the volume and composition of the body fluids. For water and virtually all electrolytes in the body, the balance between intake (due to ingestion or metabolic production) and output (due to excretions or metabolic consumption) is largely maintained by the kidneys. This regulat ...
... function is to control the volume and composition of the body fluids. For water and virtually all electrolytes in the body, the balance between intake (due to ingestion or metabolic production) and output (due to excretions or metabolic consumption) is largely maintained by the kidneys. This regulat ...
Acid – Base Physiology
... Renal Tubular Acidosis: due to a defect in H+ secretion or HCO3- reabsroption. Diarrhea: Excess HCO3- loss into the feces without time to reabsorb (most common cause). Diabetes mellitus: In the absence of normal glucose metabolism the cells metabolize fats and form acetoacetic acid, reducing pH, and ...
... Renal Tubular Acidosis: due to a defect in H+ secretion or HCO3- reabsroption. Diarrhea: Excess HCO3- loss into the feces without time to reabsorb (most common cause). Diabetes mellitus: In the absence of normal glucose metabolism the cells metabolize fats and form acetoacetic acid, reducing pH, and ...
Chapter 1 Introduction 一、名词解释 1.Human Physiology Physiology
... 1. Difference between extracellular and intracellular fluid The extracellular fluid contains large amount of sodium, chloride and nutrients for the cells, such as oxygen, glucose, fatty acids and amino acids . The intracellular fluid contains large amount of potassium, magnesium and phosphate ions. ...
... 1. Difference between extracellular and intracellular fluid The extracellular fluid contains large amount of sodium, chloride and nutrients for the cells, such as oxygen, glucose, fatty acids and amino acids . The intracellular fluid contains large amount of potassium, magnesium and phosphate ions. ...
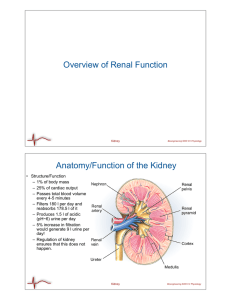
Overview of Renal Function Anatomy/Function of the Kidney
... Anatomy/Function of the Kidney • Structure/Function – 1% of body mass – 25% of cardiac output – Passes total blood volume every 4-5 minutes – Filters 180 l per day and reabsorbs 178.5 l of it – Produces 1.5 l of acidic (pH~6) urine per day – 5% increase in filtration would generate 9 l urine per day ...
... Anatomy/Function of the Kidney • Structure/Function – 1% of body mass – 25% of cardiac output – Passes total blood volume every 4-5 minutes – Filters 180 l per day and reabsorbs 178.5 l of it – Produces 1.5 l of acidic (pH~6) urine per day – 5% increase in filtration would generate 9 l urine per day ...
Renal Blood Flow and Glomerular Filtration Rate
... during volume depletion, hydrostatic pressure along the renal vasculature is decreased, leading to an initial decrease in renal blood flow and GFR (secondary to reduction of glomerular capillary hydrostatic pressure). The reduced pressure decreases the stretch of the afferent arteriole, causing the ...
... during volume depletion, hydrostatic pressure along the renal vasculature is decreased, leading to an initial decrease in renal blood flow and GFR (secondary to reduction of glomerular capillary hydrostatic pressure). The reduced pressure decreases the stretch of the afferent arteriole, causing the ...
1. The term "renal autoregulation" refers in part to the fact that A. the
... 4. A. Loss of the glomerular filtration barrier negative charge, characteristic of nephritis, leads to increased filtration of negatively-charged plasma proteins. If the protein filtered load exceeds the limited capacity of the renal tubules to reabsorb protein (Tm-Protein), the urine will contain ...
... 4. A. Loss of the glomerular filtration barrier negative charge, characteristic of nephritis, leads to increased filtration of negatively-charged plasma proteins. If the protein filtered load exceeds the limited capacity of the renal tubules to reabsorb protein (Tm-Protein), the urine will contain ...
Clinical Anatomy of the Pelvis
... • Urethral catheterization is done to remove urine from a person who is unable to micturate. It is also performed to irrigate the bladder and to obtain an uncontaminated sample of urine. • When inserting catheters and urethral sounds (slightly conical instruments for exploring and dilating a constri ...
... • Urethral catheterization is done to remove urine from a person who is unable to micturate. It is also performed to irrigate the bladder and to obtain an uncontaminated sample of urine. • When inserting catheters and urethral sounds (slightly conical instruments for exploring and dilating a constri ...
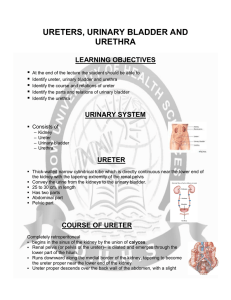
Ureters, urinary bladder and urethra
... The ureter proper is covered with peritoneum, but four sets of vessels cross in front of it, between it and the peritoneum, namely, – Right colic artery – Testicular or ovarian artery ...
... The ureter proper is covered with peritoneum, but four sets of vessels cross in front of it, between it and the peritoneum, namely, – Right colic artery – Testicular or ovarian artery ...
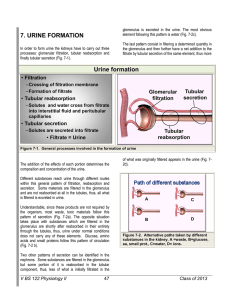
7. URINE FORMATION Urine formation
... The composition of the basement membrane determines its filtering capacity. This membrane is primarily made of proteoglycans and collagen chains interlocked, leaving large spaces through which most solutes and water can filter. Proteoglycans are charged with strong negative charges, thus preventing ...
... The composition of the basement membrane determines its filtering capacity. This membrane is primarily made of proteoglycans and collagen chains interlocked, leaving large spaces through which most solutes and water can filter. Proteoglycans are charged with strong negative charges, thus preventing ...
Acid-Base_Handling
... – Low filtered [Cl-] increases H+ secretion • Cl- is passively cosecreted with H+ secretion via H+ATPase to maintain electroneutrality thus ability to secrete H+ is enhanced with low tubular fluid [Cl-] • In setting of low tubular fluid [Cl-], Na+ reabsorption must be accompanied by H+ or K+ secreti ...
... – Low filtered [Cl-] increases H+ secretion • Cl- is passively cosecreted with H+ secretion via H+ATPase to maintain electroneutrality thus ability to secrete H+ is enhanced with low tubular fluid [Cl-] • In setting of low tubular fluid [Cl-], Na+ reabsorption must be accompanied by H+ or K+ secreti ...
The Urinary System
... urea, salts, & some water in the tubule. These metabolic wastes form urine, which is transported to the renal pelvis by the collecting tubule. ...
... urea, salts, & some water in the tubule. These metabolic wastes form urine, which is transported to the renal pelvis by the collecting tubule. ...
Urine
Urine (from Latin Urina, ae, f.) is a liquid by-product of the body secreted by the kidneys through a process called urination (or micturition) and excreted through the urethra.Cellular metabolism generates numerous by-products, many rich in nitrogen, that require clearance from the bloodstream. These by-products are eventually expelled from the body during urination, the primary method for excreting water-soluble chemicals from the body. These chemicals can be detected and analyzed by urinalysis.Human urine together with human feces are collectively referred to as human waste or human excreta.