* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Planetary Science
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
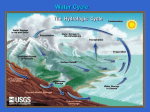
Planetary Science Why? • Since Astronomers find it difficult or impossible to visit most astronomical objects, nearby objects are examined and comparisons/extrapolations made. Earth First • We examine our planet for a basic knowledge of planetary processes. Vital Statistics • 4.5 billion years old, • 8,000 miles in diameter, • 6 X 1024 kg (6 million million million million kilograms), • Orbits the sun in 365.24 days, • Turns on its axis once every 24 hours. Crossection: • Thin (5-30 mile) crust • 1800 miles of mantle (made of magma, similar to lava) • Outer core of liquid iron • Inner core of solid iron. Interior examined: • Earthquake waves make good acoustic ‘xray’ to probe the layers, • Density calculations indicate heavy core, • Magnetic fields denote iron. Hot as Hell! • Due to radioactive decay, • High pressure (lots of weight squeezing in) • Residual heat from formation, impacts Heat Escapes • Heat escapes from the core via convection rolls in the mantle. • This heat causes eruptions through the crust of volcanoes and rifts. • This energy drives Plate Tectonics Continental Drift • NOT floating on water like lily pads! • Seven large plates carry the continents (not just landmass) around on the crust, skidding on the mantle. • Where plates meet (plate boundaries) earthquakes, subduction, volcanoes. Why Us? • Because of the surface area to volume ratio of a large rocky planet, its internal heat takes billions of years to escape. • Compare this with smaller rocky worlds! Atmosphere • Any volume of gases that surrounds a planet is called an atmosphere. • Our mixture of O2 and N2 is called “air”. • In an atmosphere, weather develops due to differential heating. • Weather changes the surface of the planet as much as plate tectonics. Look Out Below! • Another major producer of surface features is asteroidal/cometary impact. • This causes small and large craters, and in extreme cases, mass extinctions. • Evidence of cratering is erased by weather, but the earth has been hit about 20 times as much as the moon. Robert Duval or Bruce Willis? • Neither! • We cannot protect ourselves from impacts unless we know many years in advance. Our Little Buddy The Moon Vital Statistics • • • • • ¼ the size of Earth; 1/ the mass of Earth; 80 1/ the gravitational pull of Earth; 6 About 28 days to orbit the Earth. Always keeps one side towards us, therefore its “day” is 28 days long. • No permanent “dark side of the moon”; • Bone dry, no atmosphere. Formation and Age • Almost as old as the Earth. • Formed by two impacts about 4 billion years ago. • An object about ½ the size of Earth hit our planet, scattering debris from Earth and the impactor that gradually condensed into our moon. • We know this because of the ratio of isotopes we found in the lunar soil WHEN WE VISITED THERE IN 1969-1973! Tides • Caused by differential gravity, the different gravitation pulls from the Moon on opposite sides of the Earth. • The side that faces the Moon experiences the greatest gravitational force that causes the oceans to bulge. • The Earth’s center feels a lesser pull that drags it away from the far side, leaving a bulge of water. With thanks to Lock Haven University Highs and Lows • As the World Turns [sic] various landmasses move into these bulges and experience high tide. • Six hours (1/4 turn) later, these same landmasses are out of a bulge and experience low tide. Spring and Neap Tides • When the Sun and Moon are lin a line with the Earth, the Solar Tides add to the Lunar Tides and the variation of high and low is great: Spring Tides (no seasonal meaning). • One week later, the Sun and Moon at at right angles with the Earth, and tidal variation is small: Neap Tides. • Solar Tides are about 1/3 Lunar Tides. Near and Far • The prefix “peri” means near; the prefix “ap” means far. • Therefore perigee means nearest the Earth in orbit, and aphelion means farthest from the Sun in orbit. • So, tides are extra big at perigee for the Moon and perihelion for the Earth. Phases Lunar Eclipse (safe to view) Solar Eclipse (dangerous to view!)