* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download chapter 1
Customer experience wikipedia , lookup
Brand equity wikipedia , lookup
Customer relationship management wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Sales process engineering wikipedia , lookup
Internal communications wikipedia , lookup
Market segmentation wikipedia , lookup
Social media marketing wikipedia , lookup
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
Affiliate marketing wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Sports marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
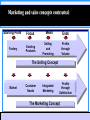
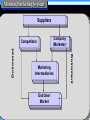
Chapter 1 Defining Marketing for the Twenty-First Century Objectives Understand the new economy. Learn the tasks of marketing. Become familiar with the major concepts and tools of marketing. Understand the orientations exhibited by companies. Objectives Learn how companies and marketers are responding to new challenges. The New Economy Consumer benefits from the digital revolution include: – Increased buying power. – Greater variety of goods and services. – Increased information. – Enhanced shopping convenience. – Greater opportunities to compare product information with others. The New Economy Firm benefits from the digital revolution include: – New promotional medium. – Access to richer research data. – Enhanced employee and customer communication. – Ability to customize promotions. Marketing Tasks Marketing practices may pass through two stages: – Entrepreneurial marketing – Formulated marketing As marketing becomes more formulated, creativity is inhibited. What Can Be Marketed? Goods Places Services Properties Experiences Organizations Events Information Persons Ideas Marketing Defined Kotler’s social definition: “Marketing is a societal process by which individuals and groups obtain what they need and want through creating, offering, and freely exchanging products and services of value with others.” Marketing Defined The AMA managerial definition: “Marketing is the process of planning and executing the conception, pricing, promotion, and distribution of ideas, goods, and services to create exchanges that satisfy individual and organizational objectives.” Core Marketing Concepts Target markets and market segmentation Exchange and transactions Marketplace, marketspace, metamarkets Relationship and networks Marketers & prospects Marketing channels Needs, wants, demands Supply chain Product offering and brand Competition Value and satisfaction Marketing program Marketing environment Core Marketing Concepts Target markets & segmentation – Differences in needs, behavior, demographics or psychographics are used to identify segments. – The segment served by the firm is called the target market. – The market offering is customized to the needs of the target market. Core Marketing Concepts Shopping can take place in a: – Marketplace (physical entity, Lowe’s) – Marketspace (virtual entity, Amazon) Metamarkets refer to complementary goods and services that are related in the minds of consumers. Marketers seek responses from prospects. Core Marketing Concepts Needs describe basic human requirements such as food, air, water, clothing, shelter, recreation, education, and entertainment. Needs become wants when they are directed to specific objects that might satisfy the need. (Fast food) Demands are wants for specific products backed by an ability to pay. Core Marketing Concepts A Product is any offering that can satisfy a need or want, while a brand is a specific offering from a known source. When offerings deliver value and satisfaction to the buyer, they are successful. Enhancing Value Marketers can enhance the value of an offering to the customer by: – Raising benefits. – Reducing costs. – Raising benefits while lowering costs. – Raising benefits by more than the increase in costs. – Lowering benefits by less than the reduction in costs. Core Marketing Concepts Exchange involves obtaining a desired product from someone by offering something in return. Five conditions must be satisfied for exchange to occur. Transaction involves at least two things of value, agreed-upon conditions, a time of agreement, and a place of agreement. Core Marketing Concepts Relationship marketing aims to build long-term mutually satisfying relations with key parties, which ultimately results in marketing network between the company and its supporting stakeholders. Core Marketing Concepts Marketing Channels Communication channels Distribution channels Service channels Deliver messages to and receive messages from target buyers. Includes traditional media, non-verbal communication, and store atmospherics. Core Marketing Concepts Marketing Channels Communication channels Distribution channels Service channels Display or deliver the physical products or services to the buyer / user. Core Marketing Concepts Marketing Channels Communication channels Distribution channels Service channels Carry out transactions with potential buyers by facilitating the transaction. Core Marketing Concepts A supply chain stretches from raw materials to components to final products that are carried to final buyers. Each company captures only a certain percentage of the total value generated by the supply chain. Core Marketing Concepts The following forces in the broad environment have a major impact on the task environment: – Demographics – Economics – Natural environment – Technological environment – Political-legal environment – Social-cultural environment Core Marketing Concepts The marketing program is developed to achieve the company’s objectives. Marketing mix decisions include: – Product: provides customer solution. – Price: represents the customer’s cost. – Place: customer convenience is key. – Promotion: communicates with customer. Company Orientations The orientation or philosophy of the firm typically guides marketing efforts. Several competing orientations exist: – Production concept-consumers favor products that are widely available and inexpensive. – Product concept-consumers favor those products that offer the most quality, performance and innovative features. – Selling concept-holds that consumers will not buy enough of products unless the firm undertakes a large scale selling and promotion effort. (for unsought goods.) – Marketing concept-instead of product centered “make and-sell” shift to a customer centered, “sense and-respond” philosophy. Instead of “hunting” marketing is “gardening”. organisational goals depends on knowing the needs and wants of target markets. Customer value and focus are the paths to sale and profits. – Societal marketing conceptunderstanding broader concerns and the ethical, environmental, legal and social context of marketing activities and programs clearly extending beyond the company and the consumers to society as a whole. Marketing and sales concepts contrasted Starting Point Factory Focus Existing Products Mean s Ends Selling and Promoting Profits through Volume The Selling Concept Market Customer Needs Integrated Marketing Profits through Satisfaction The Marketing Concept ©2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition Slide 26 in Chapter 1 Modern Marketing System Suppliers Company (Marketer) Marketing Intermediaries Environment Environment Competitors End User Market ©2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition Slide 27 in Chapter 1