* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pink Plant Flashcards - mvhs
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
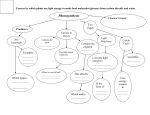
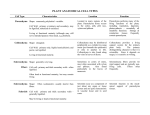
Distinguish between these 3 root types: TAP ROOT FIBROUS ROOT ADVENTIOUS ROOT SIEVE TUBE ELEMENTS XYLEM TONOPLAST COMPANION CELLS PHLOEM Define and distinguish between: APICAL MERISTEM and LATERAL MERISTEM CUTICLE CASPARIAN STRIP PALISADE MESOPHYLL Distinguish between: DERMAL TISSUE VASCULAR TISSUE GROUND TISSUE Distinguish between: Zone of Maturation Zone of Elongation Zone of Cell Division Define and distinguish between: STOMA and GUARD CELLS Distinguish between the APOPLAST PATHWAY and SYMPLAST PATHWAY in roots. SPONGY MESOPHYLL Dermal Tissue – Outer covering of plant (c________, e_________) Tonoplast - The membrane that surrounds the central vacuole of a plant cell. Allows the plant cell to store _____________. It helps the cell remain _______________ (stiff/plump). Tap – Large single root that digs deep; storage for plant. Example: ______. Fibrous – Many smaller roots stretching out. More surface area for better ___________. Adventious – Sends out roots above ________ and then starts digging in new place. Think: the root is taking an “adventure” by going above ground to seek out new places. Zone of Maturation – Area where plant cells differentiate into various types of tissue. Zone of Elongation – Area where plant cells __________. Zone of Cell Division – Area where __________ occurs and new plant cells are formed. This is also known as the apical meristem. Companion cells are part of the phloem and adjacent to _______________. They contain a nucleus and organelles to support the empty sieve tube cells. Think: Companion means a supportive friend. These cells are supportive friends of the sieve tube cells. Sieve Tube Elements are the main cells of the ___________. They are living cells that contain cytoplasm, but very few organelles. They transport sugars throughout the plant. They are supported by __________________. Stoma – Hole on a leaf to allow for_____ _____________. Phloem – the structure in vascular plants that transports____________. The phloem is made up of sieve tube elements and companion cells. Xylem – the structure in vascular plants that transports __________ and minerals. Made up of ____________ and _________________. Cuticle – Waxy outcovering of a leaf to protect from _______ ______. Apical Meristem – Primary new growth that results in ___________ of plant and organ formation. Vascular Tissue – Tissue that transports water, minerals, and sugars (_________ and ________) Ground Tissue – Photosynthetic tissue, storage tissue, and structural support tissues, Guard cells – Cells on either side of _______ that regulate the opening and closing. When guard cells are filled with water, the stoma is______. When guard cells don’t have water, then the stoma is ________. Apoplast Pathway – pathway _______ cells (between cell walls and extracellular spaces) in which materials can pass. Lateral Meristem – Secondary growth that results in w______ and b______. Symplast Pathway – pathway _______ cells (via plasmodesmata) in which materials can pass. Think “sym” = “together”, so symplast is together with (or through) a cell. Spongy Mesophyll – cells of a leaf which form ________ spaces to allow gas exchange to occur. Think: a sponge has holes. Pallisade Mesophyll – cells of a leaf which contribute most to photosynthesis. They contain many chloroplasts and are normally found on the ________ side of a leaf. Think: palisade for photosynthesis. Casparian Strip – A waterproof strip in the ______dermis of roots that forces water through a ______plast pathway.