* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download US in WWII - Ms. Mac`s Class
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
India in World War II wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
United States home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
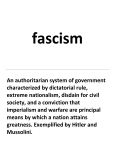
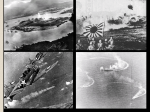
After WWI, US returned to isolationism Exceptions: Washington Naval Conference Raised tariffs Restricted immigration Insisted wartime allies pay back debts Limit size of navy Kellog-Briand Peace Pact Renounce the use of war President Hoover and Roosevelt worked to better relations with Latin American countries “Good Neighbor Policy” Not interfere with the internal affairs of Latin American countries Relations between US and the countries Latin American began to improve Rise of dictators Joseph Stalin in Russia in Russia Emperor Hirohito and General Tojo in Japan Adolf Hitler and the Nazis in Germany Benito Mussolini and the Fascists in Italy Extreme nationalistic, racist and anti-Semitic views Failure of the League of Nations Too weak to resist dictators Collective security – peaceful nations banning together to stop aggressive nations – failed when US and Soviet Union did not join League did nothing to stop Hitler rebuilding army, Italy attacking Ethiopia, Japan invading Manchuria and China… Appeasement Hitler kept annexing countries, Britain and France let him to avoid war Austria – 1938 Sudetenland (part of Czechoslovakia) Munich Conference (1938) Gave Hitler part of Czechoslovakia WITHOUT asking Czechs to avoid war Hitler decided Britain and France were weak and kept making more and more demands Hitler demands Poland; France and Britain say no Hitler signs nonaggression pact with Stalin and invade Poland September 1939 France and Britain declare war World War II begins Hitler used blitzkrieg to defeat the Poles, French, and most of Europe New technologies and bombings made it a more offensive war Still “cautiously neutral” Americans busy with Great Depression to be too involved overseas Congress starting passing laws to stay out of the war Neutrality Acts (1935-1937) – prohibited Americans from traveling on ships of nations at war Could not sell arms to countries at war either Allowed to sell non-military goods to the Brits and other non-aggressive nations on a “cash-and-carry” basis Japan invaded China in 1937, Roosevelt gives “Quarantine Speech” Growing unrest in the world and peaceful nations needed to act together to quarantine aggressive nations Boycott aggressors Most Americans opposed military action Britain didn’t want China to fall to Japan Used Burma Road to send supplies 700 mile route cut off, American volunteer fighters known as Flyer Tigers recruited to send supplies and engage with Japanese pilots Destroyed 300 Japanese aircraft 1939 – started making preparations for war just in case More Army and Navy spending, peacetime draft, Roosevelt ran for a third term 1941 – Lend-Lease Act Sell, lease, or lend war materials to “any country whose defense the President deems vital to the defense of the United States” Began protecting British ships carrying supplies for the British Roosevelt told Americans he hoped to establish a world on the Four Freedoms Freedom of speech and expression, religion, from want, and from fear 1941 – Met with British Prime Minister Winston Churchill Announced their countries wanted no territorial gains, freedom of the seas, and and end to war Atlantic Charter – laying foundation for United Nations Japan had become industrial in 19th century Needed raw materials and markets Wanted to replace European imperialism in Asia 1931 – Japan invaded Manchuria 1937 – Japan attacked the rest of China 1941 – Japan occupied southern Indochina Roosevelt froze Japanese assets in the US and cut off trade with Japan Resume trade if Japan withdrew from China Japan refused Japan decided to attack Indonesia for oil Doing so would bring US into war, so they struck first Japanese leaders believed a surprise attack would eliminate US naval power from the Pacific and allow Japan time to fortify Before US could recover, Japan would be able to finish taking over East Asia and the Pacific Americans would quickly tire of war and negotiate a peace compromise December 7, 1941 Two waves of Japanese planes attacked US Pacific fleet stationed in Pearl Harbor, Hawaii Sank or severely damaged 18 US ships More than 260 airplanes damaged or destroyed 6,000 Americans killed or injured Four days later, Germany and Italy declared war on the US US on a war of two fronts – Atlantic and Pacific Paying for the war War Bonds Citizens bought to help fund the war Reduced currency in economy to combat inflation 85 million Americans bought bonds, bring $185 billion to treasury War cost $350 billion US became debtor nation High level of volunteerism – willingness of Americans to help in the war effort. http://youtu.be/Ivqrjt TQef8 Rationing Americans asked to conserve everything for the war effort Ration books given on certain goods to avoid public anger over shortages Draft and expansion of industrial production during the war finally brought an end to the high unemployment of the Great Depression Women, African Americans, and other minorities filled in gap as workers went to war Victory Gardens Vegetable gardens to ensure enough food for everyone Food grown by farmers sent to soldiers overseas Office of War Information OWI Control of content and imagery of war messages Pro-Allied, anti Axis propaganda Own radio programs, newsreels, and required all movies to contribute in some way to war effort Voice of America Send messages overseas Stir up distrust of Germans, Italians, and Japanese leaders Lower morale of enemy soldiers Women in the work force Could not enlist in regular army, joined Women’s Army Corps or WACS Took clerical jobs in the military Replaced many jobs usually held by men More men could go into combat Rosie the Riveter 1941-1945: 6.5 million women entered the work force African Americans Many worked in war industries and government agencies Played a big role in WWII More than 2 and a half million registered for the draft One million served, even though they were in segregated units African Americans Finally allowed to form all black combat units Tuskegee Airmen Fighter group in the Air Corps Provide escorts for bombing missions Performed so well bombers asked for their support 1944 – Army had to allow African Americans to engage in combat on the ground Native Americans Enlisted for service in higher proportion than any other group More than 25,000 served in combat 40,000 left reservations to work in defense industries Mexican Americans Both Army and Navy and served in both campaigns Continued to face segregated housing, high unemployment, low wages Pearl Harbor created fear of Japanese Americans Afraid they would commit acts of sabotage Racially motivated since no evidence any more disloyal than German or Italian Americans… February 1942 – Executive Order 906 Permitted military commanders to require Japanese Americans to relocate to interior internment camps away from Western Coastal regions In camps – primitive and crowded conditions Raised constitutional issues in wartime Roosevelt justified that it was a military necessity Korematsu v. US Korematsu was Japanese citizen convicting of remaining in restricted area SC upheld that constitutional liberties may be limited in wartime 50 years later, Congress apologized and paid compensation to the families involved. Small number of German and Italian resident aliens also interned 2,000 German aliens forcibly sent back to Germany Germans also sent from Latin America to US to be used in prisoner exchanges with Germany Roosevelt decided to focus on defeating Germany first Hitler controlled most of Europe and North Africa Hitler invaded Soviet Union in June 1941 and declared war on US before defeating Britain Both big mistakes Late 1941 – Hitler stopped just before Moscow Roosevelt and Churchill promised Stalin to open a second front against Germany in the West to help relieve Soviet Army Churchill advised delay before invading Europe 1942 – Allies landed in North Africa Defeat Germans and head into Mediterranean and into Sicily and Italy in 1943 George Patton One of the commanders Military family Served under Pershing in WWI Given command of Third Army Popular commander and unconventional leader Went quickly through Europe, capturing large numbers of enemy soldiers and freeing a vast territory June 6, 1944 – D-Day 156,000 Allied troops under General Dwight Eisenhower Invaded 5 beaches of Normandy General Omar Bradley chosen to lead first American army in France Allied planes attacked Nazi forces Amphibious landing crafts carried thousands of Allied troops to the beaches of Normandy After D-Day, began moving eastward Liberated Paris in August 1944 Allies moved so quick got surprised by German counterattack in Battle of the Bulge December 1944 German attack collapsed afterward Allied troops crossed Rhine River and General Bradley pushed troops for final offensive into German American, British, and French from the west, Soviet rom the east May 1945 – Soviets captured Berlin Hitler committed suicide and Germany surrendered More than 20 million Soviet soldiers and citizens were killed Vernon Baker One of the first African American soldiers to see combat in the war 1945 – slipped through mine fields, barbed wire, and German defenses and single-handedly removed 3 machine gun nests, 2 observation posts, and 2 bunkers Nominated for Distinguished Service Cross 50 years later – President Clinton gave him the Congressional Medal of Honor The attempted genocide of the entire Jewish race Final Solution – murder all European Jews Housed and killed Jews in concentration camps 6 million Jews killed 6 million gypsies, Slavs, political prisoners, elderly, mentally disabled, and others also died in concentration camps Liberation of concentration camps During last months of the war, Allies advanced into Germany and found camps American army units the first to liberate camps Shocked to see prisoners US was separated from Japan by Pacific Ocean After Pearl Harbor, Japanese took Malaya, Burma, Indonesia, Singapore, Hong Kong, and threatened Australia, India, Midway, and Hawaii Bataan Death March – 1942 Philippines surrendered to Japanese one month after Pearl Harbor Japanese forced prisoners to walk 40 mile march through the jungle 5,000 of Americans died along the way. 1943 – War began to turn against Japan because of US “islandhopping” campaign Navajo Code Talkers Navajo language is unwritten and complex Used this language for all communication and Japanese unable to crack code Battle of Midway Turning point in the Pacific Japanese wanted to lure US Pacific fleet to battle near Midway where he believed he could destroy them US Navy deciphered Japanese codes and knew of surprise attack Battle of Midway Admiral Chester Nimitz (Commanderin-Chief of US Pacific fleet) US destroyed 4 Japanese aircraft carriers, ending Japan’s strength in the Pacific Douglas MacArthur commanded US Army in Pacific Began campaign on the Solomon Islands trying to take the Guadalcanal Series of assaults drained Japanese resources Took Philippines and Guam June 195 – captured Iwo Jima and Okinawa and close enough to launch attacks against Japanese homeland General George C. Marshall acted as Chief of Staff and “organizer of victory” Built up and supplied army of 8 million men Helped oversee creation of first atomic bomb 1939 – Albert Einstein informed Roosevelt Germany might be developing atomic bomb 1942 – Roosevelt sent team of scientists, several European refugees, to New Mexico to develop the first atomic bomb. July 1945 was successful Germany already defeated Roosevelt died of a heart attack in April 1945 (after being elected 4th time) – just before Germany surrendered President Harry Truman (Roosevelt’s vice president) feared invasion of Japan would cause too many causalities Truman decided using the atomic bomb would mean less casualties August 6, 1945 August 9, 1945 Atomic bomb on city of Hiroshima Atomic bomb on city of Nagasaki 230,000 people killed in both explosions combined Critics argued Truman could have detonated bombs on uninhabited islands Japan surrendered shortly after second explosion American leaders agreed to let Japanese emperor stay on the throne Radar, sonar, cryptic code breaking, proximity fuze, antibiotics, jet and rocket engines More than 70 million people lost their lives Most people killed were civilians, making it the deadliest conflict in history Over 100 million military personnel fought in the war, making it the largest war in history Nuremberg Trials – 19451946 Full extent of Nazi brutality revealed, Allies put surviving Nazis on trial for crimes against humanity Defended themselves claiming they had been following orders Many found guilty and were hanged or imprisoned Individuals are responsible for their actions, even in times of war Denazification of Germany Germany divided into 4 occupation zones split between US, France, Great Britain, and Soviet Union Occupying powers explained the evils of the Nazi beliefs to the German people Nazi ideas show dangers of racism, anti-Semitism, Social Darwinism, and eugenics Helped contribute to civil rights movement in US General MacArthur was assigned to rebuild and reform post-war Japan Made Japan less aggressive Overseas empire taken away, leaders put on trial and punished, renounced use of nuclear weapons and waging war Forbidden to have a large army or navy New constitution in 1947 turning Japan into a democracy