* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Natural Selection - Chadwick School: Haiku Learning
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
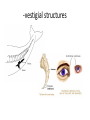
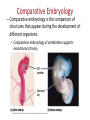
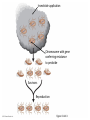
CH 13 Microevolution – How Populations Evolve Big Questions to Think About • Where do you see patterns? • Where do you see the scientific method? Evidence of Evolution – Fossil Record – Biogeography – Comparative Anatomy – Comparative Embryology – Molecular Biology The Fossil Record – Fossils • Are preserved remnants or impressions left by organisms that lived in the past. • Are often found in sedimentary rocks. – The fossil record • Is the ordered sequence of fossils as they appear in rock layers. • Reveals the appearance of organisms in a historical sequence. • Fits with other evidence of evolution. • What other information do we get from fossils? – Paleontologists • Are scientists that study fossils. • Have discovered many transitional forms that link past and present. Transitional Forms Biogeography – Biogeography • Is the study of the geographic distribution of species. • First suggested to Darwin that today’s organisms evolved from ancestral forms. Comparative Anatomy – Comparative anatomy • Is the comparison of body structure between different species. • Confirms that evolution is a remodeling process. – Homology • Is the similarity in structures due to common ancestry. -vestigial structures Comparative Embryology – Comparative embryology is the comparison of structures that appear during the development of different organisms. • Comparative embryology of vertebrates supports evolutionary theory. http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/e volution/zoo-you.html Molecular Biology – Evolutionary relationships among species • Leave signs in DNA and proteins. • Can be determined by comparing genes and proteins of different organisms. Natural Selection – Darwin’s finches • Are an excellent example of natural selection and adaptive evolution. Darwin’s Theory of Natural Selection – Darwin based his theory of natural selection on two key observations. – Observation 1: Overproduction • All species tend to produce excessive numbers. • This leads to a struggle for existence. – Observation 2: Individual variation • Variation exists among individuals in a population. • Much of this variation is heritable. – Inference: Differential reproductive success (natural selection) • Those individuals with traits best suited for the local environment leave more fertile offspring. Descent with Modification – Darwin made two main points in The Origin of Species: • Organisms inhabiting Earth today descended from ancestral species. • Natural selection was the mechanism for descent with modification. Natural Selection in Action – Examples of natural selection include • Pesticide resistance in insects. • The development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. • Drug-resistant strains of HIV. The Process of Science: Does Predation Drive the Evolution of Lizard Horn Length? Insecticide application Chromosome with gene conferring resistance to pesticide Survivors Reproduction Figure 13.14-3 Natural Selection i.e. Differential reproductive success • Those individuals with traits best suited to the local environment generally leave a larger share of surviving, fertile offspring. • First Diversity, then selection • Remember Natural selection favors traits already present • Species don’t evolve because of a need. • Biodiversity exists and the environment selects. • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=S7EhExh XOPQ Evolutionary Tree • Phylogeny