* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Communicable Diseases
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Plasmodium falciparum wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Ebola virus disease wikipedia , lookup
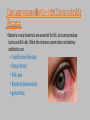
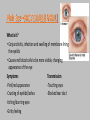
October 31, 2016 • Entry task: What are some things you can do to prevent the spread of communicable diseases? • Target: Identify risks associated with communicable diseases Communicable Diseases Cover your mouth when you sneeze, or risk spreading the disease! • A disease spread from one person or animal to another person • Caused by infective agents (pathogens) • Example: Bacteria, Virus • Pathogens multiply and damage the cells and their functioning • Most commonly spreads via airborne or bacteria • ‘Contagious’ or ‘Infectious’ used to describe communicable diseases • Airborne – direct contact not needed • Animal – come in contact with infected animal/insect • Food/Water – drinking water or eating food contaminated • Healthcare – medical waste/equipment • Respiratory/bodily fluid – when come in contact with saliva, blood, ejaculate, mucus • Not all pathogens can live for long without a Host • What is a host? • If I cough without covering but no one is around, will a person who walks in the room an hour later become infected? Who is most susceptible? •Older People •Babies •Pregnant Women •People with a weakened immune system Viruses- pieces of genetic material surrounded by a protein coat. Need living cells to reproduce, survive, and thrive Cold Flu Pneumonia Polio Measles AIDS Chicken pox EBOLA! • Bacteria- many bacteria’s are essential for life, but some produce toxins and kill cells. What the immune system does not destroy antibiotics can. food borne illnesses • Strep throat • Pink eye • Bacterial pneumonia • gonorrhea • • Protozoan's- more complex organisms than bacteria, such as pathogenic parasites, most are completely harmless but some can affect people with weakened immune system. • Malaria What is it? • Inflammation of the liver • Acute - lasts less than 6 months • Chronic - persists longer Transmission • Sexually transmitted • Shared needles (blood) • Mother to unborn child • Poor sanitation What is it? • Human immunodeficiency virus, or HIV, is the virus that causes acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). • The virus weakens a person's ability to fight infections and cancer. • Having HIV does not always mean that you have AIDS. Magic Johnson-Former NBA player Symptoms Transmission • Headache -Sharing needles • Diarrhea, vomiting -unprotected sex • Fatigue • Aching muscles What is it? • People often use the term "flu" to describe any kind of mild illness, such as a cold or a stomach virus, that has symptoms like the flu. But the real flu is different. • Flu symptoms are usually worse than a cold and last longer. The flu usually does not cause vomiting or diarrhea in adults. Transmission • Coughing/ sneezing without covering mouth • Contact with those that are sick • Unsanitary conditions What is it? • Conjunctivitis, infection and swelling of membrane lining the eyelids • Causes red blood cells to be more visible, changing appearance of the eye Symptoms Transmission -Pink/red appearance -Touching eyes -Crusting of eyelids/lashes -Blocked tear duct -Itching/burning eyes -Gritty feeling What is it? • Serious disease caused by parasite in mosquitos • You can get it from a bite by an infected mosquito. • Malaria is rare in the United States. Common in Africa, Southern Asia, Central America, and South America. Symptoms Symptoms like the flu, such as a high fever, chills, and muscle pain Can be more serious – damage to liver, heart, etc • A bite from a parasite-infected mosquito causes malaria. • The mosquito becomes infected by biting an infected person and drawing blood that contains the parasite. • When that mosquito bites another person, that person becomes infected. • Washing hands- most effective strategy for preventing the spread of disease. Before you eat, put in contacts or makeup, after the restroom, handle animals, etc. • Avoid sharing make-up, combs, and brushes, food, drinks, chapstick • Avoid unprotected sexual intercourse • Avoid unnecessary contact with people who are sick • Protect others, cover your mouth! Coughing and Sneezing •Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue when coughing or sneezing. Put your used tissue in the waste basket. Then, clean your hands, and do so every time you cough Depends on the disease! Bacterial – most commonly have medication (antiBACTERIAL, antibiotic) Viral – no true medication Hand Washing • How do you wash • When • Why • What • What are communicable diseases? • How are they spread (transmitted?) • What are the three main types of communicable diseases? • Examples? • Can you prevent? • Can you treat? Ebola?