* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Endocrine organs - Ping Pong
Bovine somatotropin wikipedia , lookup
Glycemic index wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Cryptorchidism wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (female-to-male) wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hormonal contraception wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Menstrual cycle wikipedia , lookup
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency wikipedia , lookup
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
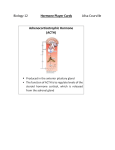
Endocrine organs Hormon, gr. = to set in motion Gabriella Smedfors Department of Neuroscience Karolinska Institutet Neuronal vs Hormonal signalling Neuronal vs Hormonal signalling Signal substance Transported in blood released from one cell directly to the next Few target cells Multiple target cells Effect < ms Effect within seconds to days Short effect Lasting effect Hormone ≠ Hormone Lipophilic hormones Peptide hormones o Eg. Adrenalin, GH o Eg. steroid hormones o Free transport in blood o Transport in blood bound to plasma proteins o Extracellular receptors o Intracellular receptors Endocrine organs Feedback system Hypothalamus Hypothalamus Thyrotropin‐releasing hormone (TRH) Hypophysis K Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) Gl. Thyroidea Thyroid hormones (T3/T4) Hypophysis Hypothalamus o Regulates the activity of the pituitary gland via the hypophyseal portal system o Controls circadian rhythm, metabolism, food intake etc. o Connects emotions and body Sella turcica Anterior pituitary / Adenohypofysis Anterior pituitary / Adenohypofysis o GH o TSH o PRL o FSH o LH o ACTH o MSH o GH = Growth hormone Stress hormone. Stimulates release of growth factors from the liver. Gigantism & Acromegaly Anterior pituitary / Adenohypofysis o GH o TSH = Thyroid-stimulating hormone Anterior pituitary / Adenohypofysis Anterior pituitary / Adenohypofysis o GH o GH o TSH o TSH o PRL = Prolactin o PRL Stimulates milk produktion o FSH = Follicle-stimulating hormone Stimulates development of follicles / initiates and enhances spermatogenesis Anterior pituitary / Adenohypofysis Anterior pituitary / Adenohypofysis o GH o GH o TSH o TSH o PRL o PRL o FSH o FSH o LH o LH = Luteinizing hormone Triggers ovulation / production of testosterone in testis Anterior pituitary / Adenohypofysis o GH o TSH o PRL o FSH o LH o ACTH o MSH= Melanocytestimulating hormone Release of melanin. o ACTH = Adrenocorticotropic hormone Stimulates the adrenal glands to release cortisol Posterior pituitary / Neurohypopfysis o Oxytocin Milk production & uterine contraction. “Bonding hormone”. o ADH = Antidiuretic hormon Retains water through increased resorption in the kidneys. Glandula Thyroidea Goitre o T3 & T4 Stimulates metabolism (growth, pulse, development of the nervous system) o Calcitonin Lowers Ca-levels in blood eg. through inhibition of skeletal breakdown. Hyperthyroidism Glandula Parathyroidea x4 Anterior view Posterior view PTH = Parathyroid hormone Increases absorption of Ca and Mg from the intestine and the kidneys. Pancreas Pancreas o o Insulin Islets of Langerhans o Lowers blood glucose levels by facilitating an increased uptake in muscles and fatty tissue o Glucagon Increases blood glucose levels by release of glucose from the liver Glandula Suprarenalis o Two parts: Cortex and medulla o 3,5 – 6 g Adrenal cortex Adrenal cortex o Aldosterone Controls blood pressure through conversation of sodium in the kidney. o Cortisol Metabolism, immunosupressing, stress, circadian rhythm. o Androgens Sex drive, weak promotor of masculine physical features. Adrenal medulla Ovarium o Adrenaline & Noradrenaline 4:1 Stress hormones o Increases pulse and releases glucose from the liver which muscles may use as energy Ovarium Estrogen and Progesterone Regulates reproduction cycle and secondary sex characteristics for women. Testis Other organs with endocrine function o Heart o Fatty tissue o Intestine o Kidneys o Thymus Testosterone Promotes sperm production and secondary sex characteristics for men. o Placenta