* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Coronary Artery Disease:
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
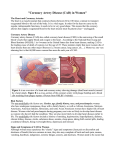
~Maria Vogel’s Med-Surg notes Ch. 33 CAD Page 1~ Coronary Artery Disease: Atherosclerosis—Fat deposits, intima of vessel walls. Arteriosclerosis—elasticity and hardening I. CAD—development of CAD A) Stages 1. fatty streak—lipids in intima of vessel walls Starts at age 15. 2. Raised fibrous plaque --Appears by age 30 --Initiated by endothelial injury Increased BP—shearing of endothelium lining called denuding injury. Increased Cholesterol Cigarettes ? inflammation? 3. complicated lesion plaque has lipid core surrounded by dead tissue. 4. collateral circulation over months or years develop collateral circulation around hallowing. A young person having a MI is worse than an older person because haven’t developed collateral circulation. Is inherited and the presence of chronic ischemia. B) Risk factors: 1. unmodifiable—age, gender, heredity, and family hx 2. Modifiable: a) Elevated serum level—lipids Cholesterol—diet and liver ~ Normal 140-200 ~Maria Vogel’s Med-Surg notes Ch. 33 CAD Page 2~ HDL normal Male >45 Females >50 ~ carries lipids AWAY from vessel LDL Should be < 130 ~ Have more cholesterol and attach to arterial walls. VLDL—contains triglycerides should be < 200. ~ ETOH and simple sugars Inc. Triglycerides Homocysteniene levels Amino acid contains sulfur ~ alters endothelial lining ~ Inc. chances of clotting ~ to decrease levels take Vit B12, B6 and folic acid SMOKING: increases BP and Decreases O2 Inc. Workload of heart and Inc. HR. II. Prevention and Treatment a) health promotion b) lifestyle changes ~ Diet—step 1 decrease sat. fat—decrease cholesterol by 10-15% Step 2 go to if no change after 6 months. ~ decrease tryglycerides—sugar and ETOH c) Rx—drug therapy 1. enhances lipid protein removal Resins lower LDL and increase HDL Welchol and Questran SE: Belching 2. Restricts lipoprotien production Niacin (B Vit.) 3. Statins-Locar SE: Rash and gas III. Manifestations of CAD 1. Angina ~Maria Vogel’s Med-Surg notes Ch. 33 CAD Page 3~ 2. MI 3. Sudden Death 1. Angina Pectoris transient (comes and goes) chest pain lasts 3-5 minutes Coronary arteries are chronically dilated Factors that affect O2 demand: Low BP Vasoconstriction—HTN Aortic stenosis Precipitating factors: a) Exertion—Increase HR and Increase O2 demand, Heart can’t meet. b) Strong emotions c) Consumption of heavy meal—blood transported to GI to digest food. d) Change of temp. Heat—vasodilation, Cold—vasoconstriction e) Cigarettes f) Sex g) Stimulates—drugs—cocaine h) Circadian rhythms—happens in AM stimulation of SNS. 2. Unstable Angina Preinfarct Progressing Unpredictable—occurs at rest or minimal exertion BIGGEST RISK—complete occlusion 3. Manifestations Signs and Symptoms Most common—pain—describe pain (squeezy, ache and heaviness) ~Maria Vogel’s Med-Surg notes Ch. 33 CAD Page 4~ Feelings of doom SOB Cold sweat—diaphoretic 4. Complications Arrhythmias PVA’s ventricular fibrillation 5. Diagnostics H and P EKG 12 lead Nuclear techniteum scan—identifies areas of inadequate circulation in heart “hot spots.” 6. Medications 1st line of treatment a) Platelet aggregate inhibitors ASA Plavix Ticlid b) Nitroglycerin Decreases preload and after load ~ Coronary vasodilators==increase flow in coronary arteries decreases workload of heart ~ Routes—SL, PO IV (titrate for effect) Transdermal (remove x 8 hr) ~ SE—headache and hypotension. c) Beta Blockers ~ decreases HR, BP and O2 consumption Lopressor Zobeta Inderal Corgard ~ Can cause bronchoconstriction ~ Obtain a baseline HR and BP, hold if pulse < 60 and Systolic <100 d) Ca Channel Blockers ~Maria Vogel’s Med-Surg notes Ch. 33 CAD Page 5~ ~ decreases systemic vascular resistance and decreases BP ~ Cause vasodilation ~ decreases myocardial contractility and decreases power ~ Decreases HR ~ Ultimately decreases workload of heart Calan / Verapamil Procardia Diltazem/Cardizem II. Myocardial infarction Ischemia—leads to irreversible damage to the heart Inferior MI—Rt coronary artery ~ Rt atrium and ventricle—SA node—conduction— Anterior MI—left anterior descending artery Left sided failure—bigger muscle mass Posterior MI—circumflex occlusion A) Signs and Symptoms Chest pain N/V Ashen and cold Sweaty 80% with symptoms have arrhythmias PVC’s, V-tach and V-fib B) Complications: Left ventricular failure—causes pulmonary edema S/S restlessness, dyspnea, crackles, wheezing and TOTAL CHF. Cardiogenic shock Pericarditis—hear rub—have pt hold breath so you can hear if it is the heart and not lungs. C) diagnostics: 1. H and P and how the pt presents himself ~Maria Vogel’s Med-Surg notes Ch. 33 CAD Page 6~ 2. EKG—done serially immediately—30 min. and 1 hr. Look for elevated ST segment, Inverted T-wave, and abnormal Q-wave 3. Cardiac markers-~ CK—creatinekinase—increases with a MI. Normal male 15-100 fem. 10-80 ~ MB band—norm 0-9 increases with acute MI will rise after 4-6 hrs after MI but returns to normal within 3-4 days. ~ Troponin—Normal T= 0-0.2 and I < 0.6 Will rise within 4-6 hours after the MI and stays elevated for up to 2 weeks. D) Collaboarative Care M—orphine O—O2 N—nitro A—ASA 1. ICU 2. EKG 3. O2—2-4 L 4. Morphine or demoral—decreases pain, fear and anxiety, decreases contractility, O2 consumption, HR BP and workload 5. Antirrythmia Rs—lidocaine—for PVCs 6. Nitro—SL or IV helps perfusion a little Thrmbolytic—therapy within 6 hours * Biggest complication of thrombolytic therapy is hemorrhage. Stop therapy immediately if there is a change in pt’s mental status. Possible bleed in the brain? Thrombolytic Drugs: tPA Streptokinas Urokinase Retavase ~Maria Vogel’s Med-Surg notes Ch. 33 CAD Page 7~ Criteria for thrmbolytic therapy : Chest pain with MI less than 6 hrs ago EKG supports/confirms MI No condition that will predispose to hemorrhage, surgery, car accident or pregnancy. Effective of thrombolytics: Decreases chest pain Return of S-T to baseline on EKG Reperfusion To prevent reocclusion Rx heparin IV with thrombolytic. Monitor PTT Treatment of CAD CABG—open heart surgery Stent placement Athrectomy Balloon Drugs: ~Inotropic drugs increase contractility increase O2 demand too Digoxin/Lanoxin Dubutrex—given IV acute lf vent. Failure. Inocor ACE inhibitors—watch for hyperkaliemia Vasotec—prevents vent. Remodeling ~ Give stool softener—vasgus nerve causes decreases HR and BP. –COLASE. ~Maria Vogel’s Med-Surg notes Ch. 33 CAD Page 8~