* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 5. Cardiovascular System: Heart and Blood Vessels The
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
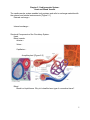
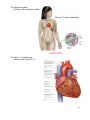
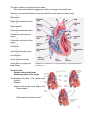
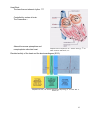
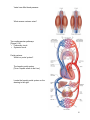
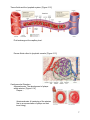
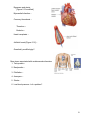
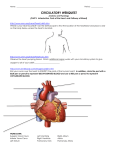
Chapter 5. Cardiovascular System: Heart and Blood Vessels The cardiovascular system enables body systems and cells to exchange materials with the external and internal environments. [Figure 5.1] External exchange – Internal exchange – Structural Components of the Circulatory System: Heart. Blood vessels. Arteries – Veins – Capillaries – A capillary bed. [Figure 5.2] Blood. Blood is a liquid tissue. Why is it classified as a type of connective tissue? 1 The lymphatic system. Function of the lymphatic system – [Figure 7.6 with modifications] The Heart – A double pump. External view. [Figure 5.3] 2 The path of blood into and through the heart: The colors below indicate oxygen poor (blue) and oxygen rich (red) blood. Superior vena cava and inferior vena cava (blood from the upper and lower body) Right atrium (Right atrioventricular valve) Right ventricle (Pulmonary semilunar valve) Pulmonary trunk (artery to lungs) Pulmonary veins (veins from lungs) Left atrium (Left atrioventricular valve) Left Ventricle (Aortic semilunar valve) Aorta (artery to upper and Adapted from Cam pbell, N. & J. Reese. Biology, 7 th ed. 2005. Pearson Education, Inc. lower body) Terms to note: Cardiac refers to the heart. Pulmonary refers to the lungs. The beating of the heart – The cardiac cycle. Systole – Diastole – Stages of the cardiac cycle. [Figure 5.5] Heart sounds – What causes the heart sounds? 3 Heart Beat: The heart has an inherent rhythm. ??? Controlled by centers in brain. The Pacemaker – Adrenal hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine stimulate heart. Adapted from Cam pbell, N. & J. Reese. Biology, 7 th ed. 2005. Pearson Education, Inc. Electrical activity of the heart and the electrocardiogram (ECG): Adapted from Hole, J.W. Human Anatomy and Physiology, 6th ed. 1993. Wm. C. Brown, Inc. 4 Blood Pressure: Systolic pressure – Diastolic pressure – Adapted from Hole, J.W. Human Anatomy and Physiology, 6th ed. 1993. Wm. C. Brown, Inc. Blood Vessels: [Figure 5.2] Veins – Arteries – Capillaries – 5 Veins have little blood pressure. What causes varicose veins? Two cardiovascular pathways. [Figure 5.10] < Pulmonary circuit. < Systemic circuit. Portal systems. What is a portal system? The hepatic portal system. [Term: Hepatic refers to the liver] Locate the hepatic portal system on the drawing to the right. 6 Tissue fluids and the lymphatic system. [Figure 5.12] Fluid exchange at the capillary level. Excess fluids collect in lymphatic vessels. [Figure 5.13] Cardiovascular Disorders: Atherosclerosis: The development of plaque within arteries. [Figure 5.14] Plaque – (Arteriosclerosis: A hardening of the arteries due to an accumulation of plaque on their inner lining.) 7 Bypasses and stents. [Figure 5.15 modified] Myocardial infarction – Coronary thrombosis – Thrombus – Embolus – Heart transplants – Artificial hearts [Figure 5.16] – Genetically modified pigs? More terms associated with cardiovascular disorders: 1. Tachycardia – 2. Bardycardia – 3. Fibrillation – 4. Aneurysm – 5. Stroke – 6. Low blood pressure. Is it a problem? 8