* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2009 DECA Ontario Regionals Test 1021 MARKETING CLUSTER
Customer relationship management wikipedia , lookup
Online shopping wikipedia , lookup
Product placement wikipedia , lookup
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
Sales process engineering wikipedia , lookup
Visual merchandising wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Social media marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Product lifecycle wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Customer engagement wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Predictive engineering analytics wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Supermarket wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
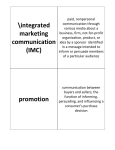
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Services marketing wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
2009 DECA Ontario Regionals Test 1021 MARKETING CLUSTER EXAM 1 1. One of the main functions of the legal procedure is to A. establish laws. C. resolve disputes. B. enact legislation. D. regulate business. 2. Jason would like to start a small business which he could operate from his home. His business would not cost a great deal to start, and he has experience and interest in that type of business. What form of ownership should he consider? A. Monopoly C. Sole proprietorship B. Partnership D. Corporation 3. What marketing function is concerned with obtaining information about the preferences, opinions, habits, trends, and plans of current and potential customers? A. Selling C. Marketing-information management B. Product/Service management D. Promotion 4. What type of intermediary would purchase baseball bats from one producer, mitts from another, and balls from still another, and then sell an assortment to sporting goods stores? A. Retailer C. Producer B. Agent D. Wholesaler 5. Electronic billing, purchase-order verification, bar-code technology, and image processing are examples of A. horizontal channel integration. C. functions of the finance department. B. integrated data between channel members. D. vertical channel integration. 6. Branch locations of a business that operate in the same city and target the same customers may experience __________ channel conflict. A. community C. vertical B. horizontal D. dominant 7. The systematic gathering, recording, and analyzing of data about problems related to the marketing of goods and services is known as A. marketing research. C. information flow. B. secondary data. D. situation analysis. 8. When Jeremy extended his hand toward Hank as they were introduced, Hank said, "Hello, Jeremy," but he ignored Jeremy's hand and kept his own hands in his pockets. What kind of nonverbal message was Hank sending? A. We have a lot in common. C. I don't want to know you. B. I am glad to meet you. D. We have met before. 9. Which of the following is a general guideline for answering the telephone in a businesslike manner: A. Identify the firm or department and yourself B. Address the caller by his/her first name C. Take immediate action on the caller's request D. Record the correct spelling of each caller's name 10. A good example of a casually operated group is a A. football team selecting a strategy or play. B. football team running laps around the field. C. few players tossing a football during practice. D. few friends talking about football. 11. Businesspeople need to use the correct words in written communication in order to make sure that the receiver __________ the message. A. understands C. accepts B. agrees with D. approves of Copyright © 2010 by MBA Research and Curriculum Center®, Columbus, Ohio 2009 DECA Ontario Regionals Test 1021 MARKETING CLUSTER EXAM 2 12. Which of the following is an example of a complimentary close: A. Enclosure C. Yours truly B. To Whom It May Concern D. Dear Occupant 13. When encouraging the reader to take a specific course of action, persuasive messages are most effective when the message source demonstrates a high level of A. credibility. C. adaptability. B. inconsistency. D. objectivity. 14. When staff members wish to discuss problems related to their jobs, they should communicate with A. their immediate supervisor. C. the company president. B. the personnel department. D. their coworkers. 15. What can you do to project to customers that they are important to the business? A. Use customer names in conversations. B. Stare at customers so they know you are listening. C. Request a supervisor's assistance in resolving problems. D. Speak loudly so that customers can easily hear your responses. 16. Sharon is a customer service representative who spends most of her day on the phone with customers. Her company prohibits her from eating at her work station so she won't be tempted to eat while talking with customers. This is an example of a(n) __________ policy. A. service C. product B. employee D. customer 17. Which of the following is not an action to take in helping the slow/methodical, or analytical, customer: A. Demonstrate merchandise carefully C. Summarize benefits of buying now B. Seek agreement on key selling points D. Show a large selection of products 18. Determine the type of utility being created in the following situation: A business offers a credit plan to allow customers to purchase items they want. A. Price C. Form B. Place D. Possession 19. A Vermont ski shop has not yet received its November shipment of ski supplies. Since the holiday rush is only days away, you would expect prices of existing stock to A. decrease. C. remain the same. B. increase. D. fluctuate. 20. Efficient resource use is an advantage of the ________ organizational structure. A. regional C. matrix B. vertex D. regulated 21. The ultimate goal of a company that redirects its marketing effort to an untapped market segment is to increase its A. profit. C. expenses. B. prices. D. output. 22. Stable prices and interdependence are characteristics of a(n) A. technical monopoly. C. monopoly. B. oligopoly. D. differentiated oligopoly. 23. What is an advantage of specialization of labor? A. Management can rotate jobs. B. It's easier to train workers. C. Worker dependency increases. D. Jobs may become obsolete. 2009 DECA Ontario Regionals Test 1021 MARKETING CLUSTER EXAM 3 24. During which phase of a business cycle does the demand for goods and services begin to exceed the production capacity of the business community? A. Trough C. Peak B. Expansion D. Contraction 25. The way that businesspeople in different countries behave is based on what is acceptable in their business A. activities. C. contracts. B. subcultures. D. policies. 26. Ultimately, employees with initiative try to further their education to prepare themselves for A. job advancement. C. membership in professional organizations. B. lateral job changes. D. certification. 27. Accepting blame for failure and credit for success is an indication of a person's A. initiative. C. consideration. B. responsibility. D. interpersonal skills. 28. An employee who consistently displays a positive attitude is likely to have A. decreased chances of promotion. C. increased self-consciousness. B. difficulty with relationships. D. increased chances of success. 29. Which of the following is a true statement regarding negative feedback: A. Most negative feedback points out a person's strengths, as well as his/her weaknesses. B. Negative feedback reinforces a message receiver's attitude or behavior. C. The primary purpose of negative feedback is to embarrass the message receiver. D. Negative feedback expresses disapproval about a specific behavior. 30. What should you develop to persuade others to believe what you say? A. Personal credibility C. Creativity B. Nonverbal language D. Speaking skills 31. Which of the following is an example of using posture to express assertiveness: A. Explaining why you must refuse a request for help B. Raising your eyebrows when you have questions C. Standing up straight when talking to other people D. Frowning when you disagree or disapprove 32. Which of the following is an example of a conflict response mode: A. Frustration C. Mediation B. Avoidance D. Exclusion 33. Tim and his classmates all feel that their teacher's grading scale is unfair. While everyone else sits around and grumbles about it, Tim decides to ask his teacher for a meeting to discuss the grading scale. Which characteristic of a change leader is Tim displaying in this situation? A. Knows how to coach others C. Loves to learn new things B. Persuasive D. Not afraid to “go for it” 34. Because the United States is made up of people from all parts of the world, it has many different A. governments. C. courts. B. cultures. D. sanctions. 35. Businesses that offer revolving charge accounts and send customers updated statements showing the status of their accounts are following which federal law? A. Equal Credit Opportunity Act C. Fair Credit Billing Act B. Truth-in-Lending Act D. Fair Credit Reporting Act 2009 DECA Ontario Regionals Test 1021 MARKETING CLUSTER EXAM 4 36. Which of the following statements about understanding your spending habits is true: A. A key aspect of opening a bank account C. The first step in creating a financial plan B. A key aspect in exceeding financial goals D. The last step in creating a financial plan 37. The Chrysler Theater is hosting the road show of "Annie." In which of the following cases would the theater be liable for damages: A. A guest trips on loose carpet in the hallway and sprains an ankle. B. During intermission, one attendee accidentally spills a drink on someone. C. An attendee's car parked in a city lot gets broken into during the performance. D. People complain that the theater-goers in front of them blocked their view of the show. 38. Business managers use accounting information to help them to A. reduce insurance premiums. C. calculate excise taxes. B. allocate their funds. D. pay labor union dues. 39. A business's buying buildings, vehicles, and equipment is an example of money flowing out in order to acquire A. products. C. staples. B. assets. D. supplies. 40. Benny's Bike Shop manufactures bicycles for its customers during the year. Benny's purchases sprockets from Spikes Sprockets, tires from Tiny's Tires, and frames from Freddie's Frames. The expense of purchasing these items is known as A. gross profit. C. revenue. B. operating expenses. D. cost of goods sold. 41. Which of the following is a measure of how well a business generates cash flow: A. Capital structure C. Return on capital B. Accounts receivable D. Accounts payable 42. Which of the following is a desired characteristic of the format of a particular budget report: A. Is flexible and unimportant C. Can change to meet a manager's needs B. Is standardized and does not change D. Is unique to each department and manager 43. In what way might a human resources manager be involved in employee benefits? A. Selecting an employee's personal plan options B. Determining eligibility and costs of benefits C. Collecting insurance payments from employees D. Choosing an employee's vacation days 44. A wholesaler breaks down a large shipment of a product and sells portions of it to several retailers. The wholesaler is reducing a discrepancy of A. installation. C. quantity. B. assortment. D. promotion. 45. As Justin is cooking, his sister reads the recipe directions to him out loud. Justin isn't sure if she said one teaspoon of vanilla or two. He gives her a puzzled look, and his sister reads the directions again. Which of the following steps for following directions does this situation illustrate: A. Accept responsibility B. Acknowledge directions verbally or nonverbally C. Take notes D. Eliminate distractions 2009 DECA Ontario Regionals Test 1021 MARKETING CLUSTER EXAM 5 46. Which of the following Internet-based marketing-research methods is most likely to raise an ethical issue regarding the users' right to privacy: A. Scan portals C. Browsers B. Cookies D. Banner ads 47. Using a database to track its customers' preferences and buying habits can usually help a business A. build strong, loyal customer relationships. B. obtain additional deductions for its semi-annual tax return. C. reduce unnecessary operational expenses. D. decrease the need for personnel to analyze marketing activities. 48. The observation method of collecting marketing-research data involves A. surveying consumers by mail. C. watching what consumers do. B. test marketing new products. D. calling consumers on the telephone. 49. Advertisers that use concept testing to obtain feedback from potential customers are conducting A. focus group analysis. C. target readership evaluation. B. primary market research. D. pretest idea measurement. 50. What do businesses create to help answer the research problem? A. Objectives C. Procedures B. Strategies D. Activities 51. How might a business use the information in salespeople's lost-business reports that indicates that customers are dissatisfied with the business's credit policies and service? A. To identify its target market C. To revise its marketing strategy B. To change its operating goals D. To update its promotional techniques 52. Which of the following is an example of a business developing a code for answers to survey questions in order to process and analyze marketing information: A. Results are tabulated according to date received. B. Questions are numbered in chronological order. C. Each survey contains an identification number. D. Each answer has a specific numeric value. 53. In addition to the wording on a questionnaire being clear, the wording should be A. ambiguous and complex. C. concise and objective. B. complex and concise. D. objective and adaptable. 54. Because of customer requests, a business decides to reorder a product that it had stopped selling. The business is using the A. distribution process. C. production process. B. promotional-mix concept. D. marketing concept. 55. The XYZ Corporation has set a goal to increase profitability by 15% within the next two years. To achieve that goal, the corporation has decided to open a new location. This strategy is the corporation's A. plan of action. C. type of risk. B. marketing mix. D. financial plan. 56. Which of the following is an example of an external change that could affect a business's sales forecast: A. A new sales rep has been hired to develop the company's territory in Texas. B. The population of a town increases when a new hospital opens in the community. C. The company plans to modify its approach to mailing catalogs to customers. D. A company plans to raise prices on its products. 2009 DECA Ontario Regionals Test 1021 MARKETING CLUSTER EXAM 6 57. Managing information regarding copyrights and trademarks helps a company to preserve its A. identity. C. correspondence. B. inventory. D. customers. 58. The scope of the Internet can be described as A. regional. B. secure. C. worldwide. D. proprietary. 59. What is the visual tool in presentation software that smoothly moves one slide into the next slide? A. Transition C. Effects B. Animation D. Formatting 60. What type of software would a business use to calculate the effect that charging higher rates would have on profit? A. Presentation C. Database B. Desktop publishing D. Spreadsheet 61. A new law was passed that affects the type of personnel records Germaine must keep at his financial services company. What is influencing the selection of records that the business must keep? A. Regulations C. Industry B. Leaders D. Size 62. Which of the following is an example of information that a manufacturing company keeps about its customers: A. Expense reports C. Payroll reports B. Tax returns D. Invoices 63. What type of trend are businesses considering when they analyze where customers live and their ethnic backgrounds? A. Demographic C. Technical B. Environmental D. Cultural 64. Which of the following forms of technology is most useful in operations: A. Smart phones C. E-mail B. Wireless internet D. Computer-aided design 65. A common cause of back injuries on the job is A. sitting in one position. B. poor posture. C. hard physical labor. D. improper lifting. 66. What do project-planning tools show you about the project? A. When you will do a similar project C. How pleased the stakeholders are B. Why you want to complete the project D. Who is doing what 67. Which of the following is a way that effective purchasing benefits a business: A. Creates jobs C. Lowers costs B. Increases assets D. Reduces sales 68. Production is often called a conversion process because it A. makes inputs from outputs. C. changes failure to success. B. creates product utility. D. turns resources into products. 69. One way that employees can help to control a business's expenses is by A. handling products casually. C. overlooking thefts. B. rotating stock daily. D. arriving at work on time. 2009 DECA Ontario Regionals Test 1021 MARKETING CLUSTER EXAM 7 70. Why is it important for businesses to maintain storage areas in a way that allows them to identify and discard products whose expiration dates have expired? A. To prevent cross-contamination C. To obtain replacement items B. To eliminate health hazards D. To follow federal guidelines 71. Personal grooming rules for hair should include keeping the hair clean, styled, and A. dandruff free. C. cut short. B. tinted. D. curled. 72. In a staff meeting, a store manager asks employees to come up with as many suggestions for improvement as they can within 15 minutes. What creativity technique is being used? A. Attribute listing C. Brainstorming B. Checklist D. Problem identification 73. Employees who arrive at work on time and direct their own work-related activities during the course of the day usually possess positive __________ skills. A. inner-qualitative C. self-management B. self-conceptual D. personal-orientation 74. Many teenagers begin searching for their first jobs by contacting A. community training programs. C. national corporations. B. employment agencies. D. neighborhood businesses. 75. What is the preferred length of a job résumé? A. As long as necessary B. Three pages C. Five pages D. From one to two pages 76. Why do many businesses provide opportunities for their employees to continue their education or receive additional training? A. To provide financial assistance C. To identify problems in the company B. To be able to promote from within D. To support the local community college 77. Informing, persuading, or reminding customers about products is known as A. product planning. C. pricing. B. promotion. D. place. 78. What is the advantage to a business of using bar-code pricing? A. Easier to change prices B. Reduces required business security C. Easier for customers to read D. Reduces number of employees needed for sales 79. Which step in the new-product development process involves seeking feedback from customers to know what response they would give to a proposed product? A. Product screening C. Idea generation B. Concept testing D. Feasibility analysis 80. A business using satellite communications systems to track a product from the time it is ordered until it is delivered is an example of technology impacting the __________ function. A. product/service management C. transportation and receiving B. marketing-information management D. selling and promotion 2009 DECA Ontario Regionals Test 1021 MARKETING CLUSTER EXAM 8 81. How does the use of grades and standards affect the buying and selling process? A. It provides product information on unsafe products. B. It enables consumers to buy without having to inspect each product. C. It enables businesses to set high prices. D. It enables salespeople to suggest products without having to determine customer needs. 82. An unwritten warranty that is understood by the customer and the seller that the product will perform as expected is a(n) __________ warranty. A. full C. limited B. implied D. express 83. Mr. and Mrs. Finetune purchased a new digital camera from Optical One. Six months after purchasing the product, it caught on fire and was damaged very badly. The Finetunes contacted the manufacturer so they could have the camera replaced. The representative gave them a control number and retailer that would provide them with another digital camera. This is an example of the manufacturer complying with which of the following federal laws: A. Fair Packaging and Labeling Act C. Consumer Product Safety Act B. Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act D. Magnuson-Moss Warranty Act 84. The assortment of products that a firm offers for sale is referred to as its product A. line. C. mix. B. consistency. D. differentiation. 85. A company packages two software programs together and sells them at a lower price than if each program were purchased individually. This is an example of product A. integration. C. bundling. B. blending. D. consolidation. 86. Before selecting a brand name for a new product, marketers should determine the acceptability of brand possibilities among different cultures. As part of this process, marketers should A. create URLs for the product in each of the countries where the product will be marketed. B. determine if the brand name would be culturally taboo where the product will be marketed. C. develop a different trade character for each of the countries where the product will be marketed. D. choose a different brand name for each country where the product will be marketed. 87. Determine whether the following statement is true or false: Promotion is nonpersonal communication of information about goods, services, images, or ideas to achieve a desired outcome. A. False, promotion can be personal or nonpersonal communication about ideas, images, goods, or services. B. False, promotion is any paid form of communication about ideas, images, goods, or services. C. True, promotion is any nonpaid form of communication about ideas, images, goods, or services. D. True, promotion is the nonpersonal communication of ideas, images, goods, or services. 88. Premiums, coupons, point-of-purchase displays, contests, and dealer incentives are all examples of the form of promotion known as A. sales promotion. C. publicity. B. advertising. D. personal selling. 89. Which of the following is an example of electronic interactive media that allows businesses to promote their products to large audiences: A. Specialty C. Transit B. Internet D. Electronic spectaculars 2009 DECA Ontario Regionals Test 1021 MARKETING CLUSTER EXAM 9 90. In a free-enterprise economic system, promotional practices are often subject to regulation by governmental systems, consumer groups, and __________ organizations. A. liability C. nonprofit B. competitive D. industry 91. Which of the following types of media may include catalogs: A. Out-of-home C. Broadcast media B. Direct mail D. Transit media 92. Which of the following statements is true regarding direct advertising strategies: A. Marketers often select their direct advertising methods based on customers' preferences. B. Use of e-mail advertising messages rewards most marketers with a very high response rate. C. Telemarketing programs are generally considered to be obsolete forms of direct advertising. D. Infomercial and home shopping television are the least effective media to send promotional messages. 93. Your partner has designed a sharp, distinctive graphic logo for your business's ad and wants you to develop a catchy phrase to use with the logo. What will you be creating? A. Headline C. Copy B. Slogan D. Illustration 94. One of the first steps in developing a promotional plan is to A. set objectives. C. design a message. B. prepare a budget. D. create a schedule. 95. Which of the following is a promotional activity that retail businesses should coordinate with their special promotions: A. Visual merchandising C. Sales training B. Information gathering D. Product planning 96. Carlos tries to respond personally to his customers' needs and wants by using communication to influence their purchase decisions. Carlos is engaged in A. distributing. C. financing. B. advertising. D. selling. 97. Maggie is in the market for a new stove, and Jan recommends Appliance World because she has purchased three different appliances there and the company backs up its promises. This is an example of which benefit of customer service? A. Profit motive C. Spirit B. Reputation D. Convenience 98. Fostering customer loyalty and goodwill helps to build a clientele, but these efforts can be wiped out by salespeople who A. implement business policies. C. avoid competition. B. fail to keep promises. D. give customers full attention. 99. New salespeople often rely on more experienced personnel to explain product information that is A. ordinary. C. technical. B. routine. D. favorable. 100. What is the primary difference between selling approaches in the retail and manufacturing industries? A. The level of communication C. The nature of the customer B. Sales volume in terms of dollars D. Business ownership structure Test 1021 MARKETING CLUSTER EXAM – KEY 10 1. C Resolve disputes. The legal procedure is the process of reviewing disputes or claims and resolving them in a fair manner. Businesses are often involved in disputes with other entities, such as suppliers or competitors. If a business believes it has been wronged by another, the business follows the appropriate legal procedure to resolve the issue. Enacting legislation, establishing laws, and regulating business are not the main functions of the legal procedure. SOURCE: BL:070 SOURCE: Miller, R.L., & Jentz, G.A. (2005). Fundamentals of business law (6th ed.) [pp. 32-40]. Mason, OH: Thomson/South-Western. 2. C Sole proprietorship. A sole proprietorship is a form of business ownership in which the business is owned by one person and is easy to open, but the owner has limited capital and limited capabilities. Jason will not need a great sum of money, and he has experience in that type of business. A partnership is a form of business ownership in which the business is owned by two or more persons who combine their capital and capabilities. It is relatively easy to start. A corporation is owned by issuing stock and is difficult to form and operate. A monopoly is a condition in which a market is controlled by one supplier, and there are no substitute goods or services readily available. SOURCE: BL:003 SOURCE: BA LAP 7—Own It Your Way 3. C Marketing-information management. This marketing function involves gathering, accessing, synthesizing, evaluating, and disseminating information for use in making business decisions. The type of information that is gathered often includes data about customers' preferences, opinions, habits, trends, and plans. Product/Service management involves obtaining, developing, maintaining, and improving a product or service mix in response to market opportunities. Selling involves determining client needs and wants and responding through planned, personalized communication that influences purchase decisions and enhances future business opportunities. Promotion is communicating information about goods, services, images, and/or ideas to achieve a desired outcome. SOURCE: IM:012 SOURCE: Farese, L.S., Kimbrell, G., & Woloszyk, C.A. (2002). Marketing essentials (3rd ed.) [pp. 211, 299, 505, 544]. Woodland Hills, CA: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill. 4. D Wholesaler. A wholesaler is a business that buys goods from producers or agents and sells them to retailers. Agents do not buy goods from producers; rather, they assist in selling and promoting a producer's goods. Producers are growers, providers, or manufacturers of goods or services. Retailers are businesses that buy consumer goods or services and sell them to the ultimate consumer. SOURCE: CM:003 SOURCE: CM LAP 1—Channel It (Channels of Distribution) 5. B Integrated data between channel members. The technology of electronic billing, purchase-order verification, bar coding, and image processing enable channel members to integrate data. Vertical and horizontal channel integration are methods of organizing distribution channels. The finance department may utilize the methods to share data, but the methods are not unique to that department. SOURCE: CM:004 SOURCE: Pride, W.M., & Ferrell, O.C. (2000). Marketing: Concepts and strategies (2000e) (pp. 355-356). Boston: Houghton Mifflin. Test 1021 MARKETING CLUSTER EXAM – KEY 11 6. B Horizontal. Horizontal conflict occurs between businesses at the same level in the distribution channel. Branch locations of a business that operate in the same community are on the same level. The branches may experience horizontal channel conflict because they are targeting, and competing for, the same customers. Vertical conflict occurs between different levels of the same channel, such as between the local branch and the corporate office. Community and dominant are not types of channel conflict. SOURCE: CM:008 SOURCE: Boone, L.E., & Kurtz, D.L. (2004). Contemporary marketing (11th ed.) [pp. 444-445]. Mason, OH: Thomson/South-Western. 7. A Marketing research. Marketing research usually focuses on a specific problem the business needs to solve. Information flow is the process of moving information through the appropriate channels or making information accessible to those who need it. A situation analysis is a determination of a firm's current business situation and the direction in which the business is headed. Marketing research gathers primary data rather than secondary data information collected for purposes other than the project at hand. SOURCE: IM:001 SOURCE: IM LAP 2—Get the Facts Straight (Marketing-Information Management) 8. C I don't want to know you. There are several situations in which nonverbal communication is a better indicator of a person's attitude than words. In this situation, Hank has made a polite verbal response, but he has indicated by refusing to shake hands that he is not glad to meet Jeremy and does not really want to know Jeremy. Even if they had met before, shaking hands would have been appropriate. SOURCE: CO:147 SOURCE: Locker, K.O. (2000). Business and administrative communication (5th ed.) [pp. 317-325]. Boston: Irwin/McGraw-Hill. 9. A Identify the firm or department and yourself. General guidelines for answering a business telephone include greeting the caller, identifying yourself and the business or department, and asking how you can be of assistance to the caller. It is not always necessary to get the correct spelling of the caller's name. Immediate action may also not be required. Callers should not be called by their first names unless they are personal acquaintances of the individual answering the telephone. SOURCE: CO:114 SOURCE: Clark, B., Sobel, J., & Basteri, C.G. (2006). Marketing dynamics (p. 681). Tinley Park, IL: Goodheart-Willcox. 10. D Few friends talking about football. If the group's purpose is to give and find out opinions, the way the group operates is casual. No real “rules” exist beyond the normal standards of common courtesy. When the football players toss the football or run laps during practice, they are likely to operate under the direction of the coach. In a similar way, selecting a strategy or play may require the football players to conduct a more formal group discussion. SOURCE: CO:053 SOURCE: QS LAP 29—Put In Your Two Cents 11. A Understands. Using the correct words in written communication is one way for businesspeople to make sure that the receiver understands the message. Correct and accurate language usage generally conveys the intended message and makes it easier for people to understand. Using the correct words will not necessarily ensure that the receiver accepts, agrees with, or approves of the message. SOURCE: CO:016 SOURCE: Locker, K.O. (2000). Business and administrative communication (5th ed.) [pp. 94-95]. Boston: Irwin/McGraw-Hill. Test 1021 MARKETING CLUSTER EXAM – KEY 12 12. C Yours truly. The complimentary close respectfully signals the end of a business letter. "Dear Occupant" and "To Whom It May Concern" are examples of impersonal salutations, which are greetings that do not use the receiver's name. The word "Enclosure" indicates that additional materials that have been referenced in the letter are in the envelope with the letter. SOURCE: CO:133 SOURCE: Locker, K.O. (2000). Business and administrative communication (5th ed.) [p. 588]. Boston: Irwin/McGraw-Hill. 13. A Credibility. The purpose of a persuasive message is to convey information that encourages the reader to take a specific course of action. Credibility is believability. A believable source demonstrates knowledge in a confident, trustworthy, and responsible manner. People are more likely to take action when they feel that the source is credible. Message receivers do not tend to take action if the source exhibits inconsistent behavior. A message receiver will first consider the source's credibility before it considers the source's adaptability. Objectivity is viewing things in an unbiased manner. Since the message sender is trying to get the message receiver to take a certain course of action, the message receiver has a specific opinion. Therefore, the message sender may exhibit some bias about the topic at hand. SOURCE: CO:031 SOURCE: Locker, K.O. (2000). Business and administrative communication (5th ed.) [p. 223]. Boston: Irwin/McGraw-Hill. 14. A Their immediate supervisor. Problems related to work should be discussed with the employee's immediate supervisor because this person should be the first to be told that a problem exists, and s/he should be given an opportunity to resolve it. The personnel department deals with problems connected to the hiring or firing of employees. Discussing problems with coworkers is often done but is not recommended. It is not part of the company president's job to deal with individual problems unless they cannot be solved by a subordinate. SOURCE: CO:014 SOURCE: Hilgert, R.R., & Leonard, E.C. (2001). Supervision: Concepts and practices of management (8th ed.) [pp. 584-591]. Cincinnati: South-Western College Publishing. 15. A Use customer names in conversations. Customers enjoy hearing their names, and they feel important when they realize employees have taken the time to learn them. You should maintain eye contact, not stare. You should speak at a comfortable volume—not too loudly or too softly. You should try, whenever possible, to resolve customers' problems without involving a supervisor. SOURCE: CR:004 SOURCE: CCJ Business Consulting. (2007). Fifteen smart ways you can start building customer loyalty today! Retrieved September 2, 2009, from http://www.ccjconsulting.com/files/CCJ_Business_Consulting_FREE_REPORT_07__15_Smart_Ways_You_Can_Start_Building_Customer_Loyalty_Today.pdf 16. B Employee. Businesses have policies that explain how employees are to act and how they are to deal with customers. Some of these policies include rules about eating and smoking on the job. Businesses make these policies to present a certain image to customers. Service policies are established to provide special features that other, similar businesses may not offer in order to persuade customers to choose their business over another. Some policies affect customers directly, such as guidelines for offering credit. A product policy is a guideline affecting the kinds of goods and services that businesses offer to customers. SOURCE: CR:007 SOURCE: International Customer Management Institute (2009). Food in the call center. Retrieved September 25, 2009, from http://www.icmi.com/knowledgecenter/queuetips/viewQuestion.aspx?id=2798 Test 1021 MARKETING CLUSTER EXAM – KEY 13 17. D Show a large selection of products. Slow/Methodical, or analytical, customers require a lot of time in making buying decisions. They want to know everything about a product so that they make the best decision. In addition, they do not buy immediately. They want time to think about and research the product. Therefore, you should avoid showing them too many products, as this will only compound their problem in reaching buying decisions. The other alternatives are guidelines for helping slow/methodical, or analytical, customers. SOURCE: CR:009 SOURCE: Tod Novak. (2009, January 26). Selling and motivating the analytical client: The Owl 1. Retrieved September 3, 2009, from http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BMaiYEATTpI 18. D Possession. Possession utility is created when the ownership of a product is transferred from the seller to the customer. Credit plans allow customers to pay for their purchases gradually, thereby increasing their ability to own (possess) more products. Place utility involves making goods and services available at the place (location) they are wanted or needed by customers. Form utility occurs when the shape or form of a product is altered to make it more useful to the customer. Price is a component of the marketing mix but is not a type of economic utility. SOURCE: EC:004 SOURCE: EC LAP 13—Use It (Economic Utility) 19. B Increase. Since the holidays usually bring people in need of ski equipment, this situation should create a seller's market in which buyers will be willing to pay higher prices to buy what they need. Prices usually increase in a seller's market instead of decreasing, remaining the same, or fluctuating. SOURCE: EC:005 SOURCE: EC LAP 11—It's the Law (Supply and Demand) 20. C Matrix. Businesses can structure the way they do their work in a variety of ways. The matrix organizational structure uses horizontal authority to integrate departmental functions with product orientation. For example, an engineer, a marketing specialist, a financial coordinator, and a manufacturing employee are members of different departments but often work together to develop or refine one product. The advantage to businesses using this organizational structure is that the business is applying its resources efficiently because a representative from each of the major departments is knowledgeable about various aspects of the product. Vertex, regional, and regulated are not terms that describe types of business organizational structures. SOURCE: EC:103 SOURCE: Gibson, J.L., Ivancevich, J.M., Donnelly, J.H., & Konopaske, R. (2003). Organizations: Behavior, structure, processes (11th ed.) [p. 385]. Boston: Irwin/McGraw-Hill. 21. A Profit. If the company can create demand in a new market segment, this will help to increase sales, which will increase profits. Increasing expenses will decrease profits. Increasing prices could decrease sales. Increasing output may be needed to meet the needs of the new market, but that is not the company's ultimate goal. SOURCE: EC:010 SOURCE: EC LAP 2—Risk Rewarded Test 1021 MARKETING CLUSTER EXAM – KEY 14 22. B Oligopoly. An oligopoly is a market structure in which there are relatively few sellers, and industry leaders usually determine the prices. Because an oligopoly has interdependent multiple sellers, product prices are usually stable. A monopoly is a condition in which a market is controlled by one supplier or single seller, and there are no substitute goods or services readily available. A technical monopoly is a type of monopoly in which the seller controls the market with one or more technical products. Differentiated oligopoly is a fictitious term. SOURCE: EC:012 SOURCE: Miller, R.L. (2005). Economics: Today and tomorrow (pp. 240-244). New York: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill. 23. B It's easier to train workers. For example, it is easier to train workers to specialize in sewing on shirt collars than to train them to perform all the tasks necessary to sew, iron, and package the finished shirts. The dependency of workers upon each other is a disadvantage. Job obsolescence is a disadvantage to workers. Management uses job rotation to overcome some of the disadvantages of specialization. SOURCE: EC:014 SOURCE: Division of labor. (2009, September 1). Retrieved September 3, 2009, from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Division_of_labour#Types_of_Specialization 24. C Peak. Peak is the phase of the business cycle when economic prosperity reaches a high point, and the demand for goods and services begins to exceed the production capacities of producers. Expansion is the beginning of growth in economic activity. Contraction occurs when the economy declines. Consumers spend less and save more, and economic activities decline. During trough, economic activities are at their lowest level. SOURCE: EC:018 SOURCE: Pride, W. M., Hughes, R. J., & Kapoor, J. R. (2008). Business (9th ed.) [pp. 19-20]. Boston: Houghton Mifflin. 25. B Subcultures. A subculture is a group with distinguishing characteristics that exists within a culture. The customs, habits, and traditions of businesspeople are considered to be a business subculture. The businesspeople in different countries have different business subcultures, which means that the businesspeople from one country share certain beliefs, values, and ideals that are different from those of people in other countries. The way they behave in business is based on those beliefs and values. Therefore, in order to trade successfully throughout the world, businesspeople need to understand what is acceptable business behavior in other countries. Business policies, activities, and contracts differ from one business to another and do not have a significant impact on business behavior. SOURCE: EC:045 SOURCE: Ball, D.A., McCulloch, W.H., Frantz, P.L., Geringer, J.M., & Minor, M.S. (2006). International business: The challenge of global competition (10th ed.) [pp. 418-419]. Boston: McGrawHill/Irwin. 26. A Job advancement. Employees with initiative seek to further their education/training to prepare themselves for career advancement. In many fields, supplemental preparation has become a prerequisite for promotion. Lateral job changes would not require advanced education. Many professional organizations offer advanced education for their members; however, that is not a membership requirement. Certifications are obtained to secure a job or advance in careers. SOURCE: EI:024 SOURCE: EI LAP 2—Hustle! (Taking Initiative at Work) Test 1021 MARKETING CLUSTER EXAM – KEY 15 27. B Responsibility. Responsible individuals are accountable for things that are within their control. Initiative is the ability and willingness to think or act without being told. Interpersonal skills are how a person gets along with others. Consideration means showing kindness or thoughtfulness to others. SOURCE: EI:021 SOURCE: PD LAP 7—Make the Honor Role (Acting Responsibly) 28. D Increased chances of success. A positive attitude means looking on the bright side of things. Expecting good things to happen is one way of increasing one's chances of success in life. People who have positive attitudes are more likely to achieve their goals. A positive attitude can help to reduce selfconsciousness and improve the ability to develop satisfactory relationships. Positive people are also more likely to be promoted. SOURCE: EI:019 SOURCE: EI LAP 3—Opt for Optimism 29. D Negative feedback expresses disapproval about a specific behavior. Negative feedback is defined as criticism or disapproval. The purpose of negative feedback is to change or improve the message receiver's behavior, rather than reinforce an existing attitude or behavior. Although negative feedback can embarrass the message receiver, its purpose is to help the message receiver improve or change a particular attitude or behavior. Negative feedback addresses a person's weaknesses, while positive feedback communicates information about his/her strengths. SOURCE: EI:003 SOURCE: EI LAP 15—Grin and Bear It (Using Feedback for Personal Growth) 30. A Personal credibility. Credibility is believability. When you are credible, others believe what you say. If people get in the habit of believing you, they are more likely to be persuaded to agree with you or follow your lead. Nonverbal, or body, language includes gestures, facial expressions, and any other way of communicating without the use of words. Creativity is the ability to generate unique ideas, goods, or services. Speaking skills involve the ability to communicate clearly with words. Although nonverbal language, creativity, and speaking skills may help you to persuade others, they will not necessarily make others believe what you say. SOURCE: EI:012 SOURCE: QS LAP 10—Win Them Over 31. C Standing up straight when talking to other people. Posture is the way in which you hold your body. Other ways you can use posture to express assertiveness include leaning toward the speaker to show your interest in what is being said or crossing your arms across your chest to indicate a negative response to what is being said. Explaining why you must refuse a request for help is an example of verbal assertiveness. Raising your eyebrows and frowning are facial expressions used in nonverbal assertiveness. SOURCE: EI:008 SOURCE: EI LAP 18—Assert Yourself (Assertiveness) 32. B Avoidance. The ways that people react to conflict are called conflict response modes. One of these modes is avoidance, which is the effort to avoid conflict. This type of behavior might include ignoring the situation or pretending that it doesn't exist. Avoidance behavior will not resolve conflict. Frustration is a negative effect of conflict rather than a response mode. Mediation is a method of resolving conflict. Exclusion is feeling left out or excluded from an activity. SOURCE: EI:015 SOURCE: EI LAP 7—Stop the Madness (Conflict Resolution in Business) Test 1021 MARKETING CLUSTER EXAM – KEY 16 33. D Not afraid to “go for it.” Instead of sitting back with the rest of the class and complaining about the unfair grading scale, Tim decides to take action. He is not afraid to “go for it.” Change leaders are people of action. They're not satisfied with sitting on the sidelines. They stand up for what they believe in and aren't afraid to challenge the status quo (the way things exist right now). Change leaders are also persuasive, love to learn new things, and know how to coach others, but these are not the characteristics Tim displays in this situation. SOURCE: EI:005 SOURCE: QS LAP 23—20/20 Foresight 34. B Cultures. The cultures of ethnic groups from all parts of the world are the customs, habits, and traditions that have been developed over time. Many people whose ancestors are from other countries retain their cultures and celebrate different holidays. The United States has one government that is a democracy which includes many different courts; but these were established to carry out different kinds of legal functions, not because U.S. citizens are from all over the world. Sanctions are trade restrictions placed by one country against another country that is violating international law. SOURCE: EI:036 SOURCE: HR LAP 24—Treating Others Fairly at Work 35. B Truth-in-Lending Act. The Truth-in-Lending Act requires businesses to provide credit customers with all the information that applies to their accounts and send customers regular updated statements showing the status of their accounts. The purpose of the Equal Credit Opportunity Act is to make the granting of credit fair by prohibiting the denial of credit based on the applicant's gender, race, age, marital status, or national origin. The Fair Credit Billing Act requires businesses which extend credit to respond within 30 days to any customer's complaint or inquiry about a billing error. The Fair Credit Reporting Act gives consumers the right to inspect the files of their credit history at any credit agency and to have any mistakes corrected. SOURCE: FI:002 SOURCE: Washoe Legal Services. (2002). Consumer law: Truth in Lending: What you must be told when getting a consumer loan or other consumer credit. Retrieved September 3, 2009, from http://www.washoelegalservices.org/truth.htm 36. C The first step in creating a financial plan. Knowing how you spend your money—understanding your spending habits—is the first step in creating a financial plan. Knowing your spending habits does not guarantee that you will exceed your financial goals. Although it's helpful to know how many checks you expect to write in a month, you don't need to understand your spending habits to open a bank account. SOURCE: FI:065 SOURCE: QS LAP 31—Set Yourself Up (Setting Financial Goals) 37. A A guest trips on loose carpet in the hallway and sprains an ankle. The theater is responsible for making sure the facility is safe and free of obstacles; therefore, it would be liable for damages. A car damaged in a parking lot owned by the city would not be the theater's responsibility. Complaining about someone blocking one's view would not bring about damage relief. The drink being spilled was an accident and is between the individuals involved. SOURCE: FI:084 SOURCE: Kaser, K., & Oelkers, D.B. (2001). Sports and entertainment marketing (p. 273). Mason, OH: South-Western. Test 1021 MARKETING CLUSTER EXAM – KEY 17 38. B Allocate their funds. Managers use the accounting information that tells them the amount of funds available in order to develop operating budgets. These budgets specify how much money may be spent for such expenses as rent, salaries, insurance, etc. Insurance premiums are the monies paid to cover a contractual agreement in which one party will pay for specified losses incurred by the other party. Excise taxes are determined by government. They apply to certain items, such as gasoline, and are paid by the buyer. Labor union dues are paid by the union members. SOURCE: FI:085 SOURCE: FI LAP 5—Show Me the Money (Nature of Accounting) 39. B Assets. Business owners must spend money to obtain assets, which are anything of value that the business owns. This results in money flowing out of a business. Some examples of business assets include land, buildings, vehicles, and equipment. Supplies are industrial goods that are constantly being purchased and used up in the operation of a business. Products are goods and services. Staples are goods for which there is constant demand. SOURCE: FI:091 SOURCE: FI LAP 6—Count the Cash (Cash Flow) 40. D Cost of goods sold. Cost of goods sold includes all costs used in obtaining or producing the goods or services that a business sells, such as materials and supplies. Operating expenses are all other expenses in operating the business such as wages, advertising, insurance, rent, and utilities expenses. Gross profit is revenue minus cost of goods sold. Revenue is the total amount of money earned by a business. SOURCE: FI:094 SOURCE: FI LAP 4—Watch Your Bottom Line (Income Statements) 41. C Return on capital. Return on capital is a measure of how well a business generates cash flow. It is a key component of managing working capital. Accounts receivable refers to money owed to the business by others. Capital structure refers to a business's mix of financing. Accounts payable refers to the money the business owes to others. SOURCE: FI:354 SOURCE: FI LAP 7—Money Matters (Role of Finance) 42. C Can change to meet a manager's needs. The format of a particular budget report can change to meet a manager's needs. Depending on what the manager wants to know, s/he may need to see only the current budget, the current budget and past budgets, or budgeted and actual figures. The format, then, is not standardized and can change. It is flexible and is very important in providing a manager with just the right information. Formats are not necessarily unique to each department and manager. SOURCE: FI:106 SOURCE: FI LAP 3—Money Tracks 43. B Determining eligibility and costs of benefits. A human resources manager might be involved in employee benefits by developing a benefits plan and determining eligibility and costs for employees. An HR manager would not be responsible for selecting an employee's personal plan options, collecting insurance payments from employees, or choosing an employee's vacation days. SOURCE: HR:410 SOURCE: HR LAP 35—People Pusher (Nature of Human Resources Management) Test 1021 MARKETING CLUSTER EXAM – KEY 18 44. C Quantity. The wholesaler is reducing a discrepancy of quantity by breaking down a large quantity of a product into smaller quantities for retailers to buy and sell to final customers. Reducing a discrepancy of assortment means making a variety of related products available in one place. There is no such thing as a discrepancy of installation or a discrepancy of promotion. SOURCE: CM:001 SOURCE: CM LAP 2—Chart Your Channels (Channel Management) 45. B Acknowledge directions verbally or nonverbally. When Justin gives his sister a puzzled look so she knows he didn't understand her directions clearly, he is acknowledging her nonverbally. It's important to let the speaker know you hear and understand what s/he is saying by nodding your head or saying you understand. If you don't understand the directions, use your nonverbal signals to alert the person so s/he can clarify things for you. These signals include raising your hand, shaking your head, or even looking at the speaker with a puzzled look. In this situation, Justin is not taking notes, accepting responsibility, or eliminating distractions. SOURCE: CO:119 SOURCE: QS LAP 24—Simon Says 46. B Cookies. Cookies are text files that are put on a web-site visitor's hard drive and then later retrieved during subsequent visits to the site in order to track shopping and buying behavior. As a result, Internet users often feel that their right to privacy is compromised. Portals are sites that are popular starting points for surfing the Web. Scan portal is not a term that is widely used to describe activities and concepts related to the Internet. A browser is the software that is needed for surfing the Internet. Banner ads are promotional messages appearing on the WWW, usually at the top of the web sites. SOURCE: IM:025 SOURCE: Churchill, G. (2001). Basic marketing research (4th ed.) [p. 55]. Mason, OH: South-Western. 47. A Build strong, loyal customer relationships. When a business understands what its customers like and dislike about its goods and services, it can incorporate activities to maintain, improve, or expand its products. When customers see that the business is showing interest in meeting their needs and wants, they are more likely to continue the relationship with the business. A business's tax deductions are not generally based on its ability to track its customers' buying behavior. Operational expenses refer to all of the expenses (costs) of running the business. A database can facilitate efficient use of a business's resources, but does not necessarily reduce operating expenses, nor does it necessarily decrease the need for personnel to analyze marketing activities. SOURCE: IM:183 SOURCE: Semenik, R.J. (2002). Promotion and integrated marketing communications (p. 355). Mason, OH: South-Western. 48. C Watching what consumers do. Observation is a marketing-research method that gathers data by watching consumers. This can be carried out by using cameras, by assigning people to watch consumers' actions, or by using scanners that record what consumers buy. Test marketing new products is part of the experiment method of collecting data. Calling consumers on the telephone and surveying consumers by mail are part of the survey method of collecting data. SOURCE: IM:010 SOURCE: Khazanchi, D. (n.d.). Data collection methods: Observation studies. Retrieved September 4, 2009, from http://www.isqa.unomaha.edu/dkhazanchi/teaching/isqa8060/slides/274,4,Observation Test 1021 MARKETING CLUSTER EXAM – KEY 19 49. B Primary market research. Concept testing involves exploring the concept, or idea, for a product in order to obtain feedback. Concept testing is one way to conduct primary market research, which results in obtaining new information specifically for the project at hand. The benefit of conducting primary market research is that it provides information that is relevant to the concept being tested. Other ways to conduct primary market research include analyzing focus groups, evaluating readership, and pretesting. SOURCE: IM:281 SOURCE: Lane, W.R., King, K.W., & Russell, J.T. (2005). Kleppner's advertising procedure (16th ed.) [pp. 468-469]. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson/Prentice Hall. 50. A Objectives. There is a strong relationship between the research purpose and the research objectives which are the goals of the research. Businesses create research objectives to help answer the research problem. For example, if the problem is service, one objective might be to determine customer satisfaction with delivery. Strategies are plans of action, or activities, for achieving goals and objectives. A procedure is the step-by-step process personnel follow in performing a specific task. SOURCE: IM:284 SOURCE: Farese, L.S., Kimbrell, G., & Woloszyk, C.A. (2006). Marketing essentials (p. 612). New York: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill. 51. C To revise its marketing strategy. Businesses monitor lost-business reports because they usually contain an explanation of why customers no longer buy from the business. The reports might indicate that customers are dissatisfied with the product, dissatisfied with the business's credit policies, or are getting better prices and more service from competitors. A business might use this information to make changes to its marketing strategy in an attempt to regain customers or to prevent other customers from taking their business elsewhere. The more information a business obtains from lost-business reports, the better able it is to make useful and effective marketing decisions. Businesses do not use the information in lostbusiness reports to change their operating goals, identify their target markets, or update their promotional techniques. SOURCE: IM:184 SOURCE: Kotler, P. (2000). Marketing management (10th ed.) [pp. 47, 633-634]. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall. 52. D Each answer has a specific numeric value. Businesses often develop surveys to obtain marketing information. To process and analyze that information, businesses often develop a code for the answers to survey questions. Coding is the process of assigning a numeric value to the various responses on a marketing questionnaire or survey. For example, there are five possible answers to a question, and the first answer has a numeric value of one. The second answer has a numeric value of two, the third answer has a numeric value of three, and so on. By using a code, businesses can quickly process the results to determine which response is selected the most or the least. Coding does not involve numbering questions in chronological order, or tabulating results according to date received. Although each survey may contain a unique identification number, that is not an example of coding. SOURCE: IM:062 SOURCE: Hair, J.F., Jr., Bush, R.P., & Ortinau, D.J. (2000). Marketing research: A practical approach for the new millennium (pp. 482-491). Boston: Irwin/McGraw-Hill. 53. C Concise and objective. A questionnaire is a set of written questions designed to gather information. So that a business can obtain the most reliable information possible, questionnaire developers should make sure that the questionnaire is clear, concise, and objective, or free of bias. If the questionnaire is designed in a way that it is ambiguous (vague), complex, or adaptable, the business risks not obtaining reliable data. SOURCE: IM:293 SOURCE: Shao, A. (2002). Marketing research: An aid to decision making (2nd ed.) [p. 275]. Mason, OH: South-Western. Test 1021 MARKETING CLUSTER EXAM – KEY 20 54. D Marketing concept. The marketing concept is based on satisfying the needs and wants of customers. By reordering a discontinued product, businesses are satisfying their customers' requests. The production process is the activity of producing goods and services. The promotional mix is the combination of communication channels a business uses. The promotional-mix concept does not result from providing previously discontinued products. Distribution involves moving, storing, locating, and/or transferring ownership of goods and services. SOURCE: MK:001 SOURCE: BA LAP 11—Have It Your Way! (Marketing) 55. A Plan of action. Businesses determine a plan of action for achieving their goals and objectives. This plan of action in marketing is known as a marketing strategy. In this example, the goal is to increase profitability, and the plan for achieving that goal is to open a new location. Marketing mix is the combination of the four elements of marketing. Although risk is involved with every plan of action, the plan of action is not a type of risk. Financial planning involves developing budgets, which includes predicting the company's sales and expenses for a specific period. SOURCE: MP:001 SOURCE: IM LAP 7—Pick the Mix (Marketing Strategies) 56. B The population of a town increases when a new hospital opens in the community. External changes occur outside the business, and the business has no control over these changes. Examples of external changes that may affect sales forecasts are population changes, economic changes, competitive changes, and market changes. Internal changes, on the other hand, are circumstances that occur within a business over which the business has some degree of control. Such factors would include changes in personnel, promotion, and pricing. SOURCE: MP:013 SOURCE: Fastlinksolutions. (n.d.). Sales forcasting: Factors that influence sales. Retrieved April 17, 2009, from http://www.fastlinksolutions.co.uk/calculat.htm#factors 57. A Identity. Managing information regarding copyrights and trademarks helps a company to preserve its identity. If a competitor tries to infringe upon this protected material, the company will be ready to stake its claim quickly. Copyrights and trademarks do not necessarily relate to inventory, correspondence, or customers. SOURCE: NF:110 SOURCE: NF LAP 3—In the Know (Nature of Information Management) 58. C Worldwide. The Internet is a worldwide network of computers that enables users to access information and communicate with others. Its scope is worldwide rather than regional because it is available to anyone who has access to a computer that has connectivity. Certain elements of the Internet are secure; however, that does not affect the scope. The Internet is not proprietary. SOURCE: NF:086 SOURCE: Farese, L.S., Kimbrell, G., & Woloszyk, C.A. (2006). Marketing essentials (p. 208). New York: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill. 59. A Transition. The transition tool provides a variety of ways for slides to move smoothly from one to the next. The effects tool is used to determine how the text or graphics will appear within the slide. Animation is the overall term for creating movement in the presentation. Formatting is the tool for creating the overall look of the presentation. SOURCE: NF:008 SOURCE: FYI Center. (n.d.). What are slide transition effects? Retrieved September 24, 2009, from http://windows.fyicenter.com/888_Tools_PowerPoint_What_Are_Slide_Transition_Effects.ht ml Test 1021 MARKETING CLUSTER EXAM – KEY 21 60. D Spreadsheet. Businesses use spreadsheet software to perform mathematical calculations quickly and accurately. One of the advantages of using spreadsheet software is that it is possible to do "what if" calculations. For example, a business might enter different rates to determine the effect that those rates would have on profit. The business can experiment with different rates before deciding which rate will be most appealing to customers and still generate the desired profit. Database software is used to arrange and sort information. Desktop publishing and presentation software are used for visual presentations. SOURCE: NF:010 SOURCE: Eggland, S.A., Dlabay, L.R., Burrow, J.L., & Ristau, R.A. (2000). Intro to business (4th ed.) [pp. 214-216]. Cincinnati: South-Western Educational. 61. A Regulations. When a law affects the records a business keeps, a regulatory factor is influencing the selection of records. Business size may also affect the selection of records, but it is not represented in this example. Leaders and the industry in which the business is involved may or may not affect the selection of records. Leaders and the industry can influence the laws that are introduced, however. SOURCE: NF:001 SOURCE: NF LAP 1—Record It (Business Records) 62. D Invoices. An invoice is a formal, printed record of a sale that includes all necessary information as to the buyer, the seller, items purchased, amounts, prices, delivery date, and credit or discount terms. Invoices can help a business track customer purchasing habits so it can plan future business activities. Tax returns are formal documents that are completed and returned to the government. Payroll reports contain data about employees' salaries and payment schedules. Expense reports contain information about the money sales personnel spend on behalf of the company to obtain or service its customers. SOURCE: NF:002 SOURCE: Burrow, J.L. (2006). Marketing (2nd ed.) [pp. 120-121]. Mason, OH: South-Western. 63. A Demographic. Demographic trends refer to the physical and social characteristics of a population. Where people live and their ethnic backgrounds are demographic characteristics. For example, there is a growing trend towards urbanization, which means that more and more people are living in cities rather than in rural areas. Also, the population of many areas is becoming more multicultural, or made up of many different ethnic groups. Businesses consider demographic trends because they realize that changes in the population have an effect on how they market their goods and services to customers. Although where customers live may affect the environment, it's not an environmental trend. Likewise, where customers live can affect their access to technology; however, it is not a technical trend. Cultural trends would involve long-term changes to people's values and beliefs. They do not relate to the ages of people. SOURCE: NF:013 SOURCE: Zikmund, W., & d'Amico, M. (2001). Marketing: Creating and keeping customers in an e-commerce world (7th ed.) [p. 67]. Mason, OH: South-Western. 64. D Computer-aided design. Computer-aided design is very useful in operations. Designing and testing products in the virtual world before trying them out in the real world can save companies a lot of time and money. Using computer software, a company can design, test, and redesign a product many times over until it's ready for production—all without wasting unnecessary resources. While wireless Internet, e-mail, and smart phones might also be useful in operations, computer-aided design stands out as the most useful and specific technology to enhance this business function. SOURCE: OP:189 SOURCE: OP LAP 3—Smooth Operations (Nature of Operations) Test 1021 MARKETING CLUSTER EXAM – KEY 22 65. D Improper lifting. Many people hurt their backs because they have not learned proper lifting techniques. They lift a load that is too heavy, stand too far from the load, or use their back and arms to do the lifting. Poor posture and sitting in one position may cause some problems, but are not common causes of back injuries. Hard physical labor does not necessarily cause back injuries. SOURCE: OP:007 SOURCE: Demby, G. (2005, May 24). Provide basic lifting instructions to prevent back injuries. Retrieved September 4, 2009, from http://www.safetyxchange.org/health-safety/providebasic-lifting-instructions-to-prevent-back-injuries 66. D Who is doing what. Project-planning tools show you what has to be done and when, who is responsible for doing it, and how the work will be monitored. Project-planning tools do not show how pleased the stakeholders are, why you want to complete the project, or when you will do a similar project. SOURCE: OP:001 SOURCE: QS LAP 28—From Here to Done 67. C Lowers costs. An important benefit of effective purchasing is that it helps businesses to keep their costs down. A business's purchasing department tries to lower costs by buying quality goods at the lowest possible price, by buying only the quantity of goods that is needed, and by making sure the goods are delivered when needed for use or for resale. Effective purchasing does not create jobs, increase assets, or reduce sales. SOURCE: OP:015 SOURCE: OP LAP 2—Buy Right (Nature of Purchasing) 68. D Turns resources into products. Production is the process or activity of producing goods or services wanted by consumers. Production takes the business's resources (inputs) and turns them into salable products (outputs). If the products produced make a profit for the business, this could change business failure to success, but that is not the reason production is called a conversion process. Product utility is usefulness or the capability of satisfying consumers' needs, which is a desirable result of the production process. SOURCE: OP:017 SOURCE: Tutor2u.com (n.d.). Introduction to production and operations management. Retrieved September 4, 2009, from http://tutor2u.net/business/production/pom_introduction.htm 69. D Arriving at work on time. Employees should arrive on time because the business pays them to work a specific amount of time. Rotating stock helps to keep merchandise fresh and appealing to customers, but daily rotation would increase expenses because of the time it would take. Employees should also help to control expenses by handling products carefully to prevent damage and by being on the lookout for thefts by customers or other employees. SOURCE: OP:025 SOURCE: Bailey, L.J. (2003). Working: Career success for the 21st century (3rd ed.) [p. 96]. Mason, OH: South-Western. 70. B To eliminate health hazards. Many products, particularly drug and food products, have expiration dates printed on their packages. These dates indicate the times after which the products should not be sold or used. It is important for businesses to routinely discard products whose expiration dates have expired to avoid using or selling items that are potential health hazards. If these products are spoiled or otherwise contaminated, the people who buy and use them may experience health problems. Businesses do not discard expired products to prevent cross-contamination, obtain replacement items, or follow federal guidelines. SOURCE: OP:032 SOURCE: Mill, R.C. (2001). Restaurant management: Customers, operations, and employees (2nd ed.) [pp. 217, 219]. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall. Test 1021 MARKETING CLUSTER EXAM – KEY 23 71. A Dandruff free. Dandruff is a scaly condition of the scalp, and some of the scales usually fall on an individual's shoulders. Preventing or controlling dandruff is important because this scattering of white scales detracts from an individual's personal appearance. Whether the hair is curled, tinted, or cut short would be a matter of personal preference. SOURCE: PD:002 SOURCE: PD LAP 13—Brand ME! (Personal Appearance) 72. C Brainstorming. Brainstorming is often used in a group setting to create as many ideas as possible in a limited time. A checklist is a prepared list that can be used in a variety of situations. Attribute listing is a listing of things that already exist, then considering the items as a source of change or improvement. Problem identification pinpoints a situation or circumstance that presents a problem. SOURCE: PD:012 SOURCE: PD LAP 2—Creativity 73. C Self-management. The ability to control one's own activities, behaviors, and attitudes in the workplace is often referred to as self-management. Employees who make a conscious effort to get to work on time each day are engaging in positive self-management skills. Other activities that employees can control in the workplace might include their ability to perform and produce quality work in a given time, willingness to learn new activities, level of flexibility, and degree of workplace socializing. Self-concept refers to how one views him/herself. Inner-qualitative and personal-orientation are not terms frequently used to describe self-control issues as they relate to the workplace. SOURCE: PD:020 SOURCE: Ludden, L. (2003). Job savvy: How to be a success at work (3rd ed.) [pp. 97-98]. Indianapolis, IN: JIST Publishing, Inc. 74. D Neighborhood businesses. Local companies where teenagers and their families do business often are good sources for first jobs. Local businesses, such as grocery stores and independent retailers, often hire teenagers on a part-time basis to work after school hours, on weekends, and during summer vacations. These businesses frequently are willing to hire the teenagers who are members of their community. Most employment agencies do not work with people looking for entry-level jobs. Teenagers usually don't find their first jobs with national corporations unless those corporations have local offices. Community training programs are intended to help train teenagers for jobs. SOURCE: PD:026 SOURCE: Bailey, L.J. (2003). Working: Career success for the 21st century (3rd ed.) [pp. 33-35]. Mason, OH: South-Western. 75. D From one to two pages. The preferred length of a résumé is one page or two pages if absolutely necessary. The most effective résumés stress the high points of the applicant's qualifications in a brief format. People who are responsible for reading the résumés do not want to spend a great amount of time trying to find out if the applicant is qualified for the position. Therefore, résumés should never be three or five pages in length. Applicants should be able to condense their experiences into a brief format and not write résumés that are as long as necessary. SOURCE: PD:031 SOURCE: Bailey, L.J. (2003). Working: Career success for the 21st century (3rd ed.) [pp. 49-51]. Mason, OH: South-Western. Test 1021 MARKETING CLUSTER EXAM – KEY 24 76. B To be able to promote from within. Many businesses prefer to promote from within whenever possible and help current employees move up the career ladder. To do this, businesses often provide opportunities for their employees to continue their education or receive additional training. As a result, they have a pool of qualified employees to choose from when higher-level jobs become available. This benefits the employees because they can advance within the business. Businesses often provide financial assistance, such as tuition reimbursement, to help employees continue their education. However, that is not the reason for providing the additional training. Businesses do not provide educational opportunities to identify problems in the company or to support the local community college. SOURCE: PD:033 SOURCE: Bailey, L.J. (2003). Working: Career success for the 21st century (3rd ed.) [pp. 480-481]. Mason, OH: South-Western. 77. B Promotion. Promotion involves getting customers to want to buy a good or service. Pricing involves determining the price at which sellers are willing to sell and buyers are willing to buy. Place involves determining where to sell products and which transportation channel to use. Product planning decisions involve the use of market research in determining product mix. SOURCE: PI:001 SOURCE: PI LAP 2—The Price is Right (Nature of Pricing) 78. A Easier to change prices. Bar codes that include price information can be scanned into a register terminal where the price is read and recorded. When a business needs to change a price, such as to offer a sale price, an employee can enter the change into the scanning system computer, and the change is made for every item. This is a faster and more economical method than manually changing prices on every item. Customers will need a scanning device to read the price. There are seldom changes in the number of security personnel or employees based on the use of bar-code pricing techniques. SOURCE: PI:016 SOURCE: Etzel, M.J., Walker, B.J., & Stanton, W.J. (2001). Marketing (12th ed.) [p. 383]. New York: Irwin/McGraw-Hill. 79. B Concept testing. During concept testing, a product concept, or idea, is explored with potential customers to determine what response they would give to a proposed product idea. Idea generation is the step of new-product development in which ideas for new products are developed. Product screening involves considering each idea for a new product and discarding ideas that seem unworkable. A feasibility analysis is the step in the new-product development process that involves examining such factors as demand, costs, competition, capital investment required, and potential profit of a product to determine how it will fit into the company's product mix. SOURCE: PM:001 SOURCE: PM LAP 17—Rapping Up Products (Nature of Product/Service Management) Test 1021 MARKETING CLUSTER EXAM – KEY 25 80. A Product/service management. Product/Service management is a marketing function that involves understanding the concepts and processes needed to obtain, develop, maintain, and improve a product or service mix in response to market opportunities. An important part of product/service management involves maintaining and improving the product or service because customers expect a quality product or service that keeps up with advances in technology. Satellite communications systems make it possible for businesses to track shipments from the time they are ordered until they are delivered to customers, thereby improving the product or service. Marketing-information management is a marketing function that involves understanding the concepts, systems, and tools needed to gather, access, synthesize, evaluate, and disseminate information for use in making business decisions. Transportation and receiving are distribution activities. Selling is a marketing function that involves determining client needs and wants, and responding through planned, personalized communication that influences purchase decisions and enhances future business opportunities. Promotion is a marketing function that involves communicating information about goods, services, images, and/or ideas to achieve a desired outcome. SOURCE: PM:039 SOURCE: Zikmund, W., & d'Amico, M. (2001). Marketing: Creating and keeping customers in an e-commerce world (7th ed.) [pp. 124-125]. Mason, OH: South-Western. 81. B It enables consumers to buy without having to inspect each product. The use of grades and standards speeds up the buying and selling process because consumers can buy without having to inspect each product. It also furnishes information that salespeople can use to justify price, to sell benefits, and to meet customer needs. The use of grades and standards enables salespeople to recommend products that best meet customer needs. Although grades and standards provide product information, they do not address unsafe products. Unsafe products should not be offered since they are a business liability. Product prices will vary based on the product's grade. Therefore, the prices will not necessarily be high. SOURCE: PM:019 SOURCE: British Standards Institute. (2009). What are the benefits of standards. Retrieved September 16, 2009, from http://www.bsi-global.com/en/Standards-and-Publications/Aboutstandards/What-are-the-benefits-of-standards/ 82. B Implied. An implied warranty is simply understood by both the marketer and the customer that the product will perform as expected. It is neither written nor spoken. An express warranty is one that is written or expressed verbally. A full warranty is one which covers the entire product. A limited warranty is one that covers only specific parts or certain repairs. SOURCE: PM:020 SOURCE: The Free Dictionary. (2009). Implied warranty. Retrieved September 4, 2009, from http://legal-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/Implied+Warranty 83. D Magnuson-Moss Warranty Act. Since the Finetunes had their digital camera for a short time when the fire occurred, the manufacturer is required to make it as easy as possible for customers to use their warranty. The Magnuson-Moss Warranty Act regulates warranties offered by businesses, requiring them to provide more and better warranties. The Consumer Product Safety Act formed the Consumer Product Safety Commission which was given jurisdiction over the safety of consumer products. The Fair Packaging and Labeling Act is a federal law requiring specific information about products and producers to be provided on a product's package or label. The Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act bans the production, transportation, and sale of misbranded or adulterated foods, drugs, cosmetics, and medical devices. SOURCE: PM:017 SOURCE: The Federal Trade Commission. (2008, October 28). A businessperson's guide to federal warranty law. Retrieved September 4, 2009, from http://www.ftc.gov/bcp/edu/pubs/business/adv/bus01.shtm#Magnuson-Moss Test 1021 MARKETING CLUSTER EXAM – KEY 26 84. C Mix. Product mix is the particular assortment of products that a business offers in order to meet its market's needs and its company's goals. Product line is a group of related products. Product differentiation is developing and promoting differences between one firm's product and similar products. Consistency is a product mix dimension that refers to how closely a firm's products are related in terms of their end use, methods of distribution and production, target market(s), and/or price range. SOURCE: PM:003 SOURCE: PM LAP 3—Mix & Match (Nature of Product Mix) 85. C Bundling. Mixed product bundling is the practice of packaging different products together. Businesses price the packages so that customers pay less for bundled items than they do if they purchase each item separately. Blending, integration, and consolidation are not terms commonly used to describe the practice of packaging products together. SOURCE: PM:041 SOURCE: Farese, L.S., Kimbrell, G., & Woloszyk, C.A. (2002). Marketing essentials (3rd ed.) [p. 604]. Woodland Hills, CA: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill. 86. B Determine if the brand name would be culturally taboo where the product will be marketed. If a brand is to be marketed in different cultures, it is important to make sure that the brand name would be acceptable in these areas of the world. A brand name that would be culturally taboo should be dropped from the list of brand name possibilities. It is not necessary to create URLs for the product in each of the countries where the product will be marketed, develop a different trade character for each of the countries, or choose a different brand name for each country. It would be better to use the same URL, trade character(s), and brand name everywhere that the product will be marketed. SOURCE: PM:021 SOURCE: PM LAP 6—It's a Brand, Brand, Brand World (Product Branding) 87. A False, promotion can be personal or nonpersonal communication about ideas, images, goods, or services. Promotion includes both paid advertising and publicity that is provided free of charge. It can be personal promotion such as personal selling or nonpersonal such as sales promotion. SOURCE: PR:001 SOURCE: PR LAP 2—Razzle Dazzle (Nature of Promotion) 88. A Sales promotion. Sales promotion is promotional activities other than advertising, personal selling, and publicity that are intended to achieve a desired outcome. Sales promotions augment advertising in an effort to stimulate sales. Advertising is any paid, nonpersonal presentation of ideas, images, goods, or services. Publicity is any nonpersonal presentation of ideas, goods, or services that is not paid for by the company or individual that benefits from it. Personal selling is planned, personalized communication intended to influence purchase decisions and enhance future business opportunities. SOURCE: PR:003 SOURCE: PR LAP 1—Promotional Mix 89. B Internet. The Internet is a worldwide network of computers that enables users to access information and communicate with others. The interactive feature of the Internet means that businesses can promote their products to large audiences throughout the world and often receive an immediate response. In many situations, businesses develop promotional messages that ask users to provide feedback or give them the opportunity to ask questions and receive an immediate answer. Customers often interact with a business's promotional message by purchasing goods and services online. Specialty and transit are not examples of interactive mass media. Electronic spectaculars do allow businesses to promote their products to large audiences; however, they are not currently interactive. SOURCE: PR:100 SOURCE: Zikmund, W., & d'Amico, M. (2001). Marketing: Creating and keeping customers in an e-commerce world (7th ed.) [pp. 501-502]. Mason, OH: South-Western. Test 1021 MARKETING CLUSTER EXAM – KEY 27 90. D Industry. Governments often restrict businesses in terms of their promotional activities. Some countries have independent groups (e.g., Public Citizen) that work to influence government regulation on the behalf of the consumer. In addition, many industries (e.g., media, financial services, utilities) have selfregulatory procedures in place to protect the integrity of their field. Competitive is a general term used to describe the level of rivalry between two or more businesses to attract scarce customer dollars. Nonprofit is a legal business structure. Liability is defined as debt. SOURCE: PR:101 SOURCE: Wells, W., Burnett, J., & Moriarty, S. (2003). Advertising principles and practice (6th ed.) [pp. 54-56]. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall. 91. B Direct mail. Direct mail is a promotional medium that comes to consumers' homes in the form of letters, catalogs, postcards, and folders. Broadcast media are promotional media such as radio and television, which use radio waves to reach consumers. Out-of-home media are promotional media to which we are exposed outside our homes such as outdoor and transit media. Transit media are out-of-home media found in various modes and locations of mass transportation. SOURCE: PR:007 SOURCE: PR LAP 3—Ad-quipping Your Business (Types of Promotional Media) 92. A Marketers often select their direct advertising methods based on customers' preferences. Customers often respond to promotional messages for certain products when those messages are transmitted via direct advertising (e.g., direct mail) rather than other media. For example, research indicates that customers generally prefer to receive information regarding grocery, health, and beauty products through direct mail rather than through other venues such as telephone or in retail establishments. Although direct advertising often rewards businesses with higher response rates than other forms of advertising, it cannot be assumed that most businesses receive high response rates. Computer messages (e.g., spam) are often deleted by users before the message is opened, which lowers response rates. Although some governments have introduced legislation to restrict telemarketing programs, the medium is not necessarily becoming obsolete. Infomercial and home shopping television shows can be very effective promotional tools that often experience immediate response from customers. SOURCE: PR:089 SOURCE: Semenik, R.J. (2002). Promotion and integrated marketing communications (pp. 359-361). Mason, OH: South-Western. 93. B Slogan. A slogan is a phrase that is easy to remember. It often becomes identified with the product or the advertiser, who may be the producer and/or seller of the product. Copy is the text of an ad. Headline is the text set in large type and usually positioned at the top of the ad. Illustration is a photograph, drawing, painting, or graphic. SOURCE: PR:014 SOURCE: Michael J. Motto Advertising. (2002). An advertising glossary. Retrieved September 4, 2009, from http://www.motto.com/glossary.html 94. A Set objectives. Objectives are goals to be reached. One of the first steps in developing a promotional plan involves deciding what the plan is trying to accomplish and establishing objectives to achieve that goal. In most cases, the primary objective of a promotional plan is to increase sales and profit. All other aspects of promotional planning are contingent on setting objectives. Preparing a budget, creating a schedule, and designing a message are steps in developing a promotional plan that take place after the objectives are set. SOURCE: PR:073 SOURCE: Burrow, J.L. (2002). Marketing (p. 419). Mason, OH: South-Western. Test 1021 MARKETING CLUSTER EXAM – KEY 28 95. A Visual merchandising. When holding special promotions, retail businesses should coordinate the various promotional activities, such as visual merchandising, signage, and advertising. The purpose of the promotion is to attract customers. Coordinating all the promotional activities usually creates a stronger focus and is more likely to attract customers. For example, the displays in the business should promote the same theme as the advertising and the special events. Product planning, information gathering, and sales training are not promotional activities. SOURCE: PR:076 SOURCE: Farese, L.S., Kimbrell, G., & Woloszyk, C.A. (2002). Marketing essentials (3rd ed.) [pp. 302-304]. Woodland Hills, CA: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill. 96. D Selling. Selling is determining customer needs and wants and responding through planned, personalized communication that influences purchase decisions and enhances future business opportunities. Carlos is, therefore, engaged in selling. Advertising is any paid form of nonpersonal presentation of ideas, goods, or services. Distribution involves moving, storing, locating, and/or transferring ownership of goods or services. Financing is a marketing function that involves understanding the financial concepts used in making business decisions. SOURCE: SE:017 SOURCE: SE LAP 117—Sell Away (The Nature and Scope of Selling) 97. B Reputation. This example shows that the business is building a loyal following and demonstrates a solid relationship by showing that it stands behind its products and cares about the customer. Customers often recommend businesses that provide good service, which also tends to build a positive reputation. Providing good customer service is essential for an organization to make a profit and stay in business. Spirit refers to the "can-do" attitude of employees in an organization. A critical aspect of customer service is putting customer convenience first. SOURCE: SE:076 SOURCE: Ingram, T.N., LaForge, R.W., Avila, R.A., Schwepker, C.H., & Williams, M.R. (2001). Professional selling: A trust-based approach (pp. 258-259). Mason, OH: South-Western. 98. B Fail to keep promises. Loyalty and goodwill can be wiped out quickly by salespeople who are discourteous, indifferent, and poorly informed. If salespeople use high-pressure sales tactics or fail to fulfill promises, businesses can expect to lose client loyalty. Avoiding competition may be detrimental to sales efforts. Implementing business policies, giving customers full attention, and understanding the products they sell will help salespeople to build clientele. SOURCE: SE:828 SOURCE: SE LAP 115—Keep Them Loyal (Building Clientele) 99. C Technical. Experienced salespeople often are well-informed about the technical aspects of the products they sell. New employees should take advantage of this knowledge and ask the experienced personnel to explain product information that may be technical or confusing to them or to customers. New salespeople usually are able to interpret routine, favorable, and ordinary product information on their own. SOURCE: SE:062 SOURCE: Churchill, G.A., Ford, N.M., Walker, O.C., Johnston, M.W., & Tanner, J.F. (2000). Sales force management (6th ed.) [pp. 391, 397, 401-402]. Boston: Irwin/McGraw-Hill. Test 1021 MARKETING CLUSTER EXAM – KEY 29 100. C The nature of the customer. Because of the limited contact with customers, retailers tend to spend little time prospecting, determining customer needs, and building relationships. This is generally because in many retail situations, customers already know what they want when they walk into the store. A manufacturing company generally sells to other businesses. The volume of customers is generally less, and the representatives need to spend more time qualifying customers and determining their needs. Since retail businesses and manufacturing companies vary within their own industries in terms of sales volume, communication levels, and business structures (e.g., corporation, hybrid), these options are not usually considered primary differences in regard to selling approaches. SOURCE: SE:048 SOURCE: Murphy, D. (2007, April 6). Marketing for B2B vs. B2C—Similar but different. Retrieved September 4, 2009, from http://vista-consulting.com/marketing-b2b-vs-b2c/