* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Structure of the Human Heart
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
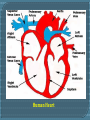
Cardiovascular system Heart: The heart is a muscular organ found in all animals with circulatory system (including all vertebrates), that is responsible for pumping blood throughout the blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions. The vertebrate heart is composed of cardiac muscle, contain involuntary striated muscle tissue found only in this organ, and connective tissue. The average human heart, beating at 72 beats per minute, will beat approximately 2.5 billion times during an average 66 year lifespan. It weighs approximately 250 to 300 grams in females and 300 to 350 grams in males. Structure of the Human Heart: Heart is actually shaped more like an upside-down pear. Heart is located almost in the center of the chest, but slightly tilted to the left. There are four cavities, or open spaces, inside the heart that fill with blood. Two of these cavities are called atria. The other two are called ventricles. The two atria form the curved top of the heart. The ventricles in bottom of the heart to form base (Tends to left side of chest). The left ventricle contracts most forcefully, so you can feel your heart pumping on the left side of your chest. The left side of the heart contains one atrium and one ventricle. The right side of the heart contains the others. Heart contain (wall), called the septum, separates the right and left sides of the heart. A valve connects each atrium to the ventricle below it. The mitral valve connects the left atrium with the left ventricle. The tricuspid valve connects the right atrium with the right ventricle. The top of the heart connects to a few large blood vessels. The largest of these is the aorta, or main artery, which carries nutrient-rich blood from the heart. Another important vessel is the pulmonary artery which connects the heart with the lungs as part of the pulmonary circulation system. The two largest veins that carry blood into the heart are the superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava. The superior is located near the top of the heart. The inferior is located beneath the superior. The heart structure makes it an efficient, the heart pumps blood , therefore, must be strong. The cardiac muscle contracts it push blood into the vessels. Nerves connected to the heart regulate the speed of muscle contract. When you run, your heart pumps more quickly. When you sleep, your heart pumps more slowly. To monitor the heart, scientists can use x-ray or scanning technology to get picture. To really explore the heart, scientists have to perform surgery. Heart surgery is very risky because the heart pumping action is so critical for survival. If the heart stops pumping, the body cannot survive. Before beginning heart surgery, doctors connect the patient to machine that pumps the blood for the heart. Human Heart