* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 啓偐䕌䕍呎剁⁙义但䵒呁佉华 - Cancer Research
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
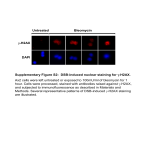
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS AND METHODS Plasmids, site-directed and deletion mutagenesis, and lentivirus production Vectors Flag- and HA-tagged pcDNA4T0, GST-tagged PGEX4-T-1, EGFP- and Cherry-tagged 3×Flag-PGK-Puro, and pLV-U6-EGFP-Puro were used in this study. HEK293T and HepG2 cells cDNA libraries were used to amplify the appropriate sequences. The following primers were used to perform site-directed and deletion mutations: 5'-GCGCTTCTCTCCTTTGCTCT-3' and 5'-TCTGCCCAGAGCAAAGGAGA-3' were used to make the mSREBP1a R321K mutant; 5'-GGGGCCAGTGTGTCCTCCA-3' and 5'-GATATCTGCAGAATTCTCAGCG-3' were used to make the mSREBP1a R321K/S430A mutant; 5'-CCCTTGCTGCCAAGGGAC-3' and 5'-TTGGCAGCAAGGGCAGTG-3' were used to make the mSREBP1a R446K 5'-CAGAATTCTCAGCGGGAGCGGTCCAGCATGCCCTTGC-3' mutant; and 5'-TCGGATCCATGGCTGACTACAAGGACGACGATGAC-3' were used to make the mSREBP1a R480K mutant; 5'-GCTTCTCTCCTGCGCTCTGGGCAGA-3' and 5'-CCCAGAGCGCAGGAGAGAAGCGCAC-3' were used to make the mSREBP1a R321A mutant; and 5'-CCAGGGCAGCACCATCAGTACCTGGACATTGG-3' and 5'-CTGATGGTGCTGCCCCTGGTGAACGCTTCC-3' were used to make the PRMT5 ΔM mutant. In lentivirus packaging, the sequence of the mSREBP1a WT or R321K mutant was inserted into the viral skeleton plasmid EGFP-tagged 3×Flag-PGK-Puro. Annealing and connection of the shRNAs were performed before insertion into the viral skeleton plasmid pLV-U6-EGFP-Puro. All products were subsequently transformed into HEK293T cells using lentivirus packaging reagents (GenePharma, Shanghai, China), according to the manufacturer’s 1 instructions, to acquire the virus. The shRNA sequences used in our research are shown in Supplementary Table S3. Immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting analyses Harvested cells were lysed in RIPA lysis buffer (Beyotime) at 4ºC. Immunoprecipitaion was carried out by incubating cell protein lysates with antibody-conjugated protein A+G sepharose beads (Thermo scientific), an anti-Flag M2 affinity gel (Sigma-Aldrich), or Pierce anti-HA agarose (Thermo scientific) at 4ºC for 3 hours. Protein samples were resolved by SDS-PAGE, transferred to polyvinylidene fluoride membranes (PVDF) (GE healthcare) and probed with the indicated primary antibodies and horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated secondary antibodies (Santa Cruz, CA, USA). The chemiluminescent HRP substrate (Millipore, Massachusetts, USA) was used to visualize antibody binding. The protein levels of Flag-mSREBP1a in different samples immunoprecipitated by anti-Flag M2 affinity gel were detected by immunoblotting analysis using antibody against Flag, followed by quantification by the image analysis software Imagine J (NIH, MD, USA), and then normalized to the same level. The antibodies used in our research are shown in Supplementary Table S4. Confocal immunofluorescence microscopy HepG2 cells harvested on coverslips were washed with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) before fixing in 4% formalin for 15 minutes. Cells were then treated with 0.25% Triton X-100 for 10 min, followed by three washes with PBS. The cells were blocked with 1% bovine serum albumin (BSA)/PBS for 1 h, followed by incubation with primary antibodies (anti-SREBP1a (1:100) (Santa Cruz, sc-13551, mouse mono-antibody) and anti-PRMT5 (1:500) (Abcam, EPR5772, rabbit mono-antibody)) for 2 hours at room temperature. After two PBS washes, the cells were 2 incubated with a secondary antibodies mixture of goat anti-rabbit IgG H&L conjuncted with Alexa Fluor® 488 (1:1000) (Thermo scientific) mixed with goat anti-mouse IgG H&L conjuncted with Alexa Fluor® 568 (1:1000) (Thermo scientific) for 1 hour. The resulting signals were visualized using a confocal laser-scanning microscope (Olympus BX61, TKY, JPN). Gene expression analysis Total RNA was isolated from cells using an E.Z.N.A total RNA Kit I (Omega bio-tek, GA, USA). cDNA was synthesized using a PrimerScript RT reagent Kit (Takara, OSTU, JPN). The real-time PCR reaction was performed according to the protocol of the SYBR Premix Ex Taq kit (Takara), and using a StepOnePlus Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems, USA). The fluorescence data of the detected genes were normalized to cyclophilin B (CB) expression using the 2-ΔΔCT method. Primers used are listed in Supplementary Table S5. Luciferase reporter assay A plasmid containing the human FASN gene promoter fused to the luciferase gene in the pGL3 vector (Promega, WI, USA) was used as a reporter vector. Cells were subcultured in 24-well culture dishes (1.5×104/well) and transfected with the luciferase reporter vector plus a renilla luciferase plasmid at a ratio of 10:1. The luciferase activity of the cell extract was analyzed using a Dual-Luciferase Assay system (Promega), according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The relative levels of FASN luciferase activity were normalized to the renilla luciferase activity levels. Oil red O staining Cells were washed with PBS before fixing in 4% formalin for 10 minutes at room temperature. After rinsing each plate quickly using 60% isopropanol, the cells were stained by 0.3% Oil red O 3 (Millipore) at room temperature for 1 hour. The plates were rinsed with 60% isopropanol and PBS in turn before the Oil red O staining was observed under a microscope. Cell growth assay HepG2 cells were plated on 24-well plates in 1% CSFBS DMEM (5000 cells per well, three parallel wells). Cells were harvested at different time points after transfection and the cell numbers on each plate were counted. Trypan blue staining was used to identify dead cells when counting. Colony formation assay Cells were suspended in 0.3% agarose (Sigma-Aldrich), and placed at 50 cells per well on the top of solidified 0.6% agarose in 24-well plates. After three weeks of cultivation, the cells were fixed in 10% formalin and stained with 0.1% crystal violet. The relative number of colonies was calculated, where the number of the control group was designated as 1. Immunohistochemistry The experiment using human tissues was approved by Human Assurance Committee of Ren Ji Hospital Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine. HCC tissue sections were obtained by surgical resection at the Ren Ji Hospital with the agreement of the patients. Patients in our research were followed-up until September 2013 (from 1 to 80 months) after surgery. All tumor biopsies had a matched normal tissue sample from the same patient, and detailed clinicopathological data were also obtained, which is shown in Supplementary Table S2. The pathological types of paraffin-embedded slides were checked again by HE staining before immunostaining. Subcutaneous tumor tissues of nude mice were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde, 4 dehydrated, paraffin embedded and cut into 4-µm sections. Cells grown on coverslips were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde after 48 hours of transfection. The endogenous peroxidase activity in the tissue sections or fixed cells was blocked with 3% hydrogen peroxide solution (Sangon biotech), the antigens were retrieved, and the nonspecific binding of the primary antibodies was blocked by 4% normal goat serum (Gibco). Subsequently, tissue sections or cells coverslips were incubated with different primary antibodies, followed by HRP-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG (1:1000, Cell signaling, MA, USA) incubation. 3,3'-diaminobenzidine (DAB) chromogen substrate solution was to visualize the results. The following antibodies were used in the immunohistochemistry experiment: anti-Ki67 rabbit polyclonal antibody (1:500, Sigma-Aldrich), an anti-321R(SDMA)-mSREBP1a rabbit polyclonal antibody designed and synthesized by Hangzhou huaan biotechnology Co., Ltd of China (1:100 in HCC tissues, 1:200 in xenograft tissues and cells fixed on coverslips). 321R(SDMA)-mSREBP1a expression in HCC tissues was scored blindly and independently by two scientists. The scores for nucleus staining frequency (0 = 0–19%, 1 = 20–39%, 2 = 40–59%, 3 = 60–79%, 4 = 80–100%) and intensity (0 = negative, 1 = weak, 2 = moderate and 3 = strong staining) were added to obtain an overall staining score (OSS). An OSS of 0–2 was deemed low, 3–5 moderate and 6–7 high. 5