* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch 4 Building Blocks
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
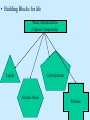
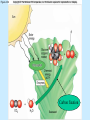
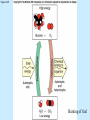
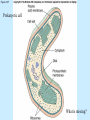
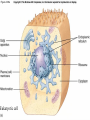
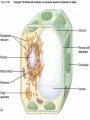
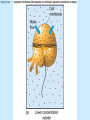
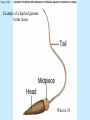
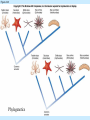
Chapter 4 Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. CO 4 What is life? All living things use energy, have the ability to do work, maintain themselves, and grow. • Building Blocks for life Water, Hydrocarbons (Organic Compounds) Carbohydrates Lipids Nucleic Acids Proteins • Carbohydrates – An organic compound that consists of chains or rings of Carbon with Hydrogen and Oxygen attached to them. – The simplest carbohydrates are glucose (simple sugars) – Used for energy, structural molecules (Chitin and Cellulose) • Proteins – Nitrogen containing organic molecules That play many crucial roles in organisms. – Protein sub units are called amino acids. – Functions as: • • • • Muscles Enzymes- speed up or catalyze specific chemical reactions Structure- hair, skin, and skeletons Hormones- chemicals that act as messengers to help different parts of the body work together • Lipids – Organic molecules that are often used by organisms in the long-term storage of energy, waterproofing, buoyancy, and insulation. • Fats, Oils, and Waxes – Whale blubber – Waterproofing from preening glands – Cuticle waxes that protect plants • hormones • Nucleic Acids – Organic compounds that store and transmit genetic information. • Nucleic acids are chains of repeated subunits called nucleotides that consist of a simple sugar joined to molecules containing Phosphorus and Nitrogen. • DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) contains all instructions for construction and maintenance within a cell. – An organisms complete genetic information is called a Genome. – The order of the different nucleotides within the DNA chain is called a Sequence. » Nucleotides contain only four different types of Nitrogen bases: Adenine, Cytosine, Thymine, and Guanine. – Each sequence is called a Gene. – RNA (ribonucleic acid) consists of chains of four types of nucleotides like DNA, but Thymine is replaced with Uracil (catalyses chemical reactions). Figure 4.01 • Fuel of Life (Energy currency of Life) – ATP( adenosine triphosphate ) a high energy molecule based on adenosine. Energy is stored as chemical energy by converting a related but lower energy molecule ADP (adenosine diphosphate), into ATP. Figure 4.04 Carbon fixation Figure 4.05 Burning of fuel Figure 4.06 Autotrophs Figure 4.07 Prokaryotic cell What is missing? Figure 4.08a Eukaryotic cell Figure 4.08b Table 4.01 Figure 4.09 Figure 4.10 Figure 4.11 Figure 4.12 Ions tend to move into homogenous solution Figure 4.13a Figure 4.13b Figure 4.13c Figure 4.14a Figure 4.14b Figure 4.15 Figure 4.16 Figure 4.17 Figure 4.18 Figure 4.19 Examples of budding (asexual reproduction) Figure 4.20b Example of a haploid gamete Germ tissue What is it? Figure 4.21d Plant reproduction strategies can also be sexual Figure 4.23 Phylogenetics Figure 4.24 • Biological Nomenclature – Organisms are identified biologically by two names. • Their Genus • Their species epithet For example: The spiny lobster found off California (Panulirus interruptus). The spiny lobster found off the Florida Keys (Panulirus argus). Same name different species Table 4.02 Deranged King Philip Can Only Find Green Socks