* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electric Motors
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistance and conductance wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Ferromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
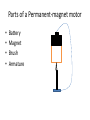
Applications • • • • • • • • Fans Blowers Machine tools (drill) Appliances (blender, food processor) Wristwatches Disk drives Pumps Etc. How it works • Simply put, an electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy (work) • They operate through interacting magnetic fields and current-carrying conductors to produce a force • (This might sound familiar) Parts of a Permanent-magnet motor • • • • Battery Magnet Brush Armature Brushed DC motor • • • • Oscillating current in wound rotor Split-ring commutator Wound or permanent magnet stator Limitations – friction as brushes press against communtator – sparks can cause shorting through adjacent sections (limits max speed, as melting of the commutator may occur) LHR for the motor principle • If the thumb points in the direction of the current flow (real current), fingers are the Bfield, palm is the force • 𝐹 = 𝐼𝑙𝐵𝑠𝑖𝑛φ • I is the current in the conductors, [A] • l is the length of the conductor in the field [m] • B is the magnetic field, [T] Time to motor • Motors are easy to make, so let’s try! • Check out the following simple designs and try to identify the parts • Make sure the force on your coil agrees with LHR