* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download TAKS Success Camp: Objective 1
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Secession in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
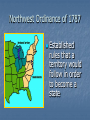
8th Grade American History TAKS Success Camp Objective 1: Issues and Events Coach Vega DATE EVENT SIGNIFICANCE 1607 Jamestown, Virginia American Revolution Constitution 1st permanent English settlement 1776 1787 1803 Louisiana Purchase 1861-1865 Civil War America rebelled against British control created a system of republican government Doubled the size of the United States Issue of slavery divided the nation Reasons for Colonization Religious Freedom: God Primarily New England Colonies Puritans of Massachusetts, Quakers of Pennsylvania Economic Gain: Gold Primarily Middle and Southern Colonies Tobacco in Virginia, Rice in South Carolina European Rivalries: Glory Extend Power England captured Dutch Colony; Renamed New York Reasons for Declaring Independence in 1776 Economic Restrictions Mercantilism policies only allowed colonies to trade with Great Britain This angered the colonists No Political Representation Colonies could not elect members to Parliament The colonists viewed this as unfair “no taxation without representation” British Policies Colonial Reaction Quartering Act Colonial resentment Sugar Act Protests, “No Taxation Without Representation” Stamp Act Protests, Formation of Sons of Liberty Tea Act Boston Tea Party Intolerable Acts First Continental Congress Important Events of the Revolutionary War Lexington and Concord: War begins Saratoga: Major American victory; turning point: French send aid to Americans Yorktown: Last battle, British surrendered Treaty of Paris of 1783: Ended the war Reasons for American Victory in the Revolutionary War Distance from Great Britain Took the British a long time to transport troops and supplies The Continental Army George Washington only fought when Americans had a clear advantage The Battle of Saratoga Convinced the French to help Northwest Ordinance of 1787 Established rules that a territory would follow in order to become a state Articles of Confederation No Chief Executive One house Congress, each state had one vote No court system No power to tax or raise an army Weak national government In 1787, delegates met in Philadelphia to revise the Articles of Confederation. They replaced it with the U.S. Constitution. Creation of the U.S. Constitution: Organization and Power of the National Government Created a strong national government Divided into three branches with some powers left to the states U.S Government Executive Legislative Judicial Creation of the U.S. Constitution: Representation in Congress States with small populations wanted each state to have the same number of legislators: The New Jersey Plan States with large populations wanted representation to be based on population: The Virginia Plan The GREAT COMPROMISE - Set up a two house congress: one with representation by population and the other with equal representation from each state Creation of the U.S. Constitution: Slavery When determining the population of a state for purposes of representation in the House of Representatives…. Northern states did NOT want slaves counted Southern states DID want slaves counted THREE-FIFTHS COMPROMISE – stated that 3/5ths of a state’s slave population would count for the purposes of representation Ratification of Constitution The Constitution was sent to the states to be ratified (approved) Federalists: Supporters of the Constitution They believed that a strong national government was necessary Anti-Federalists: Opponents of the Constitution They feared that the national government had too much power Ratification in 1788 The Constitution was ratified in 1788 after an agreement was made to add a Bill of Rights Formation of Political Parties Federalists Democratic-Republicans Alexander Hamilton Thomas Jefferson Strong National Strong State Government Governments Trade and industry Farming Wanted a national Opposed a national bank bank War of 1812 Causes Effects British pirating of America proved it American ships could defend itself Impressments of manufacturing American sailors into increased the British Navy Frontier was open to The British support of settlement Native Americans Increased patriotism Causes of Westward Expansion Economic Growth Territorial Expansion Manifest Destiny Economic Growth New England textile factories increased the demand for cotton This made cotton more profitable More farmers moved west to grow cotton Roads, canals, and railroads made travel and trade cheaper and faster Territorial Expansion Americans moved westward as the U.S. expanded The Louisiana Purchase doubled the size of the U.S. Expeditions (Lewis and Clark) brought back reports of lands full of resources This encouraged westward expansion Manifest Destiny Manifest Destiny was the belief that is was the mission of the United States to expand across the entire North American continent Effects of Westward Expansion Indian Removal The Mexican War Indian Removal In 1830 the U.S. passed the Indian Removal Act which required Native Americans to move west of the Mississippi River The Cherokee were forced to relocate: known as the Trail of Tears because of the large number of deaths that occurred The Mexican War Mexico was angered when the U.S. annexed Texas in 1845 The Mexican War: 1846-1848 Mexico signed the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo U.S. acquired territory in the southwest known as the Mexican Cession Jacksonian Democracy Idea that more people should have the right to vote and have a say in government, not just rich people More Americans were able to vote in the 1828 election because of removing the requirement of owning property in order to vote. Sectionalism Sectionalism is regional conflict between the North and South. Two main causes of sectionalism 1. Disagreements over State’s Rights 2. Expansion of Slavery in Western Territories State’s Rights and Federalism State’s Rights: idea that the power of the states should not be trampled on by the national government Federalism: a system of sharing power between the states and the national government Nullification Crisis Congress passed a tariff on imported goods John C. Calhoun and other Southerners felt the tariff was unfair South Carolina declared the tariff null and void and threatened to secede from the Union A compromise was reached: Congress lowered the tariff The Missouri Compromise Purpose: to maintain a balance between the number of slave states and free states Missouri - admitted as a slave state Maine – admitted as a free state The Compromise of 1850 Purpose: resolve dispute over slave issue in the southwest Proposed by Henry Clay California – admitted as free state Fugitive Slave Law - required capture and return of runaway slaves Kansas-Nebraska Act In 1854, Congress allowed Kansas and Nebraska to vote on whether they would allow slavery Angered Northerners because they would have been free states according to Missouri Compromise Dred Scott Case Supreme Court said that slaves were property and could not become free by moving to a free state or territory Election of Abraham Lincoln Abraham Lincoln was a Republican He did not support the spread of slavery into western lands Southerners feared that Lincoln planned to abolish slavery Southern states reacted by seceding from the Union and creating the Confederate States of America The Civil War Begins In 1861, Confederate forces bombarded Fort Sumter in South Carolina Both the North and South had skilled political and military leaders Civil War Dates and Events 1861: Southern States secede and Civil War begins 1863: Lincoln issues Emancipation Proclamation, Union victory at Gettysburg 1865: General Lee surrenders at Appomattox Courthouse, Civil War Ends, Lincoln is assassinated Civil War Leaders UNION (The North) Abraham Lincoln – President of the United States Ulysses S. Grant – Commander of the Union Army CONFEDERACY (The South) Jefferson Davis – President of the Confederacy Robert E. Lee – Commander of the Confederate Army Major Civil War Battles Ft. Sumter: Civil War beings Gettysburg: Union forces defeat Confederate forces Vicksburg: Union forces secure control of Mississippi River Reasons for Northern Advantage Larger population: more factory workers and troops More economic resources: factories, supplies, railroad lines Superior Leadership of Abraham Lincoln: great public speaker, ultimate goal was to preserve the Union Reconstruction Process of re-admitting the southern states into the union